Earthenware is a type of ceramic made from clay fired at relatively low temperatures, resulting in a porous, durable material often glazed to enhance its appearance and functionality. It has been widely used for pottery, cookware, and decorative items due to its affordability and rustic charm. Discover how earthenware's unique properties and versatile uses can enrich Your collection by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
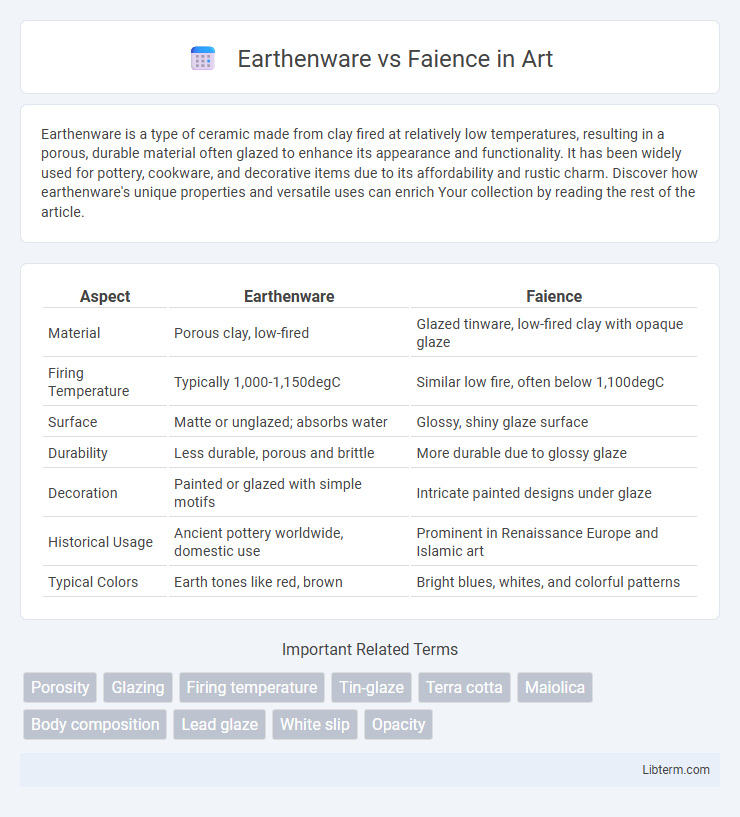
| Aspect | Earthenware | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Porous clay, low-fired | Glazed tinware, low-fired clay with opaque glaze |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1,000-1,150degC | Similar low fire, often below 1,100degC |
| Surface | Matte or unglazed; absorbs water | Glossy, shiny glaze surface |
| Durability | Less durable, porous and brittle | More durable due to glossy glaze |
| Decoration | Painted or glazed with simple motifs | Intricate painted designs under glaze |
| Historical Usage | Ancient pottery worldwide, domestic use | Prominent in Renaissance Europe and Islamic art |
| Typical Colors | Earth tones like red, brown | Bright blues, whites, and colorful patterns |
Introduction to Earthenware and Faience
Earthenware is a porous, low-fired ceramic material typically fired at temperatures between 1,000 and 1,150degC, known for its durability and rustic appearance. Faience, often considered a type of glazed earthenware, features a tin-opacified glaze that creates a distinctive opaque white or colored surface, originating from ancient Egyptian and Mediterranean pottery traditions. Both materials serve functional and decorative purposes, but faience's unique glazing technique distinguishes it in artistic and archaeological contexts.
Historical Origins and Development
Earthenware, dating back to Neolithic times around 10,000 BCE, represents one of the earliest forms of pottery, characterized by its porous and low-fired clay composition predominantly used in everyday utilitarian objects. Faience emerged in ancient Egypt around 4000 BCE as a non-clay ceramic material made from quartz mixed with alkali, notable for its bright blue-green glaze and symbolic significance in funerary and decorative art. The development of earthenware and faience reflects distinct technological advancements and cultural priorities, with earthenware widely adopted across various ancient civilizations and faience specifically associated with luxury and ritual contexts.
