Mastering the art of painting unlocks a world of creativity, allowing you to express emotions and ideas through vibrant colors and textures. Understanding different techniques and materials enhances your ability to transform a blank canvas into a captivating masterpiece. Discover how to elevate your painting skills and bring your artistic vision to life by exploring the tips and insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
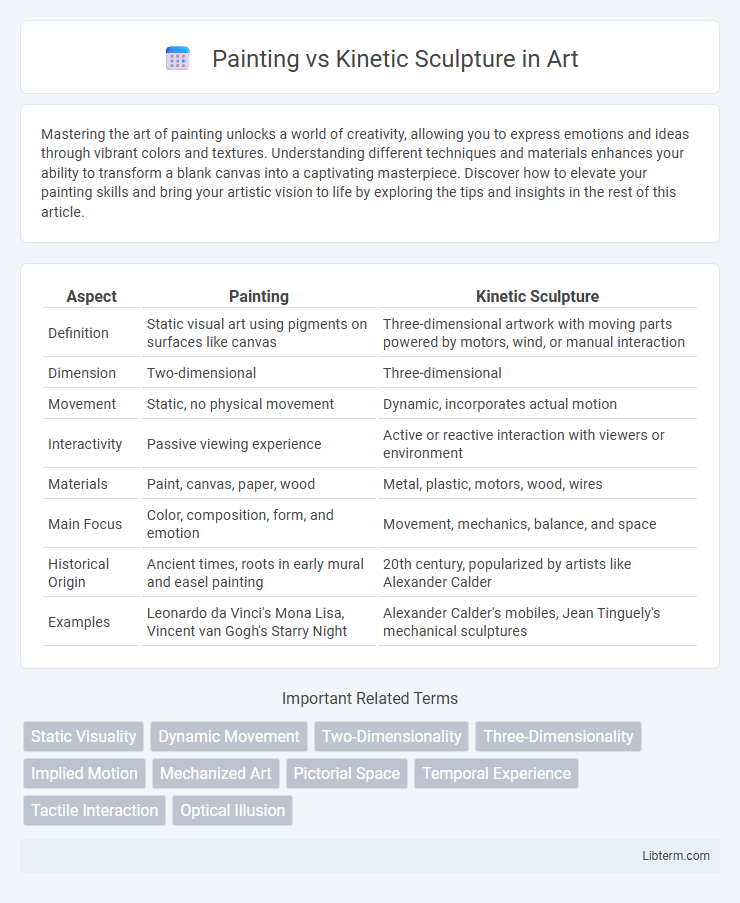
| Aspect | Painting | Kinetic Sculpture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Static visual art using pigments on surfaces like canvas | Three-dimensional artwork with moving parts powered by motors, wind, or manual interaction |
| Dimension | Two-dimensional | Three-dimensional |
| Movement | Static, no physical movement | Dynamic, incorporates actual motion |
| Interactivity | Passive viewing experience | Active or reactive interaction with viewers or environment |
| Materials | Paint, canvas, paper, wood | Metal, plastic, motors, wood, wires |
| Main Focus | Color, composition, form, and emotion | Movement, mechanics, balance, and space |
| Historical Origin | Ancient times, roots in early mural and easel painting | 20th century, popularized by artists like Alexander Calder |
| Examples | Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa, Vincent van Gogh's Starry Night | Alexander Calder's mobiles, Jean Tinguely's mechanical sculptures |
Understanding Painting: A Timeless Art
Painting remains a timeless art form characterized by the application of pigments on surfaces to create visual expressions that evoke emotion and meaning. It captures moments frozen in time, offering a static yet powerful narrative through color, texture, and composition. Unlike kinetic sculpture, which incorporates movement and physical interaction, painting emphasizes stillness and the depth of visual storytelling.
What is Kinetic Sculpture?
Kinetic sculpture is an art form that incorporates movement as a fundamental aspect, often powered by wind, motors, or human interaction, distinguishing it from static paintings. It engages viewers through dynamic motion and changing perspectives, creating an interactive experience that contrasts with the fixed visual narrative of traditional painting. This three-dimensional medium blends mechanical engineering and artistic expression, emphasizing motion and time as integral components of the artwork.
Historical Evolution: Painting vs Kinetic Sculpture
Painting, as a centuries-old medium, evolved from cave art to Renaissance masterpieces, emphasizing color, form, and still imagery to capture historical and cultural narratives. Kinetic sculpture emerged in the 20th century, pioneered by artists like Alexander Calder, integrating movement and mechanics to challenge traditional static art forms. This historical evolution marks a shift from the purely visual engagement of painting to the dynamic, interactive experience offered by kinetic sculpture.
Key Techniques in Painting
Painting employs techniques such as layering, glazing, and brushwork to create depth, texture, and color variation on a static canvas. Artists manipulate mediums like oil, acrylic, and watercolor to achieve effects ranging from realism to abstract expressionism. These techniques contrast with kinetic sculpture's use of motion and mechanical components to engage viewers dynamically.
Engineering Movement: Mechanics of Kinetic Sculpture
Kinetic sculpture incorporates engineering principles to create movement through mechanical components such as gears, motors, and linkages that convert energy into motion. Unlike static painting, kinetic sculptures rely on precise calculations of torque, balance, and momentum to achieve desired dynamic effects. The integration of materials science and mechanical engineering enables these artworks to move fluidly, responding to environmental factors like wind or human interaction.
Visual Impact: Static vs Dynamic Art
Painting offers a static visual impact through fixed compositions, colors, and textures that invite prolonged contemplation and evoke emotions via still imagery. Kinetic sculpture delivers a dynamic visual experience by incorporating movement, light, and changing perspectives, engaging viewers with evolving forms and interactive elements. The contrasting appeal lies in painting's permanence versus kinetic sculpture's fluidity, creating unique sensory engagements that cater to different artistic perceptions.
Audience Interaction and Engagement
Painting offers a primarily visual experience that invites viewers to interpret color, texture, and composition from a static perspective. Kinetic sculpture actively engages the audience through movement and physical interaction, creating dynamic, multi-sensory experiences that evolve over time. This interactive element enhances emotional connection and participation, making kinetic art more immersive compared to the contemplative nature of painting.
Material Choices: Canvas, Colors, and Components
Painting primarily utilizes canvas as the foundational material, with pigments like oil, acrylic, and watercolor defining color vibrancy and texture. Kinetic sculpture incorporates diverse components such as metals, wood, and plastics, integrating moving parts powered by motors or wind to create dynamic visual effects. Material selection in painting emphasizes pigment permanence and surface preparation, whereas kinetic sculpture demands durability and mechanical compatibility for functional movement.
Interpretative Depth and Artistic Expression
Painting offers rich interpretative depth through color, texture, and form, enabling artists to evoke emotions and conceptual narratives within a static medium. Kinetic sculpture introduces an added dimension of movement, engaging viewers through dynamic interaction and temporal change, which expands possibilities for artistic expression. Both mediums challenge perception; painting invites introspective contemplation while kinetic sculpture emphasizes experiential engagement, reflecting diverse modalities of meaning-making in contemporary art.
Future Trends in Painting and Kinetic Sculpture
Future trends in painting emphasize augmented reality integration and interactive digital canvases, blending traditional techniques with immersive technology to create dynamic visual experiences. Kinetic sculpture is evolving through the incorporation of AI-driven movement and sustainable materials, enhancing environmental responsiveness and personalization. Both art forms are converging on interdisciplinary collaborations, leveraging innovations in robotics and smart sensors to redefine audience engagement and artistic expression.
Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com