Encaustic painting involves using heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments to create vibrant, textured artworks that remain durable over time. This ancient art form allows your creativity to flow as you layer and fuse wax with heat, resulting in unique depth and luminosity. Dive deeper into the world of encaustic techniques and discover how to master this captivating medium.
Table of Comparison
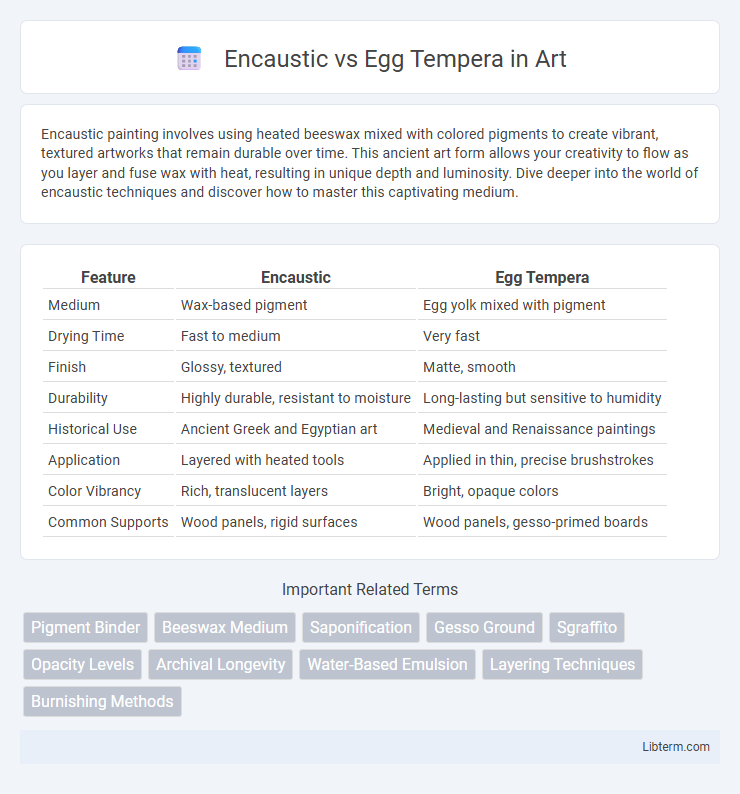
| Feature | Encaustic | Egg Tempera |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Wax-based pigment | Egg yolk mixed with pigment |
| Drying Time | Fast to medium | Very fast |
| Finish | Glossy, textured | Matte, smooth |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to moisture | Long-lasting but sensitive to humidity |
| Historical Use | Ancient Greek and Egyptian art | Medieval and Renaissance paintings |
| Application | Layered with heated tools | Applied in thin, precise brushstrokes |
| Color Vibrancy | Rich, translucent layers | Bright, opaque colors |
| Common Supports | Wood panels, rigid surfaces | Wood panels, gesso-primed boards |
Introduction to Encaustic and Egg Tempera
Encaustic painting involves using heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments, applied while molten to create vibrant, textured artworks that retain color over centuries. Egg tempera, an ancient medium, blends pigment with egg yolk, producing a fast-drying, matte finish favored for detailed and precise imagery. Both techniques emphasize durability and luminosity but differ significantly in texture, drying time, and application methods.
Historical Background of Both Techniques
Encaustic painting, dating back to ancient Greece and Egypt around 1000 BCE, involved mixing pigment with heated beeswax to create durable, vibrant artworks, notably seen in the Fayum mummy portraits of Roman Egypt. Egg tempera, emerging prominently during the early Renaissance in the 5th century CE, utilized egg yolk as a binder to produce luminous, fast-drying paintings valued for their fine detail and archival longevity. Both techniques reflect distinct historical contexts with encaustic linked to funerary traditions and egg tempera central to medieval ecclesiastical art.
Materials and Tools Needed
Encaustic painting requires beeswax, damar resin, and pigments heated on a palette, with tools such as heated metal spatulas and brushes for application and manipulation. Egg tempera relies on a mixture of egg yolk, water, and finely ground pigments, applied with fine brushes on a rigid, primed surface like wood panels. Both mediums demand specific preparation methods, with encaustic needing a heat source and egg tempera requiring rapid, precise brushwork before the paint dries.
Process and Application Methods
Encaustic painting involves melting beeswax mixed with colored pigments and applying it hot onto a surface, allowing for rapid layering and textural effects through reheating and sculpting. Egg tempera requires mixing pigments with egg yolk as a binder, applied in thin, semi-transparent layers with fine brushes on a rigid substrate, enabling detailed and durable finishes. The encaustic method suits expressive, tactile artworks, while egg tempera excels in precision and longevity due to its fast-drying, buildable application.
Color and Finish Differences
Encaustic paint uses heated beeswax mixed with pigments, creating a rich, luminous finish with vibrant, translucent colors that can be layered for depth and texture. Egg tempera, made from pigment and egg yolk, produces a matte, velvety finish with finely detailed, opaque colors that dry quickly and offer a more muted yet permanent surface. The difference in binders directly influences the color saturation and surface sheen, with encaustic's glossy translucence contrasting egg tempera's soft, subtle matte quality.
Durability and Longevity
Encaustic painting, using heated beeswax mixed with pigments, offers exceptional durability due to its resistance to moisture, cracking, and fading over centuries. Egg tempera, made from pigment and egg yolk, delivers long-lasting color stability but is more susceptible to environmental damage and requires careful preservation to maintain its vibrancy. Both mediums have demonstrated remarkable longevity in historical artworks, with encaustic favored for its robustness and egg tempera prized for its fine detail and luminosity.
Artistic Styles and Effects
Encaustic painting produces rich, textured surfaces with luminous color depth due to its wax-based medium, ideal for creating vibrant, layered effects and three-dimensional qualities in abstract and modern artistic styles. Egg tempera, characterized by its fast-drying, matte finish, allows for fine detail and precise brushwork, making it preferred in classical and Renaissance art for realistic portraits and intricate frescoes. The contrasting drying times and mediums directly influence the artistic techniques and final visual effects achieved in each style.
Common Uses and Popular Artists
Encaustic painting, known for its vibrant colors and textured surfaces, is commonly used for portraiture and contemporary art, with artists like Jasper Johns and Diego Rivera pioneering the medium. Egg tempera, favored for its fine detail and longevity, is traditionally employed in religious iconography and Renaissance portraits, exemplified by artists such as Sandro Botticelli and Duccio di Buoninsegna. Both techniques offer unique aesthetic qualities that appeal to different artistic purposes and historical contexts.
Pros and Cons of Each Medium
Encaustic offers vibrant, durable colors and a unique texture due to its wax base, but it requires specialized heating tools and can be time-consuming to master. Egg tempera provides fine detail and fast-drying properties with a matte finish, yet it is less flexible, prone to cracking, and demands precise mixture ratios with pigments. Both mediums excel in longevity, yet encaustic is favored for its luminous surface, while egg tempera appeals to artists seeking precision and historical authenticity.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Art
Encaustic painting offers rich texture and vibrant colors through heated beeswax mixed with pigments, ideal for artists looking to create layered, durable artwork. Egg tempera, composed of pigment and egg yolk, dries quickly to a matte finish and provides precise detail, making it suitable for fine lines and intricate designs. Selecting the right technique depends on your desired finish, working time, and the level of detail needed for your art.
Encaustic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com