Chisels are essential hand tools designed for carving or cutting hard materials such as wood, stone, or metal with precision. They come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored for specific tasks like woodworking, masonry, or metalworking to achieve accurate and clean results. Discover how to choose the right chisel for your project and master effective techniques by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
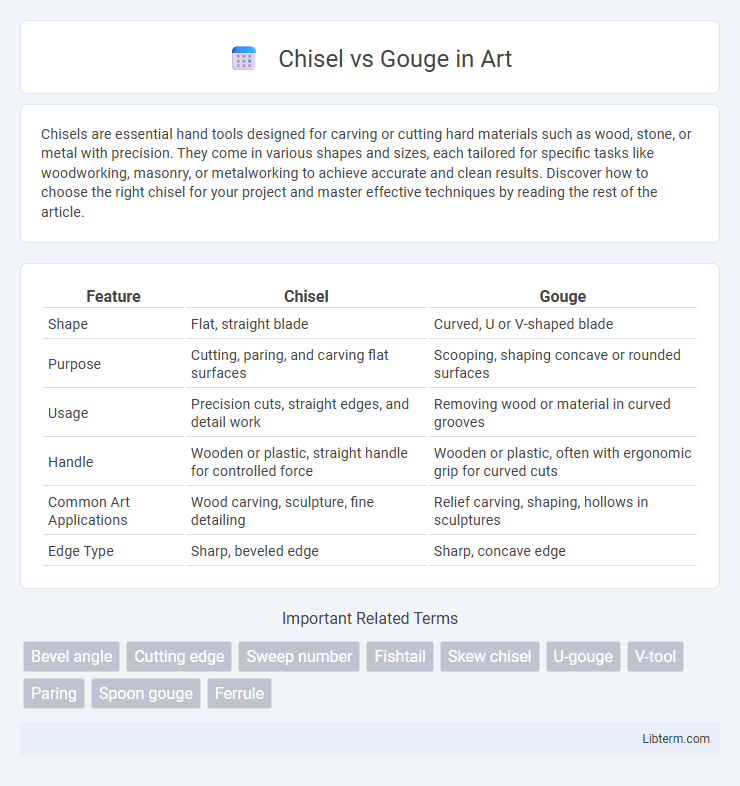
| Feature | Chisel | Gouge |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Flat, straight blade | Curved, U or V-shaped blade |
| Purpose | Cutting, paring, and carving flat surfaces | Scooping, shaping concave or rounded surfaces |
| Usage | Precision cuts, straight edges, and detail work | Removing wood or material in curved grooves |
| Handle | Wooden or plastic, straight handle for controlled force | Wooden or plastic, often with ergonomic grip for curved cuts |
| Common Art Applications | Wood carving, sculpture, fine detailing | Relief carving, shaping, hollows in sculptures |
| Edge Type | Sharp, beveled edge | Sharp, concave edge |
Introduction to Chisels and Gouges
Chisels and gouges are essential woodworking tools designed for shaping and carving wood. Chisels have a straight, flat blade ideal for precise cutting and cleaning joints, while gouges feature a curved blade suited for scooping and creating rounded grooves. Understanding their distinct blade shapes helps woodworkers choose the right tool for detailed sculpting or flat surface work.
Defining Chisels: Uses and Types
Chisels are versatile hand tools primarily used for cutting, carving, and shaping wood, metal, or stone, characterized by a sharp, beveled edge mounted on a handle. Common types include bevel edge chisels for woodworking, mortise chisels for heavy-duty cutting, and paring chisels for fine, precise work. Their applications range from removing small amounts of material to detailed carving and joinery tasks, making them essential for craftsmen and woodworkers.
Understanding Gouges: Shapes and Applications
Gouges feature a curved blade that allows for specialized tasks like carving concave shapes, hollowing out surfaces, and creating intricate details in woodworking and sculpture. Their shapes vary from shallow curves to deep U-shaped profiles, each designed to handle specific cutting angles and depths effectively. Mastery of different gouge shapes enhances precision in shaping wood, enabling smoother finishes and more detailed craftsmanship compared to flat-edged chisels.
Key Differences Between Chisels and Gouges
Chisels feature a straight, flat cutting edge ideal for precise, straight cuts and fine detailing, while gouges have a curved or U-shaped blade designed for scooping out wood and creating rounded grooves. The blade profile of gouges allows for varied curvature and depth control, making them essential for carving concave shapes, whereas chisels are primarily used for paring, trimming, and smoothing flat surfaces. Chisels generally require less force and are preferred for joinery and cabinetry, while gouges excel in artistic woodcarving tasks requiring texture and contour.
Common Materials and Construction
Chisels and gouges are essential woodworking tools designed for shaping wood, with chisels featuring a straight, flat blade ideal for cutting and paring in hardwoods like oak and maple. Gouges have a curved blade used primarily for carving softer woods such as pine and basswood, allowing for scooping and hollowing surfaces with precision. Both tools are typically made from high-carbon steel or chromium-vanadium steel to ensure durability and maintain sharpness during intricate and heavy-duty crafting tasks.
Techniques for Using Chisels Effectively
Effective chisel use involves maintaining a sharp edge and controlling the tool with steady, precise pressure to shape wood accurately. Techniques such as proper gripping, angle adjustment for different cuts, and using a mallet for enhanced force improve cutting efficiency. Mastering chip removal and avoiding excessive force helps prevent wood splitting and ensures clean, detailed finishes.
Techniques for Mastering Gouge Work
Mastering gouge techniques requires controlled wrist movement and consistent pressure to achieve smooth, curved cuts in woodcarving. Using varied gouge shapes, such as U-shaped or V-shaped, allows for detailed reliefs and rounded contours, enhancing precision in sculpting. Regular practice with sharpening and angle adjustments improves the effectiveness and lifespan of gouges compared to flat chisels.
Maintenance and Sharpening Tips
Maintaining chisels and gouges involves regular cleaning, proper storage, and periodic sharpening to ensure optimal cutting performance; chisels require flat bevel sharpening while gouges need curved bevel techniques using slip stones or diamond files. Using honing guides can improve angle consistency, and stropping with fine abrasive compounds removes burrs and polishes edges for prolonged sharpness. Proper lubrication of wooden handles and rust prevention through oiling metal parts also extend tool lifespan significantly.
Choosing Between a Chisel and a Gouge
Choosing between a chisel and a gouge depends on the desired woodworking effect and project requirements. Chisels, with their flat, straight edges, excel at creating clean, precise cuts and fine detailing, making them ideal for joinery and leveling surfaces. Gouges, featuring curved blades, are better suited for carving concave shapes, contours, and intricate designs, enabling more fluid and rounded cuts on wood.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Tool for Your Project
Choosing between a chisel and a gouge depends on the specific carving requirements and material type; chisels excel in creating straight, precise cuts on flat surfaces, while gouges are ideal for shaping curves and hollows. For woodworking projects involving detailed reliefs or rounded surfaces, gouges provide better control and smoother results. Selecting the appropriate tool enhances efficiency and ensures the desired finish, making the project more professional and refined.
Chisel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com