Representational painting captures the visible world through realistic imagery, focusing on subjects like landscapes, portraits, and everyday scenes. This art form emphasizes accurate proportions, colors, and details to evoke familiarity and emotional connection. Explore the article to discover how representational painting continues to influence modern art and your appreciation of visual storytelling.
Table of Comparison
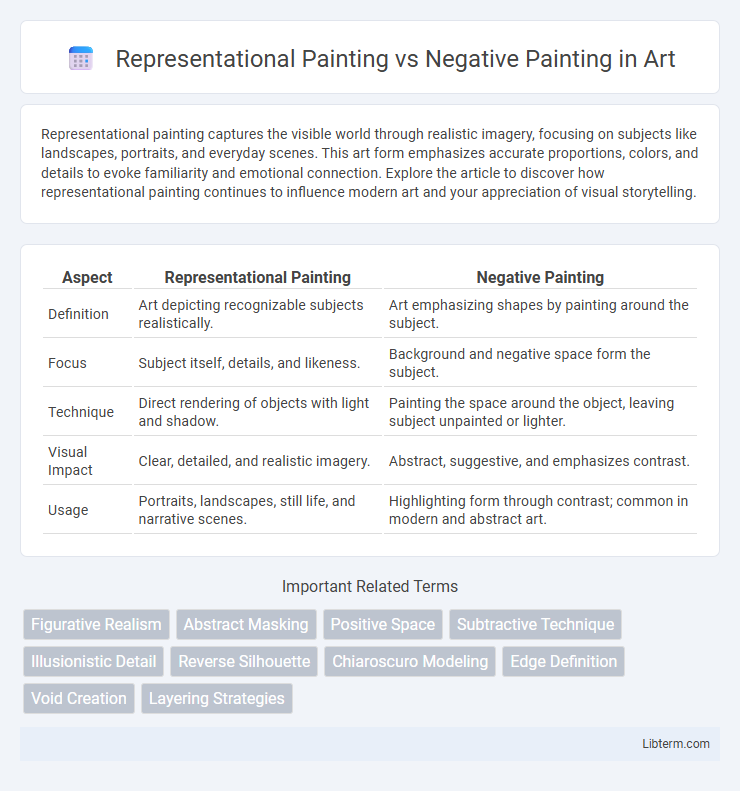
| Aspect | Representational Painting | Negative Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art depicting recognizable subjects realistically. | Art emphasizing shapes by painting around the subject. |
| Focus | Subject itself, details, and likeness. | Background and negative space form the subject. |
| Technique | Direct rendering of objects with light and shadow. | Painting the space around the object, leaving subject unpainted or lighter. |
| Visual Impact | Clear, detailed, and realistic imagery. | Abstract, suggestive, and emphasizes contrast. |
| Usage | Portraits, landscapes, still life, and narrative scenes. | Highlighting form through contrast; common in modern and abstract art. |
Introduction to Representational Painting
Representational painting captures real-world objects and scenes with accurate details, aiming to depict subjects as they appear in reality. It emphasizes visual realism, using color, light, and perspective to create a lifelike impression. This style contrasts with negative painting, which defines forms by painting around them, relying on background shapes rather than directly rendering the subject.
Defining Negative Painting Techniques
Negative painting techniques involve applying paint around the subject to define its shape through the background, contrasting with representational painting that directly depicts the subject with positive form. This method emphasizes the negative space by masking or painting around objects, creating silhouettes or outlines that highlight the subject indirectly. It is commonly used in various cultural art forms to enhance visual depth and emphasize spatial relationships.
Historical Contexts of Both Approaches
Representational painting, rooted in ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Greece, aimed to depict subjects realistically, reflecting cultural narratives and social hierarchies of the era. Negative painting emerged prominently in Indigenous art traditions, particularly among Native American tribes like the Cherokee, using background contrast to define shapes and convey symbolic meanings within ritual contexts. Both approaches illustrate evolving artistic intentions shaped by their respective historical and cultural frameworks, highlighting shifts in perception and expression across time.
Core Principles of Representational Painting
Representational painting centers on accurately depicting subjects from real life, emphasizing precise observation, detailed rendering, and the faithful reproduction of forms, colors, and textures. It relies on techniques such as chiaroscuro for creating depth and perspective drawing to establish spatial relationships within the composition. The core principles include realism, visual accuracy, and the clear portrayal of recognizable objects or figures to convey a concrete narrative or subject matter.
Fundamentals of Negative Painting
Negative painting involves creating images by painting around shapes, allowing the background to define the subject, which contrasts with representational painting where subjects are directly depicted. The fundamentals of negative painting include emphasizing the space surrounding the forms, using color contrasts to highlight shapes, and strategically leaving certain areas unpainted to build the image. This technique relies on visual perception of figure-ground relationships, making negative space as important as the painted areas in defining the composition.
Visual Outcomes: Realism vs Abstraction
Representational painting emphasizes detailed imagery and lifelike accuracy, producing visuals that mirror real-world objects and scenes with clarity and precision. Negative painting, by contrast, achieves abstraction through the strategic use of background or surrounding shapes to define subjects, creating a more symbolic and interpretive visual effect. The visual outcome of representational painting leans towards realism, while negative painting embraces abstraction, inviting viewers to engage with form and space more conceptually.
Color and Composition in Both Styles
Representational painting employs precise color palettes and structured compositions to depict recognizable subjects with realistic hues and balanced spatial arrangements. Negative painting emphasizes the use of background colors and shapes, focusing on the interplay between positive and negative spaces to define forms through contrast rather than direct color application. Color in representational art mimics natural tones, while in negative painting, color contrasts highlight contours and create dynamic compositions without explicit outlines.
Techniques and Tools Used
Representational painting employs techniques like layering oils or acrylics to build realistic textures and forms using brushes, palette knives, and fine detail tools. Negative painting focuses on creating images by outlining and painting around shapes rather than filling them, often using washes, glazes, and precise brushes to emphasize contrast and form. Tools for negative painting include fine-tip brushes and sometimes stencil aids to maintain crisp edges, while representational artists rely heavily on varied brush sizes and blending instruments for depth and realism.
Creative Possibilities and Challenges
Representational painting offers creative possibilities through detailed depictions of objects and scenes, enabling artists to explore realism and narrative depth, while its challenge lies in achieving accurate proportions and lifelike textures. Negative painting emphasizes the space around and between subjects, unlocking innovative compositions and abstract effects but demands precision in controlling background shapes and contrasts. Each technique provides distinct artistic opportunities, with representational painting focusing on direct depiction and negative painting on spatial relationships, both requiring mastery of composition and visual balance.
Choosing Between Representational and Negative Painting
Choosing between representational and negative painting depends on the desired focus and artistic intent. Representational painting emphasizes clear imagery and recognizable subjects, ideal for conveying specific scenes or narratives. Negative painting uses surrounding shapes and colors to define form, offering a more abstract and subtle approach to composition and visual balance.
Representational Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com