Figurative art captures the human form and recognizable objects, translating reality into expressive visual narratives. This genre bridges the gap between abstract and realistic styles, offering rich symbolism and emotional depth. Explore the rest of this article to discover how figurative art shapes your perception of creativity.
Table of Comparison
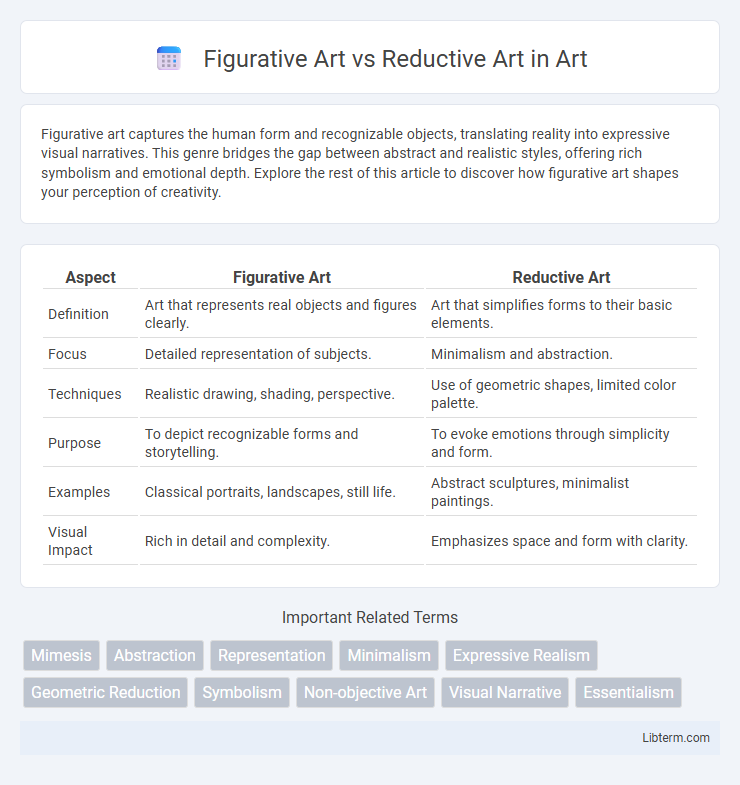
| Aspect | Figurative Art | Reductive Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art that represents real objects and figures clearly. | Art that simplifies forms to their basic elements. |
| Focus | Detailed representation of subjects. | Minimalism and abstraction. |
| Techniques | Realistic drawing, shading, perspective. | Use of geometric shapes, limited color palette. |
| Purpose | To depict recognizable forms and storytelling. | To evoke emotions through simplicity and form. |
| Examples | Classical portraits, landscapes, still life. | Abstract sculptures, minimalist paintings. |
| Visual Impact | Rich in detail and complexity. | Emphasizes space and form with clarity. |
Defining Figurative Art: Origins and Characteristics
Figurative art, rooted in ancient traditions, emphasizes realistic representation of the human form and recognizable objects, often reflecting cultural narratives and emotions. Its origins trace back to prehistoric cave paintings and classical sculptures, evolving through Renaissance naturalism to contemporary interpretations. Distinct characteristics include detailed anatomy, perspective, and expressive detail, aiming to capture the essence of subjects beyond mere abstraction.
Understanding Reductive Art: Minimalism and Beyond
Reductive art centers on simplifying forms to their essential components, emphasizing minimalism through geometric shapes, monochromatic palettes, and the elimination of ornamentation. This approach rejects representational accuracy found in figurative art, seeking instead to evoke emotion and meaning through abstraction and purity of design. Beyond minimalism, reductive art explores the balance between emptiness and presence, using negative space as a deliberate compositional element.
Historical Contexts: Evolution of Both Styles
Figurative art, rooted in ancient civilizations, evolved through the Renaissance with a focus on realistic human representation, reflecting cultural narratives and religious themes. Reductive art emerged in the 20th century as a reaction to complexity, emphasizing minimalism and abstract forms to explore purity of shape and color. The historical shift from detailed figurative depictions to reductive abstraction reflects broader artistic movements responding to changes in philosophy, technology, and social perspectives.
Key Techniques in Figurative Art
Figurative art employs techniques such as accurate proportion, anatomical precision, and expressive detail to represent human figures and natural forms realistically. Artists often use chiaroscuro to create depth and volume, alongside contour lines to define shapes clearly. These methods emphasize visual storytelling and emotional expression, distinguishing figurative art's rich narrative quality from reductive art's simplicity and abstraction.
Core Principles of Reductive Art
Reductive art centers on distilling forms to their essential shapes, emphasizing simplicity, minimal detail, and purity of composition. It seeks to eliminate superfluous elements, focusing on color, line, and space to evoke meaning rather than realistic representation. Core principles include abstraction, reduction of forms, and a focus on the intrinsic qualities of materials to create a contemplative visual experience.
Famous Artists: Figurative and Reductive Movements
Famous figurative artists like Lucian Freud and Jenny Saville emphasize realism and human form, capturing intricate emotional and physical details through representational imagery. In contrast, reductive artists such as Agnes Martin and Donald Judd focus on simplicity and abstraction, employing geometric shapes, minimal color palettes, and repetitive patterns to evoke purity and essentialism. These distinct artistic movements highlight the divergence between detailed narrative expression and minimalist abstraction in modern art history.
Visual Impact: Complexity vs Simplicity
Figurative art emphasizes detailed representation of real-world subjects, resulting in visually complex compositions rich with textures, perspectives, and emotional depth. Reductive art strips away extraneous details to focus on essential shapes and forms, creating simplicity that draws attention to color, line, and spatial relationships. The visual impact of figurative art lies in its narrative richness, while reductive art captivates through bold minimalism and clarity.
Emotional Expression in Figurative vs Reductive Art
Figurative art conveys emotional expression through recognizable human forms and gestures, enabling viewers to connect deeply with portrayed emotions. Reductive art strips away detail to focus on basic shapes and colors, evoking emotions through abstraction and minimalism rather than explicit representation. Emotional impact in reductive art relies on viewer interpretation and the subtle interplay of form and space.
Cultural Significance and Influence
Figurative art, rooted in the representation of real-world subjects, carries profound cultural significance by reflecting social narratives, historical contexts, and human experiences across civilizations. Reductive art, characterized by minimalism and abstraction, influences cultural movements by challenging perceptual norms and emphasizing the essence of form and color, often serving as a visual language for modernity and innovation. Both art forms shape cultural identity, with figurative art preserving heritage and reductive art pioneering contemporary aesthetic discourse.
Contemporary Perspectives: Bridging the Gap
Contemporary perspectives highlight the evolving relationship between figurative art and reductive art, emphasizing how artists blend representational elements with minimalistic abstraction to create nuanced visual narratives. This fusion challenges traditional boundaries by integrating symbolic forms and simplified structures, promoting a dialogue that bridges emotional depth and conceptual clarity. The ongoing convergence underscores a dynamic art landscape where meaning emerges from both detailed depiction and essentialized expression.
Figurative Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com