Grattage is a painting technique that involves scraping off layers of paint to reveal underlying colors and textures, creating a dynamic interplay of light and shadow. This method, popularized by surrealist artists like Max Ernst, adds depth and organic unpredictability to your artwork. Explore the rest of this article to discover how grattage can transform your creative process and results.
Table of Comparison
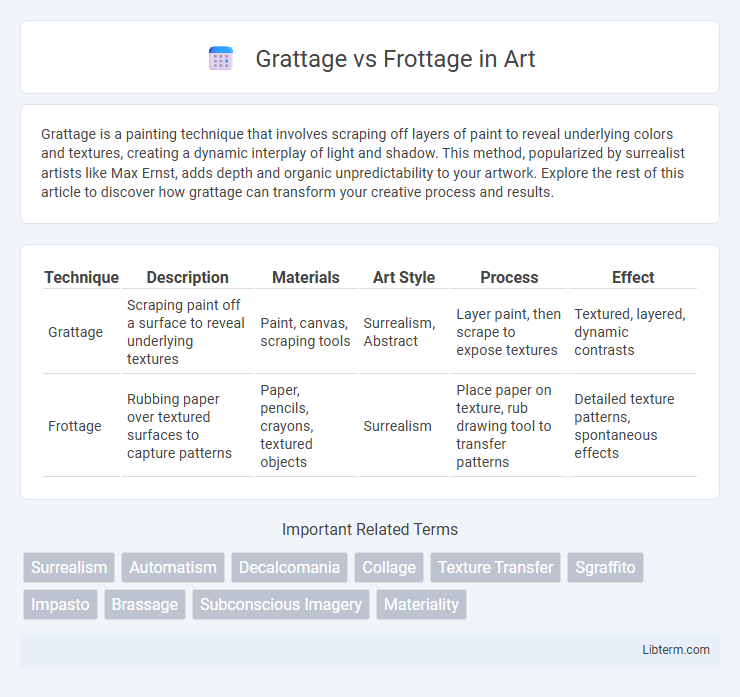
| Technique | Description | Materials | Art Style | Process | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grattage | Scraping paint off a surface to reveal underlying textures | Paint, canvas, scraping tools | Surrealism, Abstract | Layer paint, then scrape to expose textures | Textured, layered, dynamic contrasts |
| Frottage | Rubbing paper over textured surfaces to capture patterns | Paper, pencils, crayons, textured objects | Surrealism | Place paper on texture, rub drawing tool to transfer patterns | Detailed texture patterns, spontaneous effects |
Introduction to Grattage and Frottage
Grattage and frottage are distinct surrealist techniques utilized to create texture and depth in artwork. Grattage involves scraping paint off a canvas to reveal the underlying layers, generating unexpected patterns and forms. Frottage consists of rubbing a drawing tool over textured surfaces to capture the surface imprint, producing intricate and spontaneous designs.
Historical Origins of Grattage and Frottage
Grattage and frottage, both surrealist techniques, originated in the early 20th century with Max Ernst pioneering frottage in 1925 as a method of creating textures by rubbing pencil or charcoal over paper placed on an uneven surface. Grattage, developed shortly after, involved scraping layers of paint to reveal underlying textures and was further explored by Ernst to produce imaginative imagery. These methods reflect surrealism's emphasis on automatism and unconscious creativity, linking tactile manipulation with dream-like visual expression.
Key Artists in Grattage and Frottage Techniques
Max Ernst is the seminal figure in both grattage and frottage techniques, pioneering these Surrealist methods to explore subconscious imagery through texture and automatism. In grattage, Ernst scraped layers of paint to reveal underlying textures, creating abstract compositions that evoke mysterious landscapes. Frottage, involving rubbing pencil or other media over textured surfaces, was also popularized by Ernst, with other artists like Joan Miro adopting similar approaches to capture spontaneous patterns and surfaces.
Materials and Tools Used in Grattage
Grattage primarily employs thick layers of paint applied to a canvas or board, which are then scraped or scratched away using tools such as palette knives, needles, or other sharp instruments to reveal underlying textures and colors. Common materials include oil or acrylic paints, textured surfaces, and various objects for scratching or scraping to create dynamic visual effects. This technique contrasts with frottage, which involves rubbing graphite, charcoal, or crayon over paper placed on textured surfaces to capture their patterns.
Materials and Tools Used in Frottage
Frottage involves rubbing a drawing medium such as pencil, charcoal, or crayon over paper placed on textured surfaces like wood, leaves, or fabric to capture the underlying patterns. Essential tools for frottage include smooth drawing paper, soft graphite pencils or oil pastels, and textured objects that provide varied surface impressions. This technique emphasizes the interaction between the paper and diverse materials to create unique textures and visual effects.
Step-by-Step Grattage Process
The Grattage process involves applying a thick layer of paint onto a canvas, then pressing and scraping the wet surface with various textured tools or objects to reveal underlying layers and create intricate patterns. Artists carefully select tools such as palette knives, combs, or textured fabrics to scratch or scrape the paint, emphasizing contrasts between painted and exposed areas. This step-by-step technique enhances depth and texture, distinguishing Grattage from Frottage, which primarily involves rubbing pencil or crayon over paper placed on textured surfaces.
Step-by-Step Frottage Process
Frottage involves placing a textured surface beneath a sheet of paper and rubbing the paper with a drawing tool to capture the texture's details, starting by selecting a rough material such as wood grain or fabric. The process begins with securing the paper over the textured object, then systematically moving a crayon, pencil, or charcoal across the surface to transfer the pattern onto the paper. This technique enhances artistic expression by revealing unique textures, making it distinct from the scrape-based approach used in grattage.
Visual Differences: Grattage vs Frottage
Grattage reveals visual differences by creating textured surfaces through scraping or scratching paint layers, resulting in sharp, irregular patterns and a tactile quality. Frottage produces images by rubbing pencil or crayon over textured objects, generating softer, repeated patterns that mirror the underlying texture's contours. The contrasting techniques emphasize Grattage's sculptural, fragmented visuals versus Frottage's subtle, impressionistic textures.
Artistic Applications and Examples
Grattage and frottage are both surrealist techniques used to create textured effects by manipulating surfaces, with grattage involving scratching paint off a canvas while frottage entails rubbing a pencil or crayon over textured surfaces. Artists like Max Ernst applied grattage in works such as "Forest" (1927), where paint layers were scraped to reveal underlying textures, while his frottage pieces like "The Horde" (1927) showcase impressions from leaves and wood grain. These methods enhance the visual depth and evoke subconscious imagery, proving influential in experimental art and modern mixed media practices.
Choosing Between Grattage and Frottage
Choosing between Grattage and Frottage depends on the desired texture and artistic effect; Grattage involves scraping paint over a textured surface to reveal underlying layers, creating dynamic contrasts, while Frottage uses rubbing techniques over textured materials to produce subtle, organic patterns. Artists seeking bold, abstract outcomes often prefer Grattage for its spontaneity and intensity, whereas Frottage appeals to those aiming for detailed, tactile impressions inspired by natural textures. Evaluating the composition's mood and surface interaction guides the optimal technique selection for creative expression.
Grattage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com