Soft pastel offers vibrant, velvety colors that blend effortlessly for creating rich textures and delicate transitions in artwork. This medium is ideal for artists seeking to capture subtle nuances and luminous effects in portraits, landscapes, and still lifes. Discover how to master soft pastel techniques and elevate your artistic expression by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
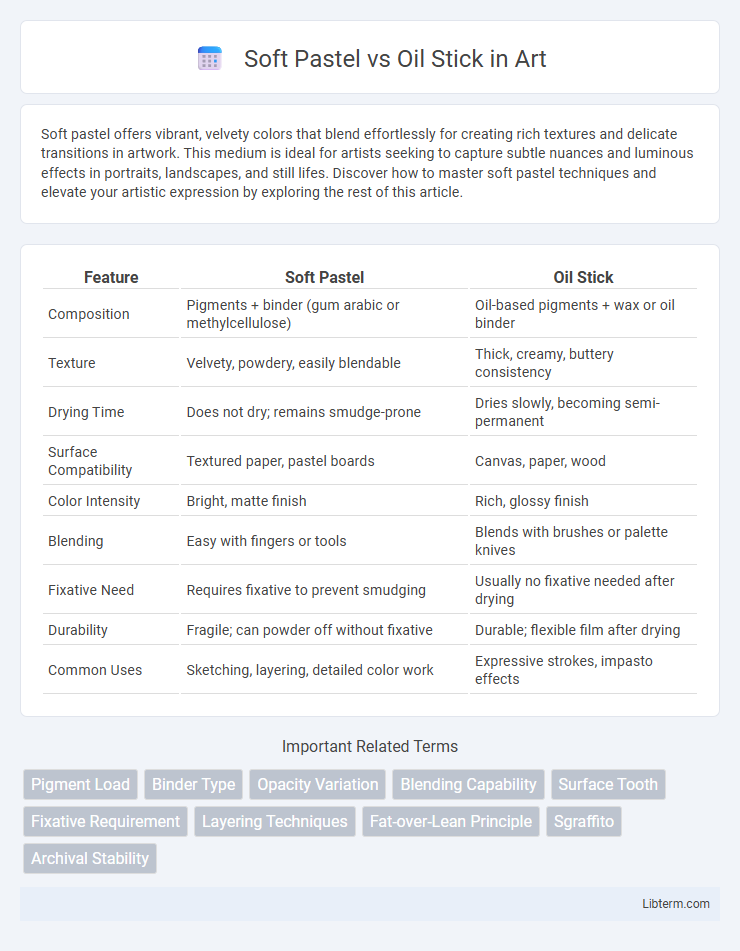
| Feature | Soft Pastel | Oil Stick |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pigments + binder (gum arabic or methylcellulose) | Oil-based pigments + wax or oil binder |
| Texture | Velvety, powdery, easily blendable | Thick, creamy, buttery consistency |
| Drying Time | Does not dry; remains smudge-prone | Dries slowly, becoming semi-permanent |
| Surface Compatibility | Textured paper, pastel boards | Canvas, paper, wood |
| Color Intensity | Bright, matte finish | Rich, glossy finish |
| Blending | Easy with fingers or tools | Blends with brushes or palette knives |
| Fixative Need | Requires fixative to prevent smudging | Usually no fixative needed after drying |
| Durability | Fragile; can powder off without fixative | Durable; flexible film after drying |
| Common Uses | Sketching, layering, detailed color work | Expressive strokes, impasto effects |
Introduction to Soft Pastels and Oil Sticks
Soft pastels consist of pure powdered pigment bound with a minimal amount of binder, allowing artists to achieve vibrant, easily blendable colors with a powdery texture ideal for detailed drawings and delicate shading. Oil sticks combine pigment with oil and wax, providing a buttery consistency similar to oil paint in stick form, enabling rich textures and bold strokes suitable for expressive and impasto techniques. Both mediums offer unique tactile experiences and color applications, with soft pastels favoring softness and blending, while oil sticks deliver a more viscous and durable finish.
