Carving transforms raw materials like wood, stone, or ice into intricate sculptures through precise cuts and shaping techniques. This timeless art form enhances both aesthetic appeal and cultural significance, showcasing skilled craftsmanship. Discover how carving can inspire your creativity and learn more by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
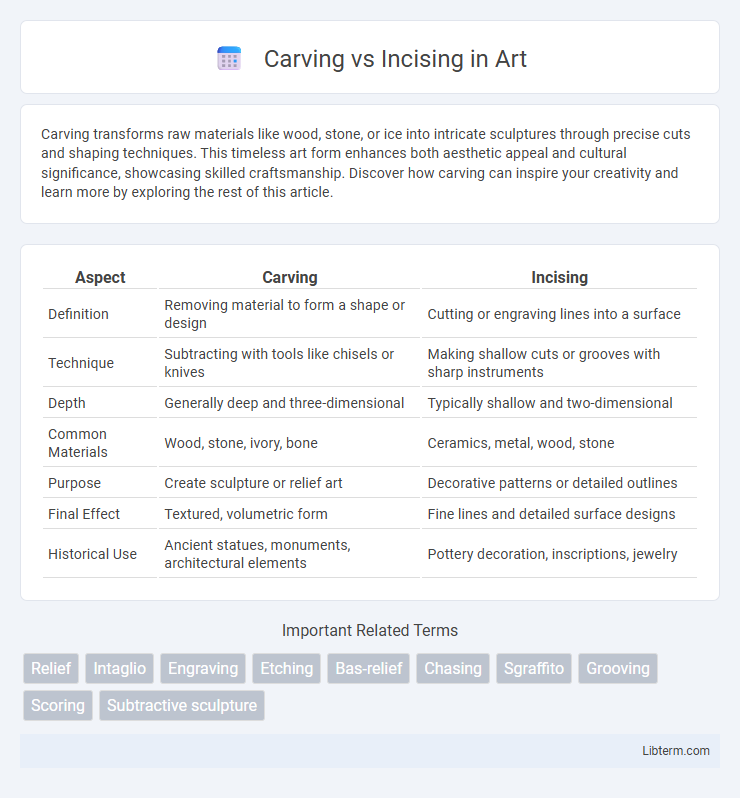
| Aspect | Carving | Incising |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removing material to form a shape or design | Cutting or engraving lines into a surface |
| Technique | Subtracting with tools like chisels or knives | Making shallow cuts or grooves with sharp instruments |
| Depth | Generally deep and three-dimensional | Typically shallow and two-dimensional |
| Common Materials | Wood, stone, ivory, bone | Ceramics, metal, wood, stone |
| Purpose | Create sculpture or relief art | Decorative patterns or detailed outlines |
| Final Effect | Textured, volumetric form | Fine lines and detailed surface designs |
| Historical Use | Ancient statues, monuments, architectural elements | Pottery decoration, inscriptions, jewelry |
Introduction to Carving and Incising
Carving involves removing material from a solid block to create a three-dimensional form, commonly used in wood, stone, and bone artworks, while incising refers to cutting or engraving lines into a surface to create detailed designs or patterns, often seen on ceramics or metal. Both techniques require precise tools and skilled craftsmanship, yet carving emphasizes subtractive shaping, whereas incising focuses on decorative or narrative surface embellishments. Understanding these methods highlights their distinct roles in art history and material expression.
Defining Carving: Techniques and Materials
Carving involves removing material from a solid block to create a three-dimensional form, typically using tools like chisels, gouges, and knives on materials such as wood, stone, or ivory. This subtractive technique demands precision and control to shape intricate details by cutting, shaving, or gouging the surface. Common carving styles include relief, in-the-round, and intaglio, each exploiting the depth and texture achievable through various tools and material properties.
What is Incising? Process and Mediums
Incising is a sculptural technique involving cutting or carving into a surface to create lines or patterns, often used for detailed decoration or inscription. The process typically involves tools like chisels, knives, or burins to remove material from mediums such as wood, metal, clay, or stone. Commonly found in pottery, metalwork, and stone reliefs, incising enhances texture and depth by producing fine, precise grooves on the artwork's surface.
Historical Evolution of Carving and Incising
Carving and incising have evolved as fundamental artistic techniques with distinct historical trajectories; carving dates back to prehistoric times, seen in ancient stone sculptures and woodwork, reflecting cultural and religious significance across civilizations. Incising, characterized by cutting fine lines into surfaces such as pottery or metal, has roots in early Mesopotamian and Egyptian artifacts, serving both decorative and communicative purposes. Over centuries, both methods advanced through technological innovations, influencing art, architecture, and craftsmanship worldwide.
Comparing Methods: Tools and Approaches
Carving involves removing material using chisels, gouges, or rotary tools to create depth and shape, often applied to wood, stone, or bone, whereas incising uses sharp instruments like knives or needles to cut fine lines or patterns into surfaces such as metal, pottery, or leather. Carving typically produces three-dimensional forms through subtraction, demanding varying tool pressure for depth control, while incising focuses on surface-level decorations or text with precise, shallow cuts. Both methods require skilled hand control, but carving emphasizes volume and shape, and incising highlights intricate linear details and delicate textures.
Key Artistic Differences
Carving involves removing material to create a three-dimensional form, emphasizing depth and volume, often seen in sculptures and statues. Incising cuts or scratches a surface to create shallow lines or patterns, primarily used for decorative or illustrative effects on materials like metal, wood, or stone. The key artistic difference lies in carving's focus on form and mass, while incising prioritizes line work and surface detail.
Common Applications in Art and Craft
Carving is commonly used in sculpture and woodworking, where artists remove material to create three-dimensional forms such as statues and furniture details. Incising, involving cutting or engraving fine lines into surfaces like ceramics, metal, or wood, is often applied in decorative arts and printmaking for intricate patterns and textures. Both techniques enhance artistic expression, with carving emphasizing depth and volume, while incising highlights detailed surface design.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Carving offers higher durability due to its deeper material removal, making it less prone to wear and damage over time compared to incising, which involves shallow cuts that can fade or erode more easily. Maintenance for carving typically requires less frequent touch-ups, as the engraved designs remain prominent despite environmental factors. Incising demands more careful upkeep to preserve fine details, often necessitating protective coatings or regular cleaning to prevent deterioration.
Choosing Between Carving and Incising
Choosing between carving and incising depends on the desired depth and texture of the artwork, as carving involves removing material to create three-dimensional forms, while incising cuts shallow lines into the surface. Carving is ideal for bold, sculptural effects with prominent shadows, whereas incising offers delicate, detailed patterns that enhance surface decoration without altering the object's overall shape. The choice is influenced by the material's hardness and the artist's intent for tactile or visual emphasis in the final piece.
Conclusion: Which Technique Suits Your Project?
Carving offers depth and a sculptural dimension ideal for projects requiring bold, three-dimensional designs, while incising provides fine, detailed line work suitable for intricate patterns and subtle textures. The choice depends on your project's material, desired visual impact, and functional purpose. For durable, tactile art, carving excels; for delicate, precise decoration, incising is preferable.
Carving Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com