Key Material Differences
Earthenware is a porous ceramic made from coarse clay fired at lower temperatures, typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a more porous and less dense material. Faience, in contrast, is a glazed non-clay ceramic material composed mainly of finely ground quartz or sand with added alkalis and colorants, fired at moderate temperatures around 950degC to 1,050degC, creating a bright, glossy surface. The key material difference lies in earthenware's clay-based composition and porous nature versus faience's silica-based composition and vitreous, glass-like finish.
Manufacturing Techniques Compared
Earthenware is fired at lower temperatures, typically between 1,000 and 1,150degC, resulting in a porous and less durable ceramic that requires glazing for waterproofing. Faience, a type of tin-glazed earthenware, involves coating the porous body with a white, opaque glaze made by adding tin oxide before firing, allowing for bright, intricate surface decoration. The manufacturing process of faience demands precise control over glaze composition and firing to achieve its characteristic glossy, vibrant finish distinct from the more matte and utilitarian nature of standard earthenware.
Physical Properties and Characteristics
Earthenware is a porous, low-fired ceramic material typically fired between 1000degC and 1150degC, resulting in a relatively soft body with a coarse texture and moderate porosity. Faience, often composed of a quartz-based body with a vitreous glaze, is characterized by a smooth, glass-like surface and a higher firing temperature range, usually between 900degC and 1050degC, which makes it more brittle but decorative. Both materials differ significantly in density, porosity, and durability, with earthenware being more porous and less durable than the harder, glazed faience.
Artistic Styles and Decorations
Earthenware often features rustic, hand-painted designs with earthy pigments and textured surfaces, highlighting traditional folk art motifs. Faience is characterized by its glossy, tin-glazed finish and vibrant, intricate patterns inspired by Mediterranean and Islamic art, emphasizing detailed floral and geometric decorations. Both mediums showcase distinct artistic styles shaped by their cultural origins and firing techniques.
Durability and Functionality
Earthenware, composed of porous clay fired at lower temperatures, offers moderate durability suitable for everyday use but requires glazing to prevent water absorption. Faience, a type of tin-glazed earthenware, provides enhanced functionality through its non-porous, glossy surface, making it more resistant to stains and easier to clean. While both materials serve decorative and utilitarian purposes, faience's superior durability and distinctive finish make it preferable for items exposed to moisture and frequent handling.
Uses and Applications in Daily Life
Earthenware, known for its porous and slightly brittle nature, is widely used in everyday items such as plant pots, cookware, and tableware due to its affordability and ease of shaping. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic with a glossy finish, is primarily employed in decorative objects, tiles, and ceremonial vessels, valued for its vibrant colors and durability. Both materials serve distinct functional and aesthetic purposes, with earthenware excelling in practical household applications while faience is favored for ornamental and artistic uses.
Maintenance and Preservation Tips
Earthenware requires careful handling to avoid chipping due to its porous and relatively fragile nature, so cleaning with mild soap and avoiding abrasive scrubbing maintains its finish. Faience, characterized by its glossy, glazed surface, benefits from regular dusting and gentle wiping with a damp cloth to preserve its vibrant colors and intricate decorations. Storing both types in stable environments with controlled humidity and temperature helps prevent cracking and glaze deterioration over time.
Choosing Between Earthenware and Faience
Choosing between earthenware and faience depends on the desired finish and durability; earthenware features a porous, unglazed body suitable for rustic, functional pottery, while faience offers a tin-glazed, glossy surface often decorated with intricate designs. Earthenware is typically fired at lower temperatures around 1000-1150degC, making it more porous and less durable than faience, which is fired at slightly higher temperatures with a glaze that enhances waterproofing and aesthetic appeal. For applications requiring decorative appeal and water resistance, faience is preferable, whereas earthenware suits utilitarian uses where strength is less critical.
Earthenware Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com