Porcelain is a highly durable, translucent ceramic material prized for its strength, smooth texture, and elegant appearance, often used in fine dinnerware, tiles, and decorative art. Its production involves firing refined clay at extremely high temperatures, resulting in a vitrified, non-porous surface that resists stains and chipping. Discover how porcelain's unique properties can enhance Your home and lifestyle as you explore the full details in this article.
Table of Comparison
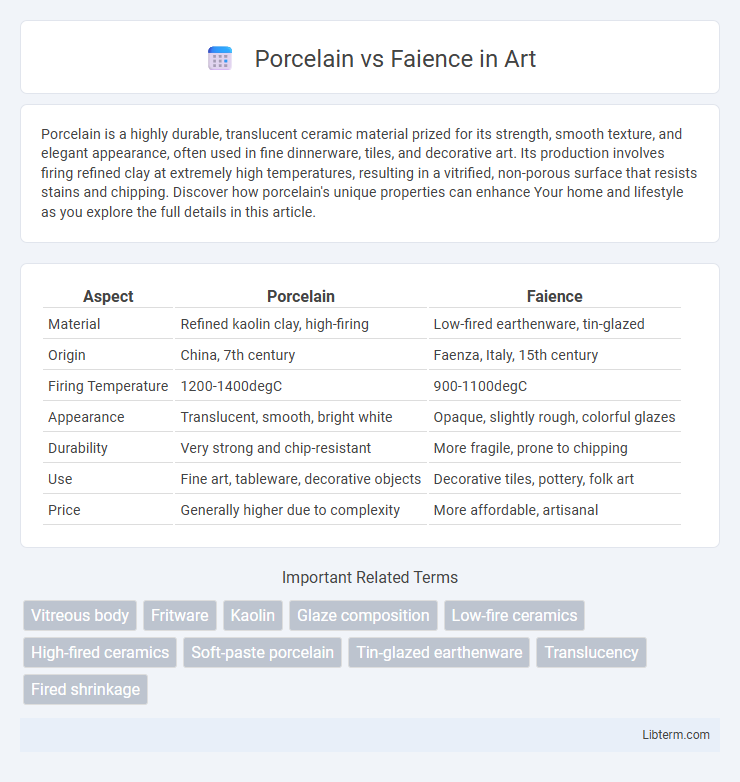
| Aspect | Porcelain | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Refined kaolin clay, high-firing | Low-fired earthenware, tin-glazed |
| Origin | China, 7th century | Faenza, Italy, 15th century |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1400degC | 900-1100degC |
| Appearance | Translucent, smooth, bright white | Opaque, slightly rough, colorful glazes |
| Durability | Very strong and chip-resistant | More fragile, prone to chipping |
| Use | Fine art, tableware, decorative objects | Decorative tiles, pottery, folk art |
| Price | Generally higher due to complexity | More affordable, artisanal |
Introduction to Porcelain and Faience
Porcelain is a high-fired ceramic characterized by its strength, translucency, and white, glassy surface, made primarily from kaolin clay and fired at temperatures above 1,200degC. Faience is a glazed earthenware pottery known for its opaque, brightly colored surfaces and lower firing temperature, typically ranging between 1,000degC and 1,100degC. While porcelain is valued for its durability and fine texture used in tableware and art, faience is prized for decorative purposes and historical significance across cultures.
Historical Background and Origins
Porcelain originated in China during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD), known for its dense, translucent quality achieved through high-temperature kiln firing of kaolin clay. Faience, with roots tracing back to Ancient Egypt and the Near East around 4000 BCE, is a glazed non-clay ceramic material crafted from powdered quartz or sand, often used for decorative objects and tiles. These distinct materials highlight different cultural advancements in ceramic technology and artistic expression across millennia.
Material Composition Differences
Porcelain is primarily made from kaolin clay combined with feldspar and quartz, resulting in a dense, vitrified, and highly durable ceramic with a smooth, white, and translucent finish. Faience, on the other hand, is composed mainly of a porous earthenware body coated with a tin-glaze, which creates a glossy surface but remains less durable and more porous than porcelain. The key material difference lies in porcelain's fine-grained, high-temperature fired composition compared to faience's low-fired, glazed earthenware base.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Porcelain is made from kaolin clay and fired at extremely high temperatures between 1,200degC and 1,400degC, resulting in a dense, vitrified, and translucent material. Faience involves a core clay body coated with a quartz-based glaze, fired at lower temperatures around 1,000degC to 1,100degC, producing a more porous and opaque finish. The manufacturing process for porcelain requires more precise control of raw materials and higher firing temperatures, contributing to its strength and fine texture compared to the more rustic and decorative faience.
Physical Appearance and Texture
Porcelain boasts a smooth, glass-like texture with a translucent, white, and often glossy finish, making it distinctively elegant compared to faience. Faience features a more porous, matte surface with a slightly rough or grainy feel, often decorated with vibrant glazes that emphasize its rustic charm. The fine, dense composition of porcelain results in a heavier and more durable material, whereas faience's softer body is lighter and more prone to chipping.
Durability and Strength
Porcelain exhibits superior durability and strength compared to faience due to its dense, vitrified structure formed at high temperatures, resulting in enhanced resistance to chipping and cracking. Faience, a type of tin-glazed earthenware, is more porous and brittle, making it less resilient under heavy use or impact. Porcelain's robustness makes it ideal for everyday dinnerware and fine art pieces requiring long-lasting durability.
Artistic Applications and Uses
Porcelain offers a smooth, translucent surface ideal for detailed painting, glazing, and sculpting in fine art ceramics, prized for its durability and elegance in decorative objects. Faience, characterized by its porous, earthenware base and vibrant tin-glaze, allows for bold, colorful, and textured artistic applications often used in tiles, pottery, and ornamental ware. Artists favor porcelain for refined, delicate works and faience for expressive, rustic designs with rich historical and cultural significance.
Cost and Market Value
Porcelain generally commands a higher market value than faience due to its durability, finer craftsmanship, and historical prestige, often fetching premium prices at auctions and among collectors. Faience, made from tin-glazed earthenware, is less expensive to produce and buy, making it more accessible but typically less valued in high-end antique markets. The cost difference reflects porcelain's higher production complexity and desirability, significantly impacting resale and collectible appeal.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Porcelain requires gentle cleaning with a soft cloth and mild detergent to maintain its glossy finish and avoid scratches. Faience, being more porous and fragile, should be cleaned with a damp cloth without harsh chemicals to prevent damage and discoloration. Both materials benefit from careful handling and avoiding abrupt temperature changes to preserve their structural integrity.
Choosing Between Porcelain and Faience
Choosing between porcelain and faience depends on the intended use and desired aesthetic; porcelain offers superior durability, translucence, and a refined finish ideal for fine dinnerware and decorative pieces. Faience, characterized by its porous body and vibrant tin-glazed surface, suits ornamental objects and rustic tableware where artistic expression and affordability are priorities. Consider porcelain for long-lasting, high-end applications, while faience provides a distinctive, colorful alternative for casual or decorative purposes.
Porcelain Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com