Expressionism captures raw emotional experience through distorted forms, bold colors, and dynamic brushstrokes, emphasizing subjective perspective over realistic representation. This art movement emerged as a reaction against traditional aesthetics, seeking to evoke intense feelings and highlight inner turmoil. Discover how Expressionism transformed modern art and influenced contemporary creativity in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
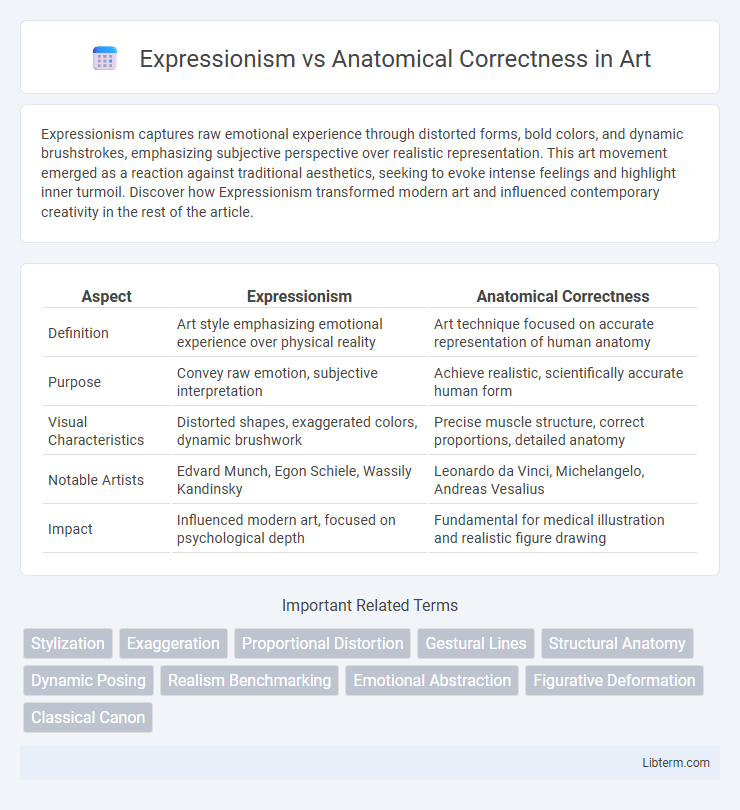
| Aspect | Expressionism | Anatomical Correctness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art style emphasizing emotional experience over physical reality | Art technique focused on accurate representation of human anatomy |
| Purpose | Convey raw emotion, subjective interpretation | Achieve realistic, scientifically accurate human form |
| Visual Characteristics | Distorted shapes, exaggerated colors, dynamic brushwork | Precise muscle structure, correct proportions, detailed anatomy |
| Notable Artists | Edvard Munch, Egon Schiele, Wassily Kandinsky | Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Andreas Vesalius |
| Impact | Influenced modern art, focused on psychological depth | Fundamental for medical illustration and realistic figure drawing |
Understanding Expressionism in Art
Expressionism in art prioritizes emotional experience over anatomical accuracy, using distorted forms and exaggerated colors to convey intense feelings and subjective perspectives. This movement emerged as a reaction against realistic representation, aiming to evoke mood and ideas rather than depict physical reality precisely. Understanding expressionism involves recognizing its emphasis on inner emotional truth as opposed to strict adherence to anatomical correctness.
Defining Anatomical Correctness
Anatomical correctness refers to the accurate representation of the human body's structure, including precise proportions, muscle placement, and skeletal alignment. This concept emphasizes detailed observation and faithful replication of biological forms to ensure realistic depictions in art and medical illustrations. In contrast, expressionism prioritizes emotional impact and subjective interpretation over anatomical precision, often distorting physical features for artistic effect.
Historical Roots of Expressionism
Expressionism emerged in early 20th-century Germany as a reaction against traditional artistic norms emphasizing anatomical correctness and realistic representation. Rooted in a desire to convey emotional experience rather than physical accuracy, artists like Edvard Munch and Egon Schiele distorted forms to evoke psychological intensity. This movement's historical significance lies in its challenge to classical anatomy-based art, prioritizing subjective perception over precise human anatomy.
The Role of Anatomy in Classical Art
Anatomy plays a crucial role in classical art by providing a foundation for accurately depicting the human form, enhancing realism and proportion in artworks. Expressionism diverges from anatomical correctness by emphasizing emotional impact and subjective interpretation over precise bodily structure, often distorting anatomy to convey deeper psychological or emotional states. Classical artists like Leonardo da Vinci studied human anatomy extensively, using detailed knowledge of muscles and bones to achieve lifelike representations that balance scientific observation with artistic expression.
Key Differences Between Art Movements
Expressionism emphasizes emotional experience through distorted forms and exaggerated colors, often prioritizing subjective interpretation over realistic representation. Anatomical correctness prioritizes precise, scientifically accurate depictions of the human body, adhering to proportions and muscle structures derived from medical knowledge. The key difference lies in Expressionism's focus on conveying inner emotions and psychological states, while Anatomical correctness aims for objective realism rooted in biological accuracy.
Artists Embracing Expression over Accuracy
Artists embracing expression over anatomical correctness prioritize emotional impact and subjective interpretation, often distorting human forms to convey psychological depth and intensity. Expressionism pioneers like Egon Schiele and Edvard Munch deliberately manipulated proportions and exaggerated features, challenging traditional realism to evoke raw, visceral reactions. This artistic approach values the power of emotional resonance over precise anatomical detail, influencing modern art movements focused on personal and cultural expression.
The Debate: Emotion vs. Precision
The debate between Expressionism and Anatomical Correctness centers on the contrast between conveying raw emotion and adhering to precise human anatomy. Expressionism prioritizes emotional impact and subjective interpretation, often exaggerating forms to evoke feelings, while anatomical correctness demands accurate representation of the body's structure and proportions. This tension highlights the artistic choice between capturing the essence of emotional experience and maintaining scientific accuracy in visual art.
Famous Artworks Exemplifying Each Approach
Edvard Munch's "The Scream" exemplifies Expressionism through its distorted forms and intense emotional impact, conveying psychological tension beyond anatomical accuracy. In contrast, Leonardo da Vinci's "Vitruvian Man" demonstrates anatomical correctness with precise human proportions and detailed musculature based on scientific observation. Expressionist works like Egon Schiele's portraits prioritize subjective emotion and exaggeration over realistic anatomy, while anatomical masterpieces such as Michelangelo's "David" showcase idealized human form grounded in detailed study of musculature and skeletal structure.
Modern Perspectives on Artistic Freedom
Modern perspectives on artistic freedom emphasize the tension between expressionism and anatomical correctness, valuing the emotional impact and subjective interpretation over strict anatomical accuracy. Expressionism prioritizes conveying inner experiences and emotions through exaggerated forms and distorted anatomy, while anatomical correctness focuses on precise representation of human body structures based on scientific knowledge. Contemporary artists and critics increasingly advocate for a balance where creativity and personal expression are not confined by rigid anatomical rules, promoting diverse artistic practices that challenge traditional norms.
Impact on Contemporary Art and Audience
Expressionism prioritizes emotional impact and subjective interpretation, often distorting anatomical accuracy to convey intense feelings, which challenges viewers to connect with the artist's inner experience. Anatomical correctness in art emphasizes realistic representation based on scientific study of the human form, appealing to audiences that appreciate technical skill and lifelike detail. The tension between these approaches shapes contemporary art by balancing emotional resonance with visual precision, influencing how audiences perceive authenticity and artistic intent.
Expressionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com