Mosaic art combines small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials to create intricate, visually stunning patterns that have been admired since ancient times. This timeless technique adds texture and vibrancy to walls, floors, and decorative objects, making it a versatile choice for enhancing your living space. Explore the rest of the article to discover creative ways to incorporate mosaics into your home.
Table of Comparison
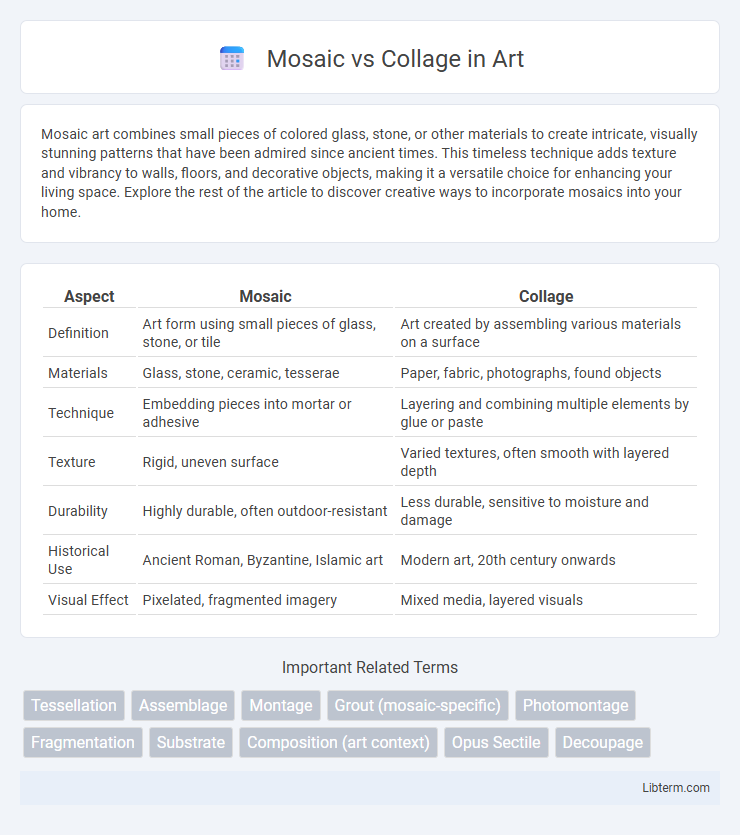
| Aspect | Mosaic | Collage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art form using small pieces of glass, stone, or tile | Art created by assembling various materials on a surface |
| Materials | Glass, stone, ceramic, tesserae | Paper, fabric, photographs, found objects |
| Technique | Embedding pieces into mortar or adhesive | Layering and combining multiple elements by glue or paste |
| Texture | Rigid, uneven surface | Varied textures, often smooth with layered depth |
| Durability | Highly durable, often outdoor-resistant | Less durable, sensitive to moisture and damage |
| Historical Use | Ancient Roman, Byzantine, Islamic art | Modern art, 20th century onwards |
| Visual Effect | Pixelated, fragmented imagery | Mixed media, layered visuals |
Introduction to Mosaic and Collage
Mosaic art involves assembling small, colored pieces of stone, glass, or ceramic called tesserae to create intricate, durable patterns or images with a textured surface. Collage art consists of combining various materials such as paper, fabric, or photographs onto a flat surface to form a composite visual composition emphasizing layering and mixed media. Both techniques offer unique artistic expressions, with mosaics rooted in ancient craftsmanship and collages emerging from modernist art movements.
Defining Mosaic Art
Mosaic art involves creating images or patterns by assembling small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials called tesserae onto a surface, often forming intricate and durable designs. Unlike collage, which typically layers paper, fabric, or found objects in a more flexible and mixed-media approach, mosaic emphasizes precision and permanence through its structured technique. This ancient art form can be traced back to classical civilizations, showcasing detailed craftsmanship and vibrant visual storytelling using tiny, uniformly sized components.
