Tonal color, or timbre, defines the unique quality of a sound that distinguishes it from others, even when they share the same pitch and volume. Understanding tonal color enhances your ability to appreciate and create diverse musical textures and emotional expressions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how tonal color shapes auditory experiences.
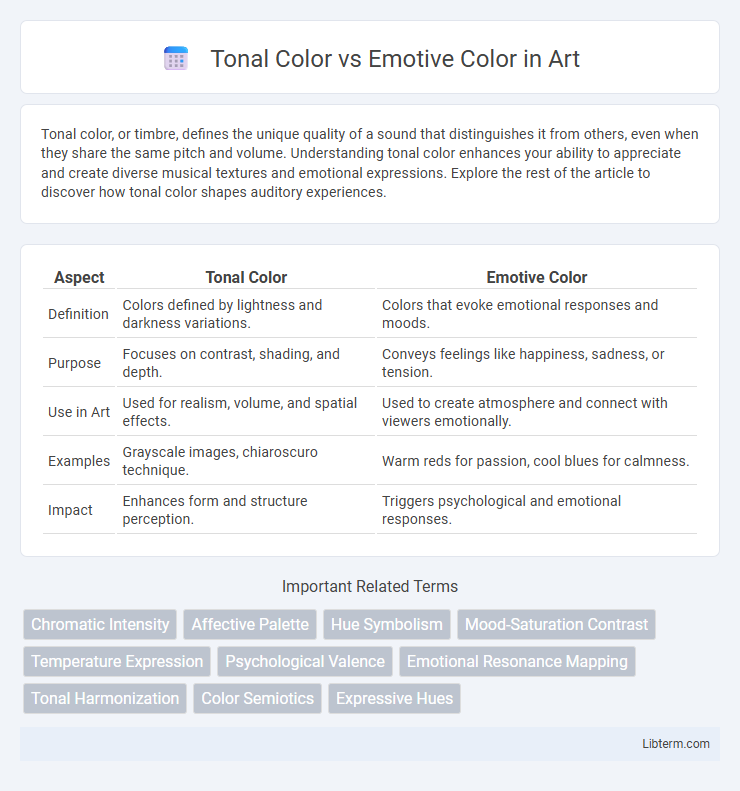
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tonal Color | Emotive Color |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Colors defined by lightness and darkness variations. | Colors that evoke emotional responses and moods. |
| Purpose | Focuses on contrast, shading, and depth. | Conveys feelings like happiness, sadness, or tension. |
| Use in Art | Used for realism, volume, and spatial effects. | Used to create atmosphere and connect with viewers emotionally. |
| Examples | Grayscale images, chiaroscuro technique. | Warm reds for passion, cool blues for calmness. |
| Impact | Enhances form and structure perception. | Triggers psychological and emotional responses. |
Understanding Tonal Color: Definition and Basics
Tonal color refers to the specific quality or character of a sound or visual element determined by its tonal properties such as pitch, timbre, and intensity. Understanding tonal color involves recognizing how subtle variations in frequency and amplitude shape the perception of an object's tone, distinguishing it from the emotional impact that emotive color conveys. Mastery of tonal color enables artists and designers to create nuanced expressions by manipulating these sensory qualities to influence audience perception without relying on emotional cues.
What Is Emotive Color? Key Characteristics
Emotive color refers to hues that evoke specific feelings and psychological responses in viewers, playing a crucial role in emotional communication through visual media. Key characteristics include saturation levels that intensify emotional impact, warm tones like red and orange that often convey passion or urgency, and cool tones such as blue and green that typically evoke calmness or melancholy. Emotive color differs from tonal color by focusing on mood influence rather than just lightness or darkness variations within a hue.
Tonal Color vs Emotive Color: Core Differences
Tonal color refers to the specific hue and intensity of a color, defining its physical attributes such as brightness, saturation, and shade, whereas emotive color relates to the psychological and emotional responses elicited by these colors. Core differences between tonal and emotive color lie in their function: tonal color focuses on the visual perception and accuracy of a color, while emotive color is concerned with the mood and feelings triggered by it. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for applications in design, art, and marketing, where color choice impacts both aesthetic appeal and emotional connection.
The Psychology Behind Tonal and Emotive Colors
Tonal color influences perception through subtle variations in brightness and hue, shaping mood and cognitive responses by creating a calm or dynamic atmosphere. Emotive color activates emotional reactions by triggering associations and memories linked to specific shades, directly affecting feelings of warmth, excitement, or tranquility. The psychology behind tonal and emotive colors reveals how different color schemes modulate human behavior, attention, and decision-making processes in environments and marketing.
How Artists Use Tonal Color for Visual Impact
Artists use tonal color to create depth and contrast, enhancing the three-dimensionality and realism of their compositions. By manipulating light and shadow through subtle variations in tone, tonal color directs viewers' attention and establishes mood without relying solely on hue. This technique allows for nuanced visual impact, emphasizing form and texture while maintaining harmonious balance within the artwork.
Harnessing Emotive Color for Emotional Expression
Harnessing emotive color involves using hues that evoke specific feelings, such as red for passion or blue for calmness, to effectively communicate emotional depth in design and art. Unlike tonal color, which emphasizes variations in lightness and darkness, emotive color directly influences mood and psychological response, making it a powerful tool for emotional expression. Strategic use of saturated, warm, or cool colors can enhance the viewer's emotional engagement and create a memorable visual impact.
Application in Design: Tonal vs Emotive Color
Tonal color in design refers to the use of hues and shades to establish visual hierarchy and clarity, enhancing readability and user interface efficiency. Emotive color, by contrast, aims to evoke specific feelings and psychological responses, influencing mood and brand perception. Effective design integrates tonal color for structure with emotive color to create meaningful, engaging user experiences.
Choosing Between Tonal and Emotive Color: Factors to Consider
Choosing between tonal and emotive color hinges on the desired impact and context of the design; tonal color emphasizes harmony and subtlety through variations in lightness and saturation, ideal for creating calm, sophisticated atmospheres. Emotive color prioritizes vibrant, saturated hues that evoke strong emotional responses, making it suitable for marketing, branding, or expressive art where viewer engagement is critical. Key factors include target audience psychology, cultural color meanings, and the message's intent to ensure the color choice aligns with the overall communication goals.
Case Studies: Tonal Color and Emotive Color in Famous Artworks
Case studies of tonal color and emotive color in famous artworks reveal how artists manipulate hue, value, and saturation to evoke specific psychological responses. In Vincent van Gogh's "Starry Night," emotive color dominates through vivid blues and swirling yellows that convey intense emotional turbulence, whereas Johannes Vermeer's "Girl with a Pearl Earring" highlights tonal color with subtle gradations of light and shadow to create realism and depth. These examples demonstrate that tonal color enhances structural form while emotive color emphasizes mood and expression in visual storytelling.
Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Color in Art and Design
Future trends in art and design emphasize the integration of tonal color's subtle gradations with emotive color's psychological impact to create immersive and dynamic visual experiences. Advances in digital technology enable precise manipulation of hue, saturation, and brightness, allowing designers to evoke stronger emotional responses while maintaining tonal harmony. The evolving role of color prioritizes multisensory interaction and personalized aesthetics, driving innovation in virtual and augmented reality environments.
Tonal Color Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com