Expressionism is an art movement focused on representing raw and intense emotions rather than realistic depictions, often using bold colors and distorted forms to evoke a visceral response. Originating in the early 20th century, it challenged traditional aesthetics by prioritizing subjective experience and inner feelings over objective reality. Explore this article to uncover how expressionism transformed art and impacted modern creative expression.
Table of Comparison
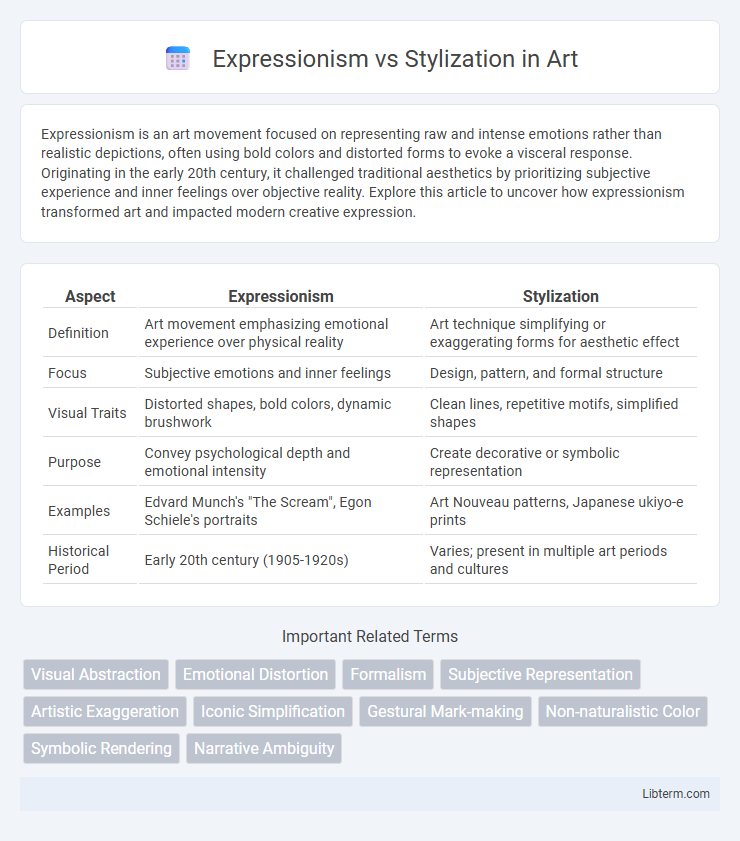
| Aspect | Expressionism | Stylization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art movement emphasizing emotional experience over physical reality | Art technique simplifying or exaggerating forms for aesthetic effect |
| Focus | Subjective emotions and inner feelings | Design, pattern, and formal structure |
| Visual Traits | Distorted shapes, bold colors, dynamic brushwork | Clean lines, repetitive motifs, simplified shapes |
| Purpose | Convey psychological depth and emotional intensity | Create decorative or symbolic representation |
| Examples | Edvard Munch's "The Scream", Egon Schiele's portraits | Art Nouveau patterns, Japanese ukiyo-e prints |
| Historical Period | Early 20th century (1905-1920s) | Varies; present in multiple art periods and cultures |
Understanding Expressionism: Key Characteristics
Expressionism emphasizes emotional experience over physical reality, using distorted forms and vivid colors to convey inner feelings and moods. Key characteristics include exaggerated shapes, intense brushwork, and a subjective perspective that prioritizes individual interpretation. This art movement often abstracts or distorts figures and environments to evoke psychological depth and raw emotion.
Defining Stylization in Art and Design
Stylization in art and design involves the deliberate simplification or exaggeration of forms to create a distinct visual language, emphasizing essential shapes and patterns over realistic representation. Unlike Expressionism, which centers on conveying intense emotional experiences through distortion, stylization prioritizes aesthetic consistency and symbolic meaning across a work. This approach is evident in diverse media, from graphic design and animation to traditional motifs, where abstraction enhances recognition and thematic clarity.
Historical Origins: Expressionism and Stylization
Expressionism originated in early 20th-century Germany as a reaction against realism, emphasizing emotional experience through distorted forms and vivid colors to evoke subjective feelings. Stylization dates back to ancient art forms, such as Egyptian hieroglyphics and Asian ink paintings, where artists abstracted natural forms into simplified, decorative patterns to convey symbolic meaning. Both movements reflect distinct historical contexts and artistic intentions, with Expressionism rooted in personal emotion and Stylization in cultural symbolism.
Techniques of Expressionism vs Stylization
Expressionism techniques emphasize vivid, exaggerated brushstrokes, distorted forms, and intense color contrasts to evoke emotional experiences and subjective perspectives. Stylization techniques simplify shapes, use uniform lines, and apply decorative patterns to create a consistent and recognizable visual language that abstracts reality into symbolic or iconic forms. Expressionism prioritizes emotional depth through dynamic, often chaotic visuals, while stylization focuses on controlled, deliberate alterations that enhance aesthetic appeal and thematic clarity.
The Role of Emotion in Expressionism
Expressionism emphasizes raw, intense emotion by distorting reality to evoke subjective feelings and inner experiences, prioritizing emotional impact over realistic representation. The use of bold colors, exaggerated forms, and dynamic brushstrokes in Expressionist art serves to communicate psychological states and evoke empathy from the viewer. Unlike stylization, which simplifies or exaggerates forms for decorative or symbolic effect, Expressionism centers on conveying personal and emotional truths through visual distortion.
Abstraction and Form in Stylized Art
Stylization in art emphasizes abstraction by simplifying and exaggerating forms to highlight essential shapes and patterns, often departing from realistic representation to create a unique visual language. Expressionism focuses on conveying intense emotional experiences through distorted and dynamic forms, prioritizing subjective perception over formal accuracy. While Expressionism uses abstraction to evoke mood and psychological depth, stylized art abstracts form primarily to achieve decorative or symbolic effects.
Influential Artists: Expressionists and Stylists
Expressionism features influential artists like Edvard Munch and Egon Schiele, who emphasized emotional intensity and distorted forms to evoke psychological depth. Stylization includes artists such as Gustav Klimt and Alphonse Mucha, known for their decorative, ornate designs and use of simplified, repeated patterns. Both movements shaped modern art by exploring subjective interpretation versus aesthetic refinement.
Contemporary Interpretations: Expressionism vs Stylization
Contemporary interpretations of Expressionism emphasize raw emotional intensity and psychological depth, using distorted forms and vivid colors to evoke personal and societal experiences. Stylization in modern art focuses on the deliberate simplification or exaggeration of shapes and motifs to create a distinct aesthetic language that often prioritizes design over realism. Both approaches challenge traditional representation but diverge in intent: Expressionism seeks to communicate inner feelings, while Stylization explores formal abstraction and visual identity.
Visual Impact: Comparing Viewer Experience
Expressionism emphasizes intense emotional impact through exaggerated forms and bold color contrasts, creating a visceral and immersive viewer experience. Stylization simplifies and abstracts details to enhance clarity and design coherence, offering a controlled and often symbolic visual experience. The visual impact of expressionism tends to evoke raw emotional responses, while stylization guides viewers toward interpretive appreciation through refined artistic conventions.
Choosing Between Expressionism and Stylization
Choosing between Expressionism and Stylization depends on the desired emotional impact and visual clarity of the artwork. Expressionism emphasizes raw, intense emotional experiences through distorted forms and bold colors, making it ideal for conveying psychological depth and subjective reality. Stylization focuses on simplifying and exaggerating features to create a recognizable, often decorative aesthetic, which enhances clarity and iconic representation without sacrificing artistic expression.
Expressionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com