Romanticism emphasizes emotion, individualism, and the beauty of nature, countering the rationalism of the Enlightenment. This artistic and intellectual movement inspired groundbreaking works in literature, music, and visual arts by valuing imagination and personal expression. Discover how Romanticism shapes our cultural heritage and influences modern creativity by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
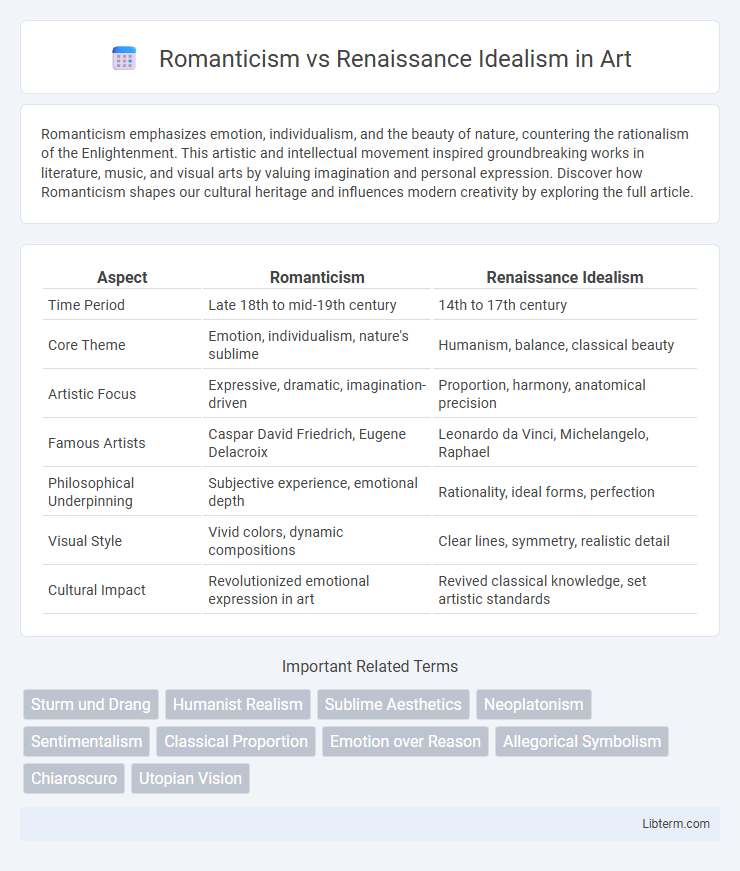
| Aspect | Romanticism | Renaissance Idealism |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | Late 18th to mid-19th century | 14th to 17th century |
| Core Theme | Emotion, individualism, nature's sublime | Humanism, balance, classical beauty |
| Artistic Focus | Expressive, dramatic, imagination-driven | Proportion, harmony, anatomical precision |
| Famous Artists | Caspar David Friedrich, Eugene Delacroix | Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Raphael |
| Philosophical Underpinning | Subjective experience, emotional depth | Rationality, ideal forms, perfection |
| Visual Style | Vivid colors, dynamic compositions | Clear lines, symmetry, realistic detail |
| Cultural Impact | Revolutionized emotional expression in art | Revived classical knowledge, set artistic standards |
Introduction to Romanticism and Renaissance Idealism
Romanticism emphasizes emotion, individualism, and the sublime in nature, contrasting sharply with Renaissance Idealism's focus on reason, harmony, and human perfection inspired by classical antiquity. Romanticism emerged in the late 18th century as a reaction against the Enlightenment's rationalism and industrial revolution, celebrating creativity and the irrational mind. Renaissance Idealism, flourishing during the 15th and 16th centuries, centers on human potential and intellectual achievement, exemplified by figures like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo.
Historical Contexts: Emergence and Influence
Romanticism emerged in the late 18th century as a reaction to the Enlightenment and Industrial Revolution, emphasizing emotion, individualism, and nature over the rationality and order promoted by Renaissance Idealism. Renaissance Idealism, rooted in the 14th to 17th centuries, reflected a revival of classical thought, focusing on human potential, harmony, and proportion as seen in the works of figures like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo. The historical contexts of these movements shaped their influence on art, literature, and philosophy, with Renaissance Idealism inspiring the pursuit of human perfection and Romanticism valuing personal expression and the sublime.
