Continuity ensures seamless progression and consistency across various platforms, enhancing audience engagement and retention. It maintains the integrity of your brand story, creating a cohesive experience that builds trust and recognition. Discover how mastering continuity can elevate your content strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
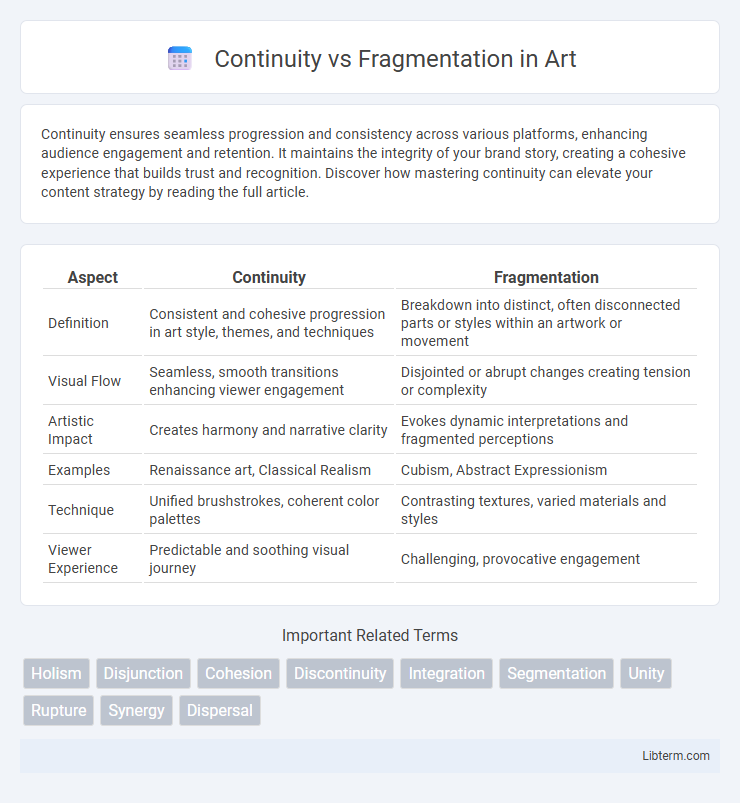
| Aspect | Continuity | Fragmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistent and cohesive progression in art style, themes, and techniques | Breakdown into distinct, often disconnected parts or styles within an artwork or movement |
| Visual Flow | Seamless, smooth transitions enhancing viewer engagement | Disjointed or abrupt changes creating tension or complexity |
| Artistic Impact | Creates harmony and narrative clarity | Evokes dynamic interpretations and fragmented perceptions |
| Examples | Renaissance art, Classical Realism | Cubism, Abstract Expressionism |
| Technique | Unified brushstrokes, coherent color palettes | Contrasting textures, varied materials and styles |
| Viewer Experience | Predictable and soothing visual journey | Challenging, provocative engagement |
Defining Continuity and Fragmentation
Continuity refers to the seamless progression and coherence within a system, ensuring consistent development and integration over time. Fragmentation denotes the breakdown or division of a system into disconnected or isolated parts, disrupting flow and unity. In fields like digital services, urban planning, and communication, maintaining continuity enhances user experience, while fragmentation often leads to inefficiencies and confusion.
Historical Perspectives: Continuity vs Fragmentation
Historical perspectives on continuity versus fragmentation analyze how societies either maintain cultural, political, and social traditions over time or experience breaks and disruptions due to wars, migrations, or ideological shifts. The concept of continuity emphasizes the persistence of institutions, customs, and collective identities that provide stability, while fragmentation highlights periods of disintegration and transition leading to the emergence of new structures or identities. Scholars examine primary sources, archeological evidence, and historiographical debates to understand how civilizations navigate between continuity and fragmentation during critical historical junctures.
Causes and Factors Influencing Continuity
Causes and factors influencing continuity include cultural transmission, social institutions, and shared values that promote stability over time. Economic structures and political systems also play key roles in maintaining consistent societal frameworks. Environmental conditions and technological advancements further contribute to the persistence or adaptation of cultural practices and social norms.
Drivers and Consequences of Fragmentation
Fragmentation in organizational structures often arises from factors such as technological advances, geographical dispersion, and diverse stakeholder interests, leading to communication barriers and decision-making delays. These drivers cause inefficiencies, reduced collaboration, and increased operational costs, undermining overall performance and innovation capacity. Addressing fragmentation requires integrating information systems, fostering cross-functional teams, and aligning strategic objectives to enhance continuity and organizational coherence.
Continuity in Social and Cultural Contexts
Continuity in social and cultural contexts preserves traditions, values, and collective identities across generations, fostering social cohesion and stability. It ensures the transmission of language, rituals, and customs that maintain a group's distinct cultural heritage. This ongoing cultural continuity supports community resilience amidst social change and globalization.
Fragmentation in Modern Societies
Fragmentation in modern societies refers to the breakdown of social cohesion and shared values, leading to increased divisions along ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic lines. This phenomenon is often exacerbated by rapid technological change, globalization, and urbanization, which disrupt traditional community bonds and create isolated subgroups. The resulting social fragmentation can undermine political stability, reduce trust in institutions, and hinder collective action on pressing societal challenges.
Impact on Personal and Collective Identity
Continuity in personal and collective identity fosters a stable sense of self and community cohesion by maintaining shared memories, traditions, and values across time, which strengthens resilience and social unity. Fragmentation, however, disrupts this coherence, leading to identity confusion, social alienation, and weakened group solidarity as individuals and communities struggle to integrate diverse or conflicting narratives. The balance between continuity and fragmentation critically shapes psychological well-being and cultural preservation in dynamic, multicultural societies.
Continuity vs Fragmentation in Technology
Continuity in technology emphasizes seamless integration and consistent user experience across devices and platforms, enabling efficient data flow and stable system performance. Fragmentation occurs when hardware, software, or network standards diverge, causing compatibility issues, increased maintenance costs, and hindered innovation. Addressing fragmentation through unified protocols and interoperable technologies enhances scalability and long-term reliability in tech ecosystems.
Balancing Stability and Change
Balancing stability and change requires managing continuity and fragmentation to foster organizational resilience and adaptability. Maintaining core values and long-term goals ensures stability, while embracing innovation and flexible structures addresses fragmentation. Effective leadership integrates consistent processes with dynamic strategies to optimize performance amidst evolving environments.
Future Implications and Strategies
Future implications of continuity emphasize sustained growth through consistent processes, fostering resilience and long-term success in organizations. Fragmentation demands adaptive strategies that prioritize agility, innovation, and modular approaches to rapidly respond to dynamic market conditions and technological disruptions. Balancing continuity and fragmentation enables businesses to leverage stable foundations while embracing transformative opportunities for competitive advantage.
Continuity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com