Defining Collage Art
Collage art involves assembling various materials such as paper, fabric, photographs, and found objects onto a surface to create a unified composition, emphasizing texture and layering. Unlike mosaic, which uses small, uniform pieces of tile or glass to form images, collage allows for greater variability in materials and dimensions, often resulting in mixed-media artworks. This technique highlights creativity through juxtaposition and the interplay of disparate elements to convey complex narratives or abstract concepts.
Historical Origins of Mosaic and Collage
Mosaic art traces back to ancient Mesopotamia and Greece, where small pieces of stone, glass, or ceramic were meticulously arranged to create intricate images and patterns primarily for architectural decoration. Collage, emerging in the early 20th century with artists like Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, revolutionized art by assembling diverse materials such as paper, newspaper clippings, and fabric onto surfaces, reflecting modernist experimentation. The historical origins of mosaic emphasize durable, ornamental craftsmanship in ancient civilizations, while collage represents a transformative, mixed-media approach rooted in avant-garde movements.
Key Materials Used in Mosaic vs Collage
Mosaic art primarily uses small, durable pieces called tesserae, which are commonly made of glass, ceramic, stone, or marble to create detailed, long-lasting images. Collage incorporates a wide variety of materials such as paper, fabric, photographs, and found objects, offering greater versatility in texture and form. The distinct material choices influence the visual and tactile qualities unique to each art form, with mosaics emphasizing permanence and collages highlighting mixed media experimentation.
Artistic Techniques and Processes
Mosaic art involves assembling small pieces of glass, stone, or ceramic called tesserae to create intricate patterns or images with durable texture and depth. Collage technique uses layering and gluing various materials such as paper, fabric, or photographs onto a surface, emphasizing texture and juxtaposition to convey meaning. Both processes require meticulous placement but differ in materials, with mosaics often demanding precise cutting and setting, while collages prioritize creative composition and mixed media experimentation.
Visual Effects: Patterns vs Compositions
Mosaic art creates visual effects through repeated geometric patterns formed by small, uniformly shaped pieces called tesserae that produce intricate, often symmetrical designs. Collage relies on diverse materials and images layered to generate dynamic compositions with varied textures, colors, and forms, emphasizing artistic contrast and thematic depth. These distinct methods result in mosaics showcasing structured, rhythmic visual patterns, while collages highlight eclectic, expressive visual arrangements.
Applications in Modern Art and Design
Mosaic and collage techniques play distinct roles in modern art and design, with mosaics often used in architectural facades and public installations for their durability and textured visual impact. Collage allows artists to incorporate diverse materials such as paper, fabric, and found objects, promoting mixed media exploration and conceptual storytelling. Both mediums enhance spatial aesthetics, with mosaics emphasizing pattern and permanence, and collages prioritizing juxtaposition and narrative complexity.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Technique
Mosaic art offers durability and vibrant, long-lasting color through its use of small, rigid pieces like tiles or glass, making it ideal for outdoor or architectural applications, though it can be labor-intensive and costly due to material and installation complexity. Collage allows for greater creative flexibility and mixed-media experimentation by combining various paper, fabric, and found objects, but it tends to be less durable and more vulnerable to environmental damage such as fading or tearing. Both techniques provide unique aesthetic appeal; mosaics excel in structural permanence while collages offer dynamic textural variety, with each requiring different maintenance considerations based on materials used.
Choosing Between Mosaic and Collage
Choosing between mosaic and collage depends on the desired artistic effect and materials available; mosaics use small, uniform pieces like tiles or glass to create durable, textured images ideal for detailed, long-lasting installations. Collages incorporate varied media such as paper, fabric, and photographs, allowing for more expressive, layered compositions suited to mixed-media projects and experimentation. Consider the level of permanence, textural complexity, and visual style when deciding which technique best fits the creative vision.
Mosaic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com