Key Differences Between Soft Pastels and Oil Sticks
Soft pastels are composed of powdered pigment and a binder, resulting in a dry, chalky texture that blends easily for soft, matte finishes, while oil sticks contain pigment mixed with oil and wax, offering a creamy consistency that provides a glossy, rich texture similar to oil paints. Soft pastels allow for quick layering and smudging, ideal for delicate transitions and detailed work, whereas oil sticks require more drying time but enable bold, textured strokes and thicker applications. The primary difference lies in their medium: soft pastels are dry and suitable for paper or textured surfaces, whereas oil sticks function as oil paint in stick form, compatible with primed canvases and creating durable, vibrant results.
Texture and Application Techniques
Soft pastels offer a velvety, powdery texture ideal for blending and layering colors smoothly, making them suitable for delicate shading and subtle transitions. Oil sticks provide a creamy, buttery consistency that allows for bold, textured strokes and impasto effects, enabling artists to build rich surface textures and vibrant color intensity. Application techniques differ as soft pastels work best with fingertip blending, sponges, or tortillons, while oil sticks require direct application, palette knives, or brushes for manipulating thick, tactile layers.
Color Vibrancy and Blendability
Soft pastels offer exceptional color vibrancy with their rich, pigmented powders that easily deposit intense hues on paper, while oil sticks provide a creamy consistency that yields bold, saturated colors with a slightly glossy finish. Blendability in soft pastels excels due to their powdery texture, allowing artists to seamlessly merge and layer colors for smooth gradients and subtle transitions. Oil sticks blend through direct manipulation and smudging, giving a textured, painterly effect but with less subtlety compared to the fine control of soft pastel blending.
Surface Compatibility and Preparation
Soft pastels require textured, toothy surfaces such as sanded paper or pastel boards to hold pigment effectively, while oil sticks perform best on primed canvases or smooth surfaces that can absorb oil-based mediums. Preparation for soft pastels often involves selecting abrasive papers or adding primers to enhance grip, whereas oil sticks need a well-primed surface, typically acrylic or oil ground, to prevent oil absorption and ensure durability. Both mediums benefit from surface preparation tailored to their composition to maximize adhesion and color vibrancy.
Layering and Mixing Capabilities
Soft pastels offer exceptional layering capabilities due to their powdery texture, allowing artists to build vibrant colors and subtle gradients with ease. In contrast, oil sticks provide rich, buttery layers that blend smoothly on canvas, enabling strong mixing capabilities directly on the surface. Both mediums excel in color intensity, but soft pastels achieve delicate transitions while oil sticks deliver bold, textured effects.
Drying Time and Fixatives
Soft pastels dry instantly as they consist of pure pigment and minimal binder, requiring no drying time, whereas oil sticks contain oil-based binders that remain wet longer and may need several hours to fully dry. Fixatives are often essential for soft pastels to prevent smudging and preserve the artwork surface, with workable fixatives allowing layering without altering texture. In contrast, oil stick artworks benefit from varnishing after drying to protect the surface but rarely require fixatives during the painting process.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Soft pastels require gentle cleaning with a soft brush or cloth to remove dust and prevent smudging, while oil sticks need careful wiping with a cloth or paper towel to manage residue and prevent oil buildup. Storing soft pastels in boxes with individual compartments reduces breakage, whereas oil sticks should be capped tightly and stored upright to avoid drying out. Regular maintenance for both mediums ensures longevity, with soft pastels benefiting from fixative sprays and oil sticks requiring occasional conditioning to maintain texture.
Best Uses for Soft Pastels and Oil Sticks
Soft pastels are best for creating delicate, easily blendable textures and vibrant color effects in portraits, landscapes, and still life artwork due to their powdery consistency and wide color range. Oil sticks excel in producing bold, textured strokes and impasto effects, making them ideal for expressive, dynamic paintings that require rich, glossy colors and durability. Both mediums offer unique tactile experiences, with soft pastels suited for fine detail and subtle gradients, while oil sticks provide robust coverage and a painterly finish.
Choosing the Right Medium for Your Art Style
Soft pastels offer vibrant colors and ease of blending, ideal for artists who favor smooth transitions and soft textures, while oil sticks provide rich, buttery application and strong pigment that suit bold, expressive strokes and impasto techniques. Choosing between soft pastels and oil sticks depends on your preferred finish and working method, as pastels dry quickly and require fixatives to preserve, whereas oil sticks remain workable longer and create textured surfaces. Understanding the characteristics of both mediums empowers artists to select the best tool for realism, abstraction, or mixed media projects.
Soft Pastel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com