An abstract provides a concise summary of a research paper, highlighting key objectives, methods, results, and conclusions. It allows readers to quickly determine the relevance of the study to their interests or work. Explore the full article to gain in-depth knowledge and insights.
Table of Comparison
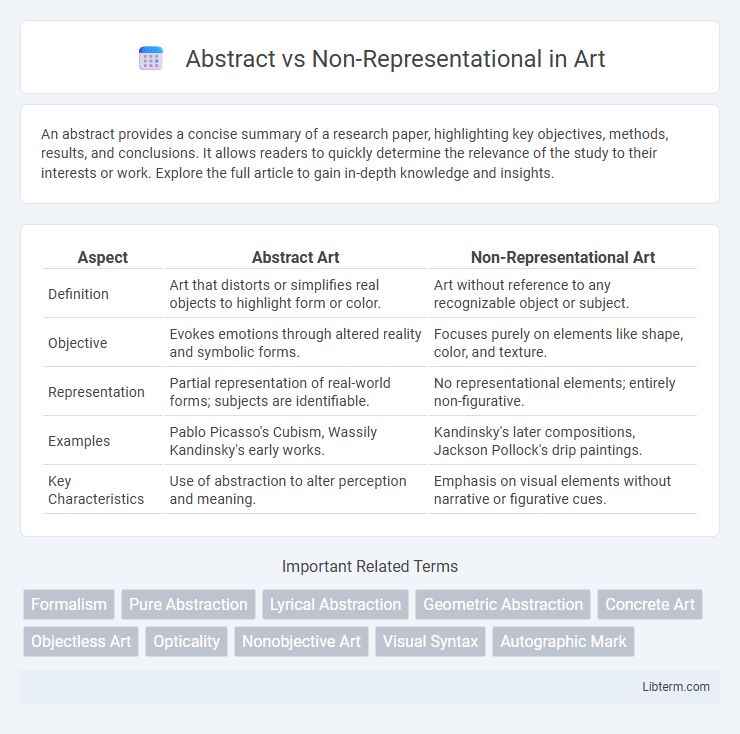
| Aspect | Abstract Art | Non-Representational Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art that distorts or simplifies real objects to highlight form or color. | Art without reference to any recognizable object or subject. |
| Objective | Evokes emotions through altered reality and symbolic forms. | Focuses purely on elements like shape, color, and texture. |
| Representation | Partial representation of real-world forms; subjects are identifiable. | No representational elements; entirely non-figurative. |
| Examples | Pablo Picasso's Cubism, Wassily Kandinsky's early works. | Kandinsky's later compositions, Jackson Pollock's drip paintings. |
| Key Characteristics | Use of abstraction to alter perception and meaning. | Emphasis on visual elements without narrative or figurative cues. |
Understanding Abstract and Non-Representational Art
Abstract art emphasizes shapes, colors, and forms without depicting real objects, creating visual experiences that evoke emotions and ideas. Non-representational art goes further by completely avoiding recognizable subjects, focusing solely on elements like line, color, and texture to convey meaning. Both styles challenge traditional representation, encouraging viewers to interpret art beyond literal depictions.
Defining Key Terms: Abstract vs Non-Representational
The informal sector often lacks legal protections, social security, and minimum wage guarantees, exposing workers to exploitation and poor working conditions. In contrast, the formal sector provides regulated employment with enforced labor laws, social benefits, and access to healthcare and pensions, promoting worker stability and well-being. The disparity significantly impacts social equity, as informal workers face higher vulnerability without formal rights or institutional support.
Historical Origins and Influences
Abstract art originated in the early 20th century, influenced by movements like Cubism and Expressionism, emphasizing the simplification and distortion of forms to convey emotions and ideas. Non-representational art, emerging slightly later, completely rejects any depiction of recognizable subjects, focusing instead on pure color, shape, and texture to evoke meaning. Both styles trace roots to avant-garde experiments and philosophical shifts away from traditional representation, driven by artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Kazimir Malevich.
Differences in Artistic Intent
Abstract art simplifies or distorts real objects to explore shapes, colors, and forms while retaining some connection to the visible world. Non-representational art abandons any reference to recognizable subjects, focusing solely on visual elements like texture, line, and color to convey meaning or evoke emotions. The primary difference lies in artistic intent: abstract art interprets reality, whereas non-representational art creates a completely independent visual experience.
Visual Characteristics and Techniques
Abstract art emphasizes simplified or exaggerated forms, often reducing subjects to geometric shapes and bold colors to convey emotions or ideas. Non-representational art, by contrast, avoids recognizable objects entirely, focusing on pure visual elements such as lines, textures, and color interactions to create an autonomous composition. Techniques in abstract art include stylization and distortion, while non-representational art employs spontaneous brushwork, layering, and experimentation with materials to highlight the medium itself.
Emotional and Intellectual Impact
Abstract art evokes emotional responses through ambiguous forms and colors, allowing viewers to project personal interpretations and feelings. Non-representational art removes recognizable subjects entirely, emphasizing pure visual elements such as shape, line, and texture to engage the intellect with form and composition. Both styles challenge traditional perception, but abstract art often balances emotion and intellect, while non-representational prioritizes conceptual engagement over emotional narrative.
Notable Artists and Works
Abstract art features notable artists like Wassily Kandinsky, whose work "Composition VII" exemplifies vibrant color and form without depicting reality. Non-representational art, pioneered by artists such as Piet Mondrian with his "Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow," emphasizes pure geometric shapes and lines to express ideas beyond visual references. Both styles revolutionized modern art by prioritizing emotion and concept over realistic representation.
Reception and Interpretation by Audiences
Abstract art often engages audiences through recognizable forms distorted or simplified, allowing personal emotional connections and varied interpretations based on familiar references. Non-representational art, lacking identifiable subjects, challenges viewers to focus purely on color, shape, and composition, eliciting responses driven by aesthetic experience rather than narrative meaning. Audience reception of both forms depends heavily on cultural background, artistic context, and individual perception, influencing the depth and nature of interpretation.
The Role of Color, Form, and Composition
In abstract art, color, form, and composition are deliberately manipulated to evoke emotions and ideas without depicting recognizable objects, emphasizing subjective interpretation. Non-representational art further detaches from reality by focusing solely on these elements as independent subjects, creating visual experiences free from figurative references. The role of color intensity, shape dynamics, and spatial arrangement in both styles facilitates a direct sensory impact, encouraging viewers to engage with the artwork's intrinsic aesthetic qualities.
Contemporary Trends and Future Perspectives
Contemporary trends in Abstract art emphasize the deconstruction of form and color to evoke emotional responses beyond literal representation, while Non-Representational art fully rejects recognizable subjects to foreground pure visual language and conceptual exploration. Advances in digital media and AI-driven creativity are expanding possibilities, enabling artists to manipulate non-figurative elements with unprecedented complexity and interactivity. Future perspectives suggest a convergence of Abstract and Non-Representational practices, integrating immersive technologies and multisensory experiences to redefine audience engagement and artistic expression.
Abstract Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com