Digital vectors offer scalable, high-quality graphics essential for modern design projects, allowing for sharp, clear images at any size without loss of resolution. They are widely used in branding, web design, and print media due to their flexibility and ease of modification. Explore the rest of the article to learn how digital vectors can transform Your creative work.
Table of Comparison
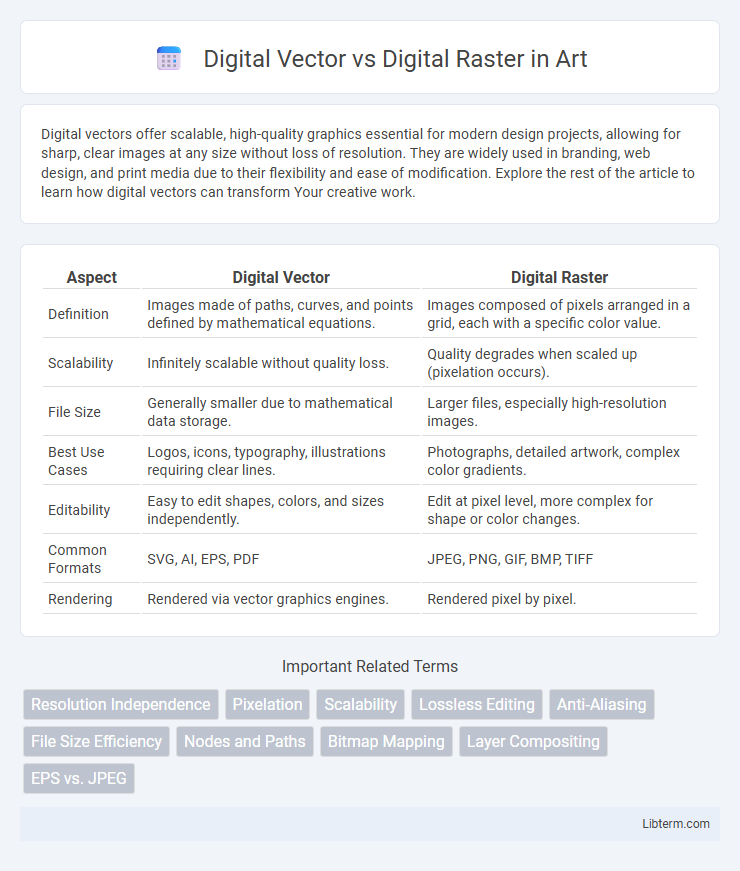
| Aspect | Digital Vector | Digital Raster |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Images made of paths, curves, and points defined by mathematical equations. | Images composed of pixels arranged in a grid, each with a specific color value. |
| Scalability | Infinitely scalable without quality loss. | Quality degrades when scaled up (pixelation occurs). |
| File Size | Generally smaller due to mathematical data storage. | Larger files, especially high-resolution images. |
| Best Use Cases | Logos, icons, typography, illustrations requiring clear lines. | Photographs, detailed artwork, complex color gradients. |
| Editability | Easy to edit shapes, colors, and sizes independently. | Edit at pixel level, more complex for shape or color changes. |
| Common Formats | SVG, AI, EPS, PDF | JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, TIFF |
| Rendering | Rendered via vector graphics engines. | Rendered pixel by pixel. |
Introduction to Digital Vector and Raster Graphics
Digital vector graphics use mathematical equations to create scalable images composed of paths, points, and shapes, ensuring resolution independence and crisp quality at any size. In contrast, digital raster graphics consist of pixels arranged in a grid, where image quality depends on resolution and can degrade when scaled. Vector graphics are ideal for logos, illustrations, and designs requiring flexibility, while raster graphics are commonly used for detailed photos and complex color variations.
Defining Vector Graphics: Features and Uses
Vector graphics are composed of paths defined by mathematical equations, enabling infinite scalability without loss of quality. Key features include crisp edges, small file sizes, and ease of editing, making them ideal for logos, typography, and technical illustrations. Common vector formats like SVG, AI, and EPS support precise designs used extensively in digital branding and print media.
Understanding Raster Graphics: Core Characteristics
Raster graphics consist of pixels arranged in a grid, each pixel representing a specific color value, which provides detailed and complex images. The resolution of raster images is defined by their pixel dimensions, making them susceptible to quality loss when scaled beyond their original size. Common raster file formats include JPEG, PNG, and GIF, widely used for digital photography and web graphics due to their ability to represent rich color gradients.
Key Differences Between Vector and Raster Images
Vector images use mathematical equations to create scalable graphics without loss of quality, making them ideal for logos and illustrations requiring precision. Raster images consist of pixels arranged in a grid, with fixed resolution, which can result in pixelation when scaled up, commonly used for photographs. Key differences include scalability, file size, and image detail, with vectors offering smaller files and infinite scaling, while rasters provide rich detail and complex color variations.
Resolution and Scalability: Vector vs Raster
Digital vector graphics use mathematical equations to represent images, ensuring infinite resolution and perfect scalability without loss of quality. Digital raster graphics consist of a fixed grid of pixels, where resolution depends on pixel density, causing pixelation when scaled beyond the original size. Vector files are ideal for logos and illustrations requiring resizing, while raster files suit detailed images like photographs where fixed resolution is critical.
File Formats: Vector vs Raster Standards
Digital vector files such as SVG, AI, and EPS use mathematical equations to represent images, ensuring scalability without loss of quality and are standard in graphic design, logo creation, and CAD applications. Digital raster files like JPEG, PNG, GIF, and BMP consist of a fixed grid of pixels, making them ideal for detailed photographs but prone to pixelation when scaled. Understanding these file format standards is crucial for selecting the right type depending on use cases involving resolution, editing flexibility, and print versus digital display requirements.
When to Use Vector Graphics
Vector graphics excel when precision and scalability are essential, such as in logo design, typography, and technical illustrations, because they use mathematical equations to create smooth lines and shapes. They maintain image quality at any size, making them ideal for print media, large banners, and detailed artwork that requires resizing without losing clarity. Use vector graphics when the design demands clean, crisp lines, easy color modifications, and efficient file sizes for cutting machines or digital displays.
When to Choose Raster Graphics
Raster graphics excel in detailed images like photographs where pixel-level precision captures color gradients and textures accurately. They are ideal for complex visuals requiring intricate shading and subtle color variations that vector graphics cannot replicate. Choose raster formats such as JPEG, PNG, or TIFF for digital photography, web images, and projects mandating rich detail and realistic effects.
Editing and Workflow: Vectors Compared to Rasters
Digital vectors use mathematical equations to create scalable images, enabling easy editing of individual shapes without loss of quality in design workflows. Raster formats consist of pixels that can become distorted when scaled, complicating detailed edits and requiring more intensive adjustments in software like Photoshop. Vectors streamline workflow efficiency by allowing seamless resizing and modification, whereas rasters are better suited for complex color gradients and photo-realistic detail but demand greater computational power and time for precise edits.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Format for Your Project
Choosing between digital vector and digital raster depends on the project's needs for scalability and detail. Vector graphics excel in logos and illustrations due to their infinite scalability without quality loss, while raster images are ideal for detailed photos with rich color depth. Assessing factors like resolution requirements and editing flexibility ensures selecting the optimal format for professional results.
Digital Vector Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com