Engraving is a precise art form that involves carving designs onto various materials such as metal, wood, or glass to create intricate and lasting patterns. This technique is widely used for personalization, awards, jewelry, and decorative purposes, enhancing the value and uniqueness of your items. Explore the rest of the article to learn about different engraving methods and how to choose the best one for your project.
Table of Comparison
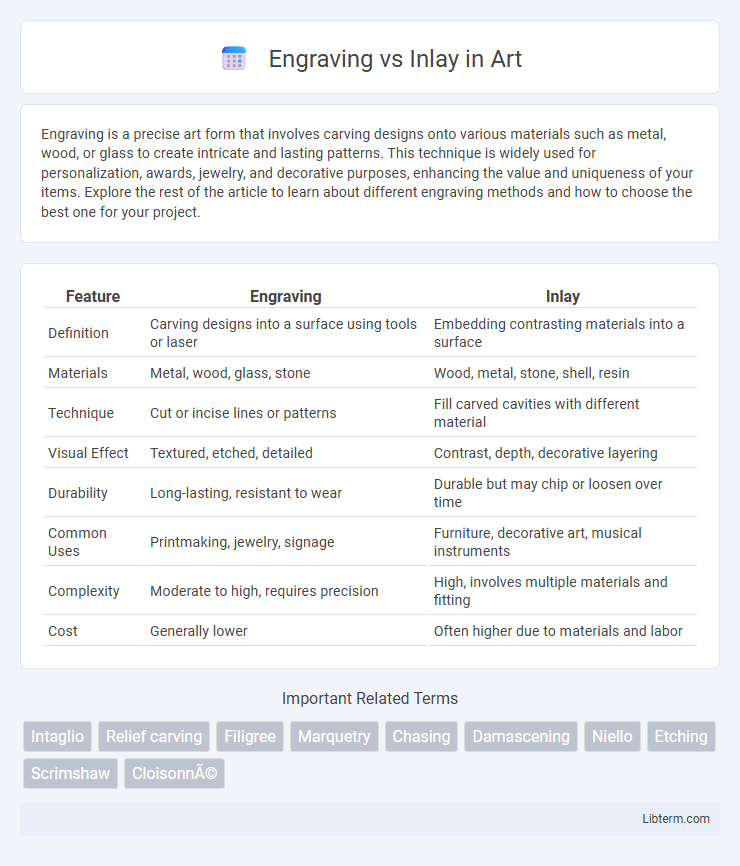
| Feature | Engraving | Inlay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Carving designs into a surface using tools or laser | Embedding contrasting materials into a surface |
| Materials | Metal, wood, glass, stone | Wood, metal, stone, shell, resin |
| Technique | Cut or incise lines or patterns | Fill carved cavities with different material |
| Visual Effect | Textured, etched, detailed | Contrast, depth, decorative layering |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resistant to wear | Durable but may chip or loosen over time |
| Common Uses | Printmaking, jewelry, signage | Furniture, decorative art, musical instruments |
| Complexity | Moderate to high, requires precision | High, involves multiple materials and fitting |
| Cost | Generally lower | Often higher due to materials and labor |
Understanding Engraving: Definition and Process
Engraving involves incising a design directly onto a hard surface, typically metal, wood, or glass, using specialized tools or laser technology to create precise and detailed patterns. The process starts with preparing the surface, followed by carefully etching the desired artwork or text, which results in a permanent, tactile mark often used for personalization or decoration. This technique differs from inlay, where materials like metal or wood are embedded into the surface, making engraving a distinct method focused on carving or cutting into the substrate itself.
Inlay Explained: Techniques and Materials
Inlay involves embedding contrasting materials such as wood, metal, or resin into a base surface to create intricate designs, offering depth and texture beyond traditional engraving. Techniques include marquetry, intarsia, and damascening, each varying in complexity and precision, with materials chosen based on durability and aesthetic appeal. The process requires careful carving of the base and precise fitting of the inlay material, resulting in a decorative finish prized in woodworking, jewelry, and metalwork.
Historical Origins of Engraving and Inlay
Engraving traces back to prehistoric times with ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Mesopotamians using sharp tools to carve symbols and images into metal, stone, and bone. Inlay techniques originated during the Bronze Age, with cultures such as the Etruscans and Celts embedding precious metals or stones into carved recesses to create intricate decorative patterns. Both methods evolved across continents, reflecting cultural artistry and technological advancements in metalwork and woodworking.
Key Differences Between Engraving and Inlay
Engraving involves cutting or carving designs directly into the surface of materials like metal or wood, creating recessed patterns that enhance texture and depth. Inlay refers to embedding contrasting materials, such as metals, stones, or wood, into carved-out spaces on the base surface, resulting in a flush, decorative design. The key difference lies in engraving's subtractive process producing grooves versus inlay's additive method incorporating separate materials for visual contrast.
Applications in Jewelry and Decorative Arts
Engraving in jewelry and decorative arts involves carving designs directly into metal surfaces, creating intricate patterns that enhance texture and detail, commonly seen in personalized rings and watch cases. Inlay techniques embed contrasting materials such as wood, enamel, or gemstones into the engraved recesses, adding vibrant color and depth to items like brooches, pendants, and decorative boxes. Both methods elevate aesthetic appeal and craftsmanship, with engraving emphasizing precision and line work while inlay highlights material contrast and surface complexity.
Durability and Longevity: Engraving vs Inlay
Engraving offers superior durability as the design is carved directly into the material, resisting wear and fading over time, making it ideal for objects exposed to frequent handling or harsh conditions. Inlay involves embedding different materials into a base surface, which may be more susceptible to damage or loosening, especially under impact or heavy use. For long-term longevity, engraving generally maintains its clarity and detail better, whereas inlay requires careful maintenance to preserve its appearance and structural integrity.
Aesthetic Appeal and Artistic Expression
Engraving offers a timeless aesthetic appeal through intricate lines and detailed textures that create depth and character on various materials, making each piece uniquely expressive. Inlay showcases vibrant contrasts by embedding different materials such as wood, metal, or stone into surfaces, enhancing artistry with rich color and texture combinations. Both techniques highlight artistic expression, with engraving emphasizing fine detail and precision, while inlay delivers bold visual interplay and material harmony.
Cost Factors: Which Technique is More Affordable?
Engraving typically costs less than inlay due to its simpler process requiring fewer materials and less labor time. Inlay involves embedding additional materials like metals or stones, increasing both material expenses and craftsmanship complexity. For budget-conscious projects, engraving offers a more affordable solution without compromising on detail.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Engraving requires minimal maintenance as the design is carved into the surface, making it resistant to wear and easy to clean with mild soap and water. Inlay involves embedding different materials into a base, which may need more careful cleaning to prevent debris from accumulating in the recessed areas and special care to avoid damage or loosening over time. Regular inspection and gentle handling are essential for inlaid pieces to preserve their intricate detailing and ensure longevity.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Engraving involves carving designs directly into materials like metal or wood, offering precise and durable detailing ideal for intricate patterns and personalized gifts. Inlay embeds contrasting materials such as metal, stone, or wood into a base surface, creating a striking visual effect suited for decorative art and jewelry. Selecting between engraving and inlay depends on project requirements including desired aesthetic, material compatibility, and budget constraints.
Engraving Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com