Collograph etching combines textured collage techniques with traditional etching processes to create unique printmaking artworks featuring rich, layered surfaces. This method allows for expressive detail and depth by using various materials to build the plate's surface before inking and pressing. Discover how you can master collagraph etching to enhance your artistic portfolio in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
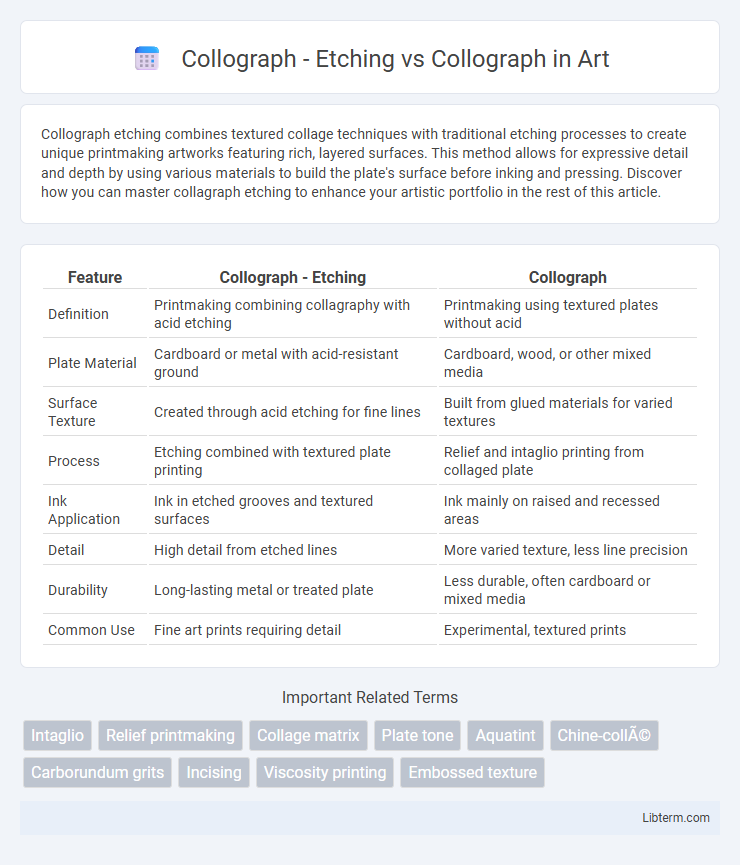
| Feature | Collograph - Etching | Collograph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Printmaking combining collagraphy with acid etching | Printmaking using textured plates without acid |
| Plate Material | Cardboard or metal with acid-resistant ground | Cardboard, wood, or other mixed media |
| Surface Texture | Created through acid etching for fine lines | Built from glued materials for varied textures |
| Process | Etching combined with textured plate printing | Relief and intaglio printing from collaged plate |
| Ink Application | Ink in etched grooves and textured surfaces | Ink mainly on raised and recessed areas |
| Detail | High detail from etched lines | More varied texture, less line precision |
| Durability | Long-lasting metal or treated plate | Less durable, often cardboard or mixed media |
| Common Use | Fine art prints requiring detail | Experimental, textured prints |
Introduction to Collograph and Etching
Collograph is a printmaking technique that involves creating textured plates by gluing various materials onto a rigid surface, offering rich, tactile qualities and unique visual effects. Etching, in contrast, uses acid to bite into a metal plate, producing fine lines and detailed imagery through controlled corrosion. Both methods provide distinct approaches to plate preparation and image creation, with Collograph emphasizing texture and relief, while Etching focuses on intricate line work and tonal variation.
Understanding the Collograph Printing Technique
Collograph printing combines collage and intaglio methods, using textured materials glued to a rigid plate to create varied surfaces for inking, offering rich visual depth. Etching involves incising designs into a metal plate with acid, producing fine lines and detailed imagery through precise control of line quality and depth. Understanding collograph requires appreciating its tactile layering and printing versatility, contrasting with etching's chemical process and emphasis on line etching for intricate detail.
What is Etching in Printmaking?
Etching in printmaking is a process where a metal plate, usually copper or zinc, is coated with a resistant ground, then drawn on to expose the metal; the plate is subsequently immersed in acid, which bites into the exposed lines, creating grooves that hold ink. This technique enables artists to achieve fine, detailed lines and varied textures by controlling the acid exposure time. Compared to collograph, which involves building up surfaces with glued materials for textured printing, etching primarily creates images through line incisions, emphasizing precision and delicacy in the printed result.
Materials Used in Collograph vs Etching
Collograph printmaking primarily uses a variety of textured materials such as cardboard, fabric, and string affixed to a rigid surface to create a raised matrix, while etching relies on metal plates, typically copper or zinc, that are chemically etched with acid to form recessed lines. In collograph, artists build a relief surface that can be inked and printed, emphasizing tactile textures, whereas etching requires careful preparation of the metal plate with ground coatings and acid baths to achieve fine, precise line work. The materials in collograph allow for more experimental and mixed-media approaches, contrasting with the traditional and chemical-intensive process demanding metal plates and acid handling in etching.
Process Differences: Collograph vs Etching
Collograph and etching differ significantly in their printing processes, where collograph uses a collage of materials glued onto a plate to create texture and relief, while etching involves using acid to bite into a metal plate, creating recessed lines. Collograph printing emphasizes build-up and texture for a tactile surface, whereas etching focuses on precise line work achieved through controlled acid exposure. The collograph process is generally more accessible and experimental, while etching requires specialized equipment and chemical handling for detailed intaglio prints.
Artistic Effects: Comparing Textures and Tones
Collograph printing produces rich, textured surfaces by layering materials on plates, creating varied relief effects that yield bold contrasts and tactile depth. Etching, in contrast, uses acid to incise fine lines on metal plates, allowing for precise, delicate tones and detailed gradations through controlled line work. The combination of raised textures in collograph and the intricate line variations in etching offers artists unique expressive possibilities in texture and tonal range.
Advantages of Collograph Printing
Collograph printing offers unique advantages over etching by enabling artists to create textured, multi-dimensional prints using a variety of materials on the plate, resulting in rich, tactile effects. Unlike etching, which relies on acid to bite lines into metal, collographs allow for safer, more versatile plate preparation without hazardous chemicals. The technique also permits quicker and more experimental printmaking, making it ideal for artists seeking diverse textures and dynamic compositions.
Advantages of Etching
Etching offers superior precision and detail due to the chemically incised lines on metal plates, enabling artists to achieve intricate textures and fine tonal variations. The durability of etched plates allows for multiple high-quality prints without loss of image integrity, making it ideal for producing consistent editions. Moreover, etching techniques provide greater control over line depth and shading, enhancing the overall richness and depth of the final artwork compared to the more textural and relief-based nature of collographs.
Choosing Between Collograph and Etching
Choosing between collograph and etching depends on the desired texture and complexity of the print. Collograph offers a more tactile, relief-based approach using textured materials glued to a plate, ideal for bold, varied surfaces, while etching involves chemical processes on metal plates, allowing for fine lines and detailed, precise imagery. Artists seeking experimental, varied textures often prefer collograph, whereas those aiming for intricate, delicate detail typically opt for etching.
Conclusion: Which Technique is Right for You?
Choosing between collograph and etching depends on your artistic goals and preferred materials; collograph offers textured, layered prints using collage techniques, ideal for experimental artists seeking tactile effects. Etching provides precise, intricate lines through acid-resistant coatings on metal plates, suited for detailed, traditional printmaking. Assess your style, desired texture, and complexity to select the technique that best complements your creative vision.
Collograph - Etching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com