Core Philosophical Foundations
Romanticism centers on individual emotion, intuition, and the sublime experience of nature, emphasizing personal freedom and subjective creativity as core philosophical foundations. In contrast, Renaissance Idealism is grounded in humanism, rationality, and the pursuit of universal truths through reason, reflecting a belief in the inherent perfectibility of mankind and the harmony of the cosmos. These divergent philosophies reveal Romanticism's focus on emotional depth and the irrational, while Renaissance Idealism prioritizes balance, order, and the revival of classical knowledge.
Artistic Expression and Aesthetic Values
Romanticism emphasizes emotional intensity, individual creativity, and the sublime in artistic expression, valuing imagination and subjective experience over classical formality. Renaissance Idealism centers on harmony, proportion, and balance in art, reflecting human potential and rationality through precise anatomical accuracy and realistic perspective. Both movements celebrate beauty but diverge in their pursuit--Romanticism prioritizes emotional depth and nature's mystery, whereas Renaissance Idealism upholds classical ideals and intellectual clarity.
Representations of Nature and Human Experience
Romanticism emphasizes the sublime and emotional aspects of nature, portraying it as a dynamic, spiritual force that reflects human imagination and individual experience, contrasting with Renaissance Idealism's focus on harmony, balance, and the rational order of the natural world. Renaissance artists and thinkers idealize human nature through classical forms and proportion, seeking to represent an elevated, perfected version of humanity aligned with divine reason. In contrast, Romanticism celebrates subjective emotion and the unpredictable, often wild qualities of both nature and human existence, highlighting personal connection and inner truth over universal ideals.
Individualism: Romantic Subjectivity vs Renaissance Humanism
Romanticism emphasizes individual emotional experience and personal imagination, valuing subjective expression as the core of artistic and intellectual life. Renaissance Idealism centers on humanism, celebrating the potential and rationality of individuals within a balanced and universal framework that harmonizes human nature and classical ideals. The contrast lies in Romanticism's embrace of emotional depth and individuality, while Renaissance Humanism prioritizes reason, collective progress, and the rediscovery of classical knowledge.
Approaches to Emotion and Rationality
Romanticism emphasizes intense emotional expression and values imagination over rational thought, prioritizing individual experience and subjectivity. Renaissance Idealism centers on balanced rationality and harmonious proportions, advocating for reason as the guiding principle to achieve intellectual and artistic perfection. The contrast lies in Romanticism's preference for emotional depth and spontaneity versus Renaissance Idealism's structured, reasoned approach to understanding human nature and the world.
Impact on Literature and the Arts
Romanticism revolutionized literature and the arts by emphasizing emotion, individualism, and nature, contrasting with Renaissance Idealism's focus on harmony, proportion, and classical ideals drawn from antiquity. Romantic artists and writers like William Wordsworth and Caspar David Friedrich explored subjective experience and sublime landscapes, fostering innovation in poetic form and visual expression. In contrast, Renaissance figures such as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo championed humanism and anatomical precision, shaping the foundation of Western art and literature through balanced composition and idealized beauty.
Lasting Legacies in Modern Culture
Romanticism's lasting legacy in modern culture is evident through its emphasis on individual emotion, nature, and artistic expression, influencing contemporary literature, visual arts, and music with themes of passion and personal freedom. Renaissance Idealism contributes enduring principles of humanism, balanced proportion, and classical beauty, shaping modern architecture, education, and philosophical thought. Together, these movements underpin contemporary cultural values by blending emotional depth with rationality, inspiring ongoing innovation across creative and intellectual fields.
Conclusion: Contrasts and Convergences
Romanticism emphasizes emotional depth, individualism, and the sublime in nature, while Renaissance Idealism focuses on human reason, classical harmony, and balanced proportions. Despite these differences, both movements share a pursuit of human potential and a reaction against previous artistic conventions. Their interplay highlights a dynamic tension between emotion and reason that continues to influence modern artistic and philosophical thought.
Romanticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com