Multimedia integrates text, audio, images, animation, and video to create engaging and interactive content that enhances user experience across digital platforms. It plays a critical role in education, entertainment, advertising, and communication by making information more accessible and impactful. Discover how mastering multimedia can transform your projects by exploring the detailed insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
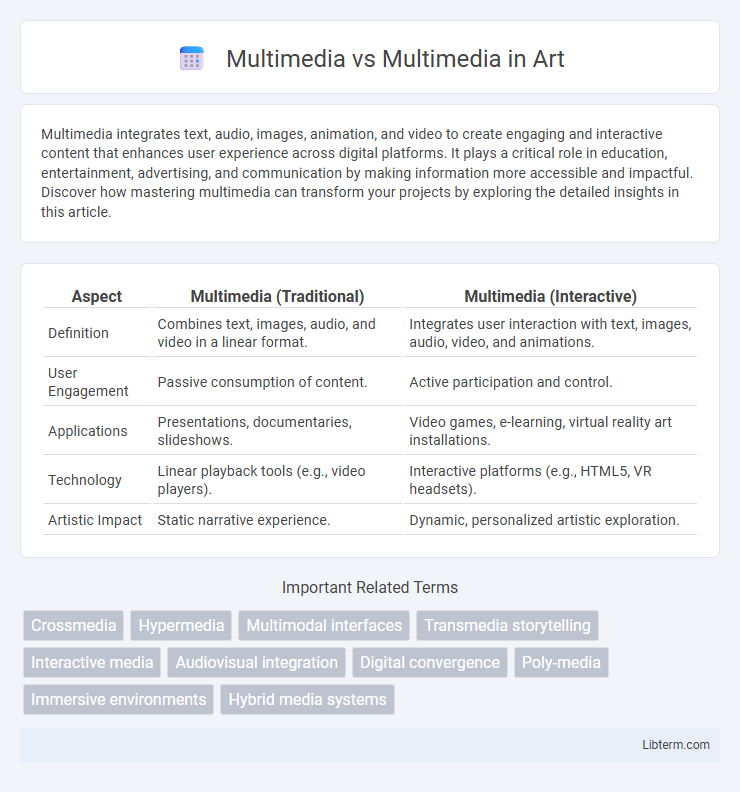
| Aspect | Multimedia (Traditional) | Multimedia (Interactive) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines text, images, audio, and video in a linear format. | Integrates user interaction with text, images, audio, video, and animations. |
| User Engagement | Passive consumption of content. | Active participation and control. |
| Applications | Presentations, documentaries, slideshows. | Video games, e-learning, virtual reality art installations. |
| Technology | Linear playback tools (e.g., video players). | Interactive platforms (e.g., HTML5, VR headsets). |
| Artistic Impact | Static narrative experience. | Dynamic, personalized artistic exploration. |
Understanding the Term: What Does “Multimedia” Mean?
Multimedia refers to the integration of multiple content forms such as text, audio, images, animations, video, and interactive content to enhance user experience and communication. This term encompasses various digital and electronic platforms where different media types are combined to convey information effectively. Understanding multimedia involves recognizing how these diverse elements interact to create engaging and dynamic presentations or applications.
The Evolution of Multimedia in Technology
The evolution of multimedia in technology has transformed from simple text and static images to immersive virtual reality and augmented reality experiences. Advances in computing power, high-speed internet, and sophisticated software have enabled seamless integration of video, audio, animation, and interactive content. This progression has revolutionized industries such as gaming, education, advertising, and entertainment by offering richer user engagement and dynamic information delivery.
Types of Multimedia: Interactive vs. Passive
Interactive multimedia engages users through inputs and real-time feedback, commonly found in video games, virtual reality, and educational software, enhancing user experience and learning outcomes. Passive multimedia delivers content without user interaction, typical in videos, slideshows, and music presentations, optimized for straightforward message reception. Both types leverage audio, video, text, and graphics but differ fundamentally in user engagement and control mechanisms.
Key Components of Multimedia Systems
Key components of multimedia systems include hardware elements like input devices, output devices, and storage units, which facilitate the capture, display, and preservation of multimedia content. Software components encompass authoring tools, multimedia players, and network protocols that enable content creation, playback, and distribution across platforms. Integration of text, audio, images, video, and animation is essential for delivering rich, interactive user experiences in various applications such as education, entertainment, and communication.
Multimedia Platforms: Comparing Hardware and Software
Multimedia platforms encompass both hardware components, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and display devices, and software solutions like content creation tools, media players, and editing programs. Hardware performance directly affects the quality and responsiveness of multimedia applications, while software determines compatibility, user interface, and functionality. Effective multimedia experiences depend on the seamless integration of advanced hardware capabilities with optimized software platforms to support diverse media formats and interactive features.
Multimedia Applications in Education and Business
Multimedia applications in education enhance learning experiences through interactive elements like videos, animations, and simulations, promoting better retention and engagement among students. In business, multimedia facilitates effective communication, marketing, and training by integrating text, audio, and visuals to create compelling presentations and e-learning modules. Both sectors leverage multimedia technology to improve information delivery, collaboration, and user interaction, driving productivity and learning outcomes.
Multimedia Content Creation: Tools and Techniques
Multimedia content creation involves using various tools and techniques to produce engaging visual, audio, and interactive elements. Popular software like Adobe Creative Suite, Final Cut Pro, and Blender facilitate video editing, graphic design, and 3D modeling, while techniques such as storyboarding, layering, and animation enhance storytelling and user engagement. Effective multimedia content integrates diverse media types to optimize communication and deliver immersive user experiences.
Multimedia Delivery: Online vs. Offline Methods
Multimedia delivery methods contrast significantly between online and offline approaches, impacting accessibility and user experience. Online multimedia streaming leverages high-speed internet for real-time content delivery, enabling interactive elements and continuous updates, whereas offline methods rely on storage mediums like DVDs or USB drives, offering consistent access without connectivity dependence. The choice between these delivery methods depends on factors such as bandwidth availability, content size, and the need for interactivity or portability.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Multimedia
Multimedia enhances learning and communication by integrating text, images, audio, and video, making content more engaging and accessible to diverse audiences. Benefits include improved information retention and the ability to cater to various learning styles, while challenges involve high production costs, technical issues, and the need for user digital literacy. Effective multimedia implementation requires balancing creativity with usability to maximize impact and minimize distractions.
Future Trends in Multimedia Technology
Future trends in multimedia technology emphasize immersive experiences through augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) applications that integrate seamlessly with 5G networks and AI-driven content creation tools. Enhanced interactive multimedia platforms leverage real-time data processing and cloud computing to deliver personalized, adaptive user experiences across devices. The convergence of multimedia with blockchain technology is set to revolutionize content ownership, digital rights management, and secure distribution channels.
Multimedia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com