Acrylic is a versatile synthetic polymer widely used in manufacturing, art, and construction due to its lightweight, shatter-resistant, and transparent properties. It offers excellent weather resistance and clarity, making it an ideal material for windows, displays, and signage. Explore the full article to discover how acrylic can enhance your projects with durability and style.
Table of Comparison
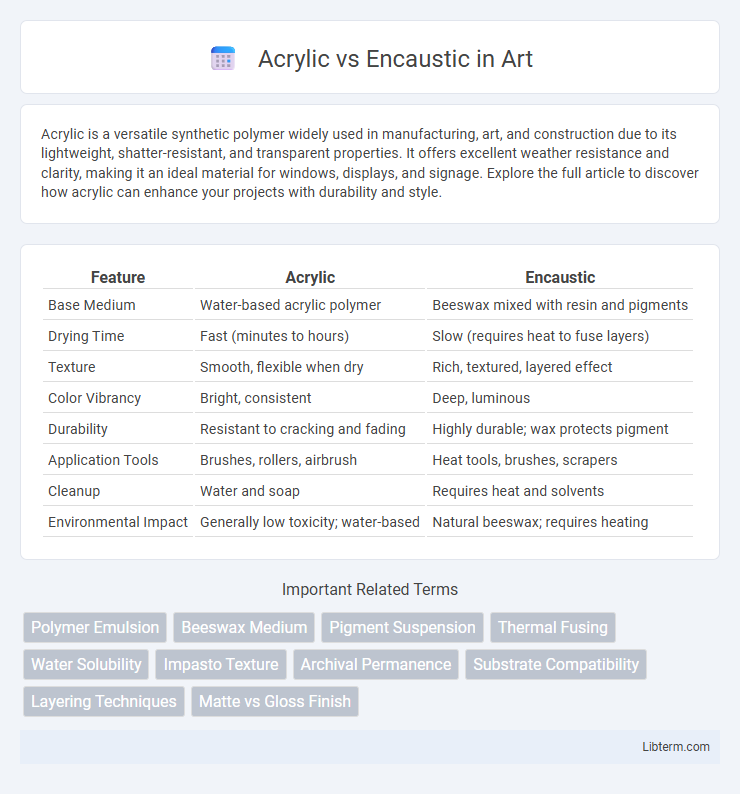
| Feature | Acrylic | Encaustic |
|---|---|---|
| Base Medium | Water-based acrylic polymer | Beeswax mixed with resin and pigments |
| Drying Time | Fast (minutes to hours) | Slow (requires heat to fuse layers) |
| Texture | Smooth, flexible when dry | Rich, textured, layered effect |
| Color Vibrancy | Bright, consistent | Deep, luminous |
| Durability | Resistant to cracking and fading | Highly durable; wax protects pigment |
| Application Tools | Brushes, rollers, airbrush | Heat tools, brushes, scrapers |
| Cleanup | Water and soap | Requires heat and solvents |
| Environmental Impact | Generally low toxicity; water-based | Natural beeswax; requires heating |
Understanding Acrylic and Encaustic Painting
Acrylic painting involves water-based pigments suspended in a synthetic polymer, known for fast drying times and versatility on various surfaces. Encaustic painting utilizes heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments, allowing for rich texture and depth through layering and carving techniques. Both mediums offer distinct artistic benefits, with acrylics favored for their durability and encaustics prized for their luminous, tactile qualities.
Brief History of Acrylic and Encaustic Art
Acrylic paint, developed in the 1930s and commercially available by the 1950s, revolutionized modern art with its fast-drying properties and versatility, gaining popularity among artists like Andy Warhol and David Hockney. Encaustic art, dating back to ancient Greece and Egypt, involves using heated beeswax mixed with pigment, preserved in well-known works such as the Fayum mummy portraits. The resurgence of encaustic painting in contemporary art highlights its unique texture and luminous qualities compared to the vibrant, synthetic nature of acrylics.
Key Materials and Tools Needed
Acrylic painting requires synthetic polymer paint, water, brushes, palettes, and canvas or paper, offering fast drying times and versatility with various mediums like gels and retarders. Encaustic painting uses pigmented beeswax combined with damar resin, heated tools like a hot palette and encaustic irons or heat guns, along with wood panels for support, enabling rich texture and layering effects. Mastery of temperature control is essential in encaustic art, while acrylic demands skillful manipulation of paint consistency and drying speed.
Application Techniques Compared
Acrylic paint offers versatility with techniques such as layering, glazing, and impasto, allowing artists to achieve a wide range of textures and finishes due to its quick drying time and water solubility. Encaustic painting involves applying heated beeswax mixed with pigment, enabling techniques like fusing, carving, and embedding materials, which create rich, textured surfaces with durable, luminous qualities. While acrylic techniques emphasize flexibility and speed, encaustic methods demand heat manipulation and provide a uniquely tactile and dimensional aesthetic.
Color Vibrancy and Texture Differences
Acrylic paint offers intense color vibrancy with a glossy finish that enhances brightness and saturation on various surfaces. Encaustic paint, composed of pigmented beeswax, provides rich, luminous hues with a uniquely textured, layered appearance that adds depth and tactile quality. The hardened wax surface of encaustic art can create intricate textures not achievable with acrylic, which generally dries flat but can be manipulated for added texture using mediums.
Durability and Longevity of Each Medium
Acrylic paint offers high durability due to its water-resistant properties and resistance to fading, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor artwork with a lifespan that can exceed 50 years if properly preserved. Encaustic painting, made from pigmented beeswax, provides exceptional longevity as it is highly stable, resistant to moisture and UV damage, and can last for centuries without significant deterioration. Both mediums demonstrate strong preservation qualities, but encaustic's natural wax composition often surpasses acrylic in long-term resilience under ideal care conditions.
Safety Considerations and Cleanup
Acrylic paint is water-based, making it safer for indoor use and easier to clean with soap and water, while encaustic involves hot wax and fumes from heated pigments, requiring proper ventilation and caution to prevent burns. Protective gloves and masks are recommended when working with encaustic to minimize exposure to toxic fumes and skin irritation. Cleanup of encaustic materials demands solvents like mineral spirits, whereas acrylic tools and spills can be effectively managed with water, simplifying post-work maintenance.
Best Surfaces for Acrylic vs Encaustic
Acrylic paint performs best on a variety of surfaces including canvas, wood panels, and textured paper due to its fast-drying, versatile nature that allows for layering and blending. Encaustic painting requires a rigid, non-porous surface such as wood, specifically birch panels, to support the heated wax medium and prevent cracking or warping. Both mediums demand proper surface preparation, but encaustic benefits most from smooth, sealed surfaces while acrylic can adapt to a broader range of textures and supports.
Artistic Styles Suited to Each Medium
Acrylic paint offers versatility, vibrant colors, and quick drying time, making it ideal for styles like abstract, pop art, and modern expressionism that benefit from layering and rapid adjustments. Encaustic painting, with its unique texture and depth created by heated beeswax mixed with pigments, suits encaustic portraiture, mixed media, and textured, layered art emphasizing tactile qualities and natural luminosity. Artists seeking experimentation with translucency and surface manipulation often prefer encaustics, while those prioritizing ease of use and bright color palettes favor acrylics.
Choosing Between Acrylic and Encaustic for Your Art
Choosing between acrylic and encaustic painting depends on the desired texture, drying time, and layering techniques. Acrylics offer fast drying, vibrant colors, and versatility suitable for detailed work and mixed media applications. Encaustic painting provides rich, luminous surfaces with a unique depth through molten wax layers, ideal for artists seeking textured and archival-quality finishes.
Acrylic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com