Painting transforms blank spaces into vibrant expressions of creativity and emotion, using color, texture, and form to convey meaning beyond words. This art form spans from classical masterpieces to contemporary abstract works, each offering unique insights and inspiration. Explore the rest of this article to discover techniques, styles, and tips that will enhance your understanding and appreciation of painting.
Table of Comparison
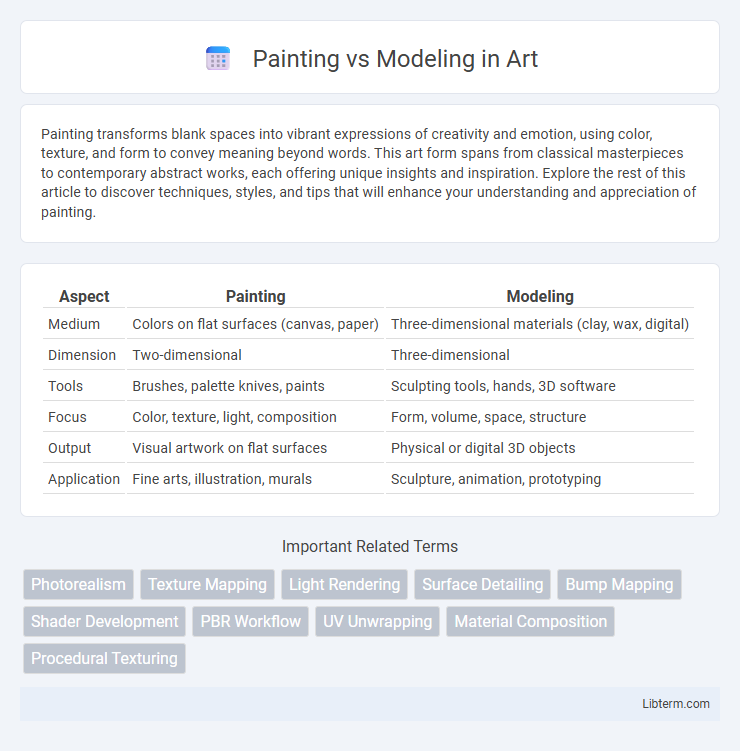
| Aspect | Painting | Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Colors on flat surfaces (canvas, paper) | Three-dimensional materials (clay, wax, digital) |
| Dimension | Two-dimensional | Three-dimensional |
| Tools | Brushes, palette knives, paints | Sculpting tools, hands, 3D software |
| Focus | Color, texture, light, composition | Form, volume, space, structure |
| Output | Visual artwork on flat surfaces | Physical or digital 3D objects |
| Application | Fine arts, illustration, murals | Sculpture, animation, prototyping |
Introduction to Painting and Modeling
Painting involves applying pigments on surfaces such as canvas or walls to create visual art, relying on techniques like color theory, texture, and brushwork to convey emotions and narratives. Modeling refers to crafting three-dimensional representations using materials like clay, digital software, or 3D printers to shape objects with depth, form, and spatial accuracy. Both disciplines require a deep understanding of composition and material properties to effectively communicate artistic concepts.
Defining Painting: Techniques and Styles
Painting encompasses diverse techniques such as oil, acrylic, and watercolor, each offering unique textures and visual effects that shape artistic expression. Styles range from realism and impressionism to abstract and surrealism, defining the painter's approach to color, form, and composition. Mastery of brushwork, layering, and color blending distinguishes painting as a dynamic medium focused on two-dimensional visual storytelling.
What is Modeling? An Overview
Modeling is the process of creating three-dimensional digital representations of objects, characters, or environments using specialized software like Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max. It emphasizes the construction of geometric shapes and surfaces, allowing for detailed manipulation of vertices, edges, and faces to achieve realistic or stylized forms. Unlike painting, which focuses on texture and color application, modeling builds the foundational structure essential for animation, simulation, and rendering in various industries such as gaming, film, and virtual reality.
Historical Evolution of Both Art Forms
Painting originated as one of the earliest forms of human expression, dating back to prehistoric cave art around 40,000 years ago, evolving through periods like the Renaissance, Baroque, and Impressionism with advances in techniques and materials. Modeling, emerging prominently during the prehistoric era as well with clay and stone sculptures, matured notably during Classical Antiquity and the Renaissance, where artists like Michelangelo elevated it to fine art through highly detailed three-dimensional forms. Both art forms have continually influenced each other's development, with painting providing color and narrative depth while modeling contributes spatial and tactile dimensions to artistic expression.
Tools and Materials: Painting vs Modeling
Painting primarily uses brushes, acrylics, oils, watercolors, and canvases or paper as its main tools and materials, allowing artists to manipulate color, texture, and light on flat surfaces. Modeling involves sculpting tools, clay, wax, plaster, or digital software for 3D design, enabling the creation of tangible or virtual three-dimensional forms. Both disciplines require specialized instruments tailored to their distinct mediums and techniques for effective artistic expression.
Creative Processes Compared
Painting involves the direct application of color and texture on surfaces, emphasizing brushstroke techniques and color blending to evoke emotions and visual narratives. Modeling requires shaping three-dimensional forms, often using clay or digital tools, to create tangible or virtual representations with depth and spatial awareness. Both creative processes rely on artistic intuition and iterative refinement but differ fundamentally in their manipulation of materials and the perception of dimensionality.
Expression and Interpretation in Art
Painting allows artists to convey emotions and abstract concepts through color, brushstrokes, and texture, creating a direct sensory experience that invites subjective interpretation. Modeling, often in sculpture or 3D forms, emphasizes the physicality and dimensionality of shapes, enabling viewers to explore spatial relationships and tactile qualities that influence emotional resonance. Both mediums offer unique avenues for expression, with painting focusing on visual symbolism and modeling highlighting form and presence in artistic interpretation.
Skill Sets Required for Painting and Modeling
Painting requires skills in color theory, brush techniques, and surface preparation to create texture and depth on two-dimensional surfaces. Modeling demands proficiency in sculpting, spatial awareness, and familiarity with 3D software or traditional materials to accurately shape and visualize three-dimensional forms. Both disciplines benefit from a strong understanding of anatomy, composition, and light interaction.
Popularity and Accessibility
Painting remains one of the most popular art forms worldwide due to its rich history and accessibility through basic materials like brushes and canvases. Modeling, often associated with digital tools or sculpting mediums, has gained traction as technology advances but requires more specialized equipment and skills. Both mediums offer creative expression, yet painting's lower cost and ease of entry maintain its dominant popularity among beginners and hobbyists.
Choosing Between Painting and Modeling
Choosing between painting and modeling depends on your creative interests and desired outcomes. Painting emphasizes color theory, brush techniques, and two-dimensional composition, ideal for expressing emotions and abstract ideas on canvas. Modeling focuses on shaping materials like clay or digital software to create three-dimensional representations, suitable for tactile artistry and detailed spatial visualization.
Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com