Printmaking transforms artistic visions into multiple originals using techniques like etching, lithography, and screenprinting. This method allows artists to experiment with textures and layers, producing unique works rich in detail and depth. Discover how mastering printmaking can elevate your creative expression by exploring the techniques outlined in this article.
Table of Comparison
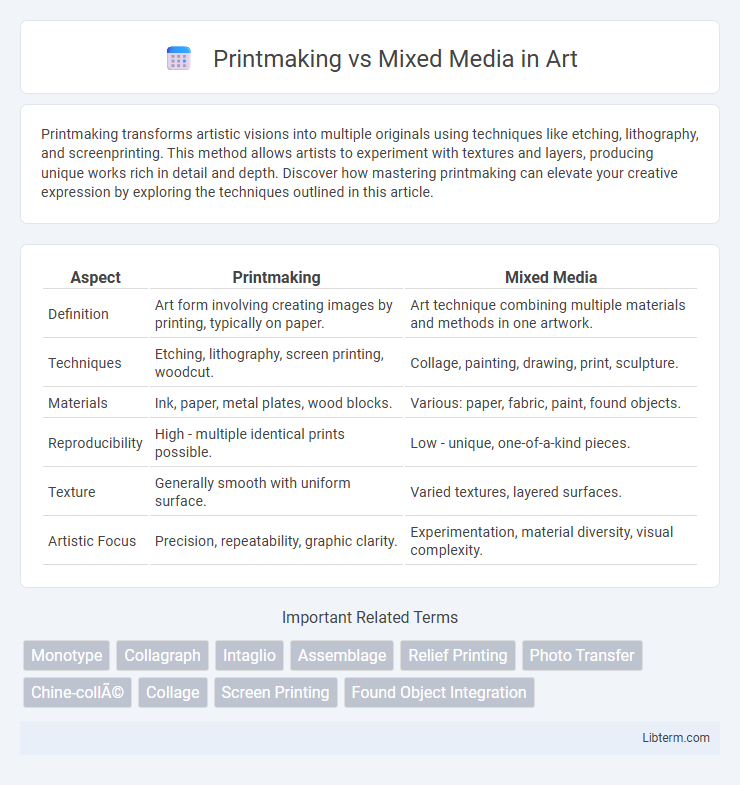
| Aspect | Printmaking | Mixed Media |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art form involving creating images by printing, typically on paper. | Art technique combining multiple materials and methods in one artwork. |
| Techniques | Etching, lithography, screen printing, woodcut. | Collage, painting, drawing, print, sculpture. |
| Materials | Ink, paper, metal plates, wood blocks. | Various: paper, fabric, paint, found objects. |
| Reproducibility | High - multiple identical prints possible. | Low - unique, one-of-a-kind pieces. |
| Texture | Generally smooth with uniform surface. | Varied textures, layered surfaces. |
| Artistic Focus | Precision, repeatability, graphic clarity. | Experimentation, material diversity, visual complexity. |
Understanding Printmaking: Definition and Techniques
Printmaking is an artistic process that involves creating images by transferring ink from a matrix, such as a carved woodblock, metal plate, or screen, onto paper or fabric. Key techniques include relief printing, intaglio, lithography, and screen printing, each offering unique textures and effects that define the final artwork's character. Understanding these methods allows artists to explore repetition, layering, and variations in tonal quality, distinguishing printmaking from mixed media, which combines multiple art forms and materials in a single composition.
What is Mixed Media? Exploring Its Artistic Scope
Mixed media is an art technique that combines various materials such as paint, ink, fabric, paper, and found objects to create multidimensional artworks. Unlike printmaking, which primarily involves transferring ink onto surfaces through processes like etching or screen printing, mixed media allows for greater experimentation with textures and layers. This artistic approach broadens creative possibilities by blending traditional and unconventional materials, enhancing visual depth and narrative complexity.
Historical Evolution: Printmaking and Mixed Media
Printmaking originated in the 15th century with woodcuts and engravings, evolving through techniques like etching and lithography, shaping the dissemination of art and ideas across Europe and beyond. Mixed media emerged prominently in the 20th century, propelled by Modernist artists who combined traditional painting with collage, photography, and found objects to challenge conventions. Both printmaking and mixed media reflect key historical developments in artistic experimentation, with printmaking rooted in reproducibility and mixed media emphasizing material diversity and conceptual innovation.
Materials and Tools Used in Printmaking vs Mixed Media
Printmaking employs specialized materials such as linoleum blocks, etching plates, and screen printing meshes, along with tools including brayers, carving tools, and printing presses to create multiple copies of an image. Mixed media combines a diverse range of materials like acrylic paints, collage elements, fabric, and found objects with various tools such as brushes, palette knives, and adhesives to produce textured, layered artworks. The distinct focus on reproducibility in printmaking contrasts with the experimental and textural emphasis found in mixed media art.
Distinctive Processes: Step-by-Step Methods
Printmaking involves creating images through techniques like etching, lithography, or screen printing, where a plate or screen transfers ink onto paper or fabric in multiple copies. Mixed media combines various materials such as paint, collage, and found objects applied layer by layer, allowing for diverse textures and visual effects in a single artwork. Each printmaking step typically follows precise, repeatable processes, whereas mixed media embraces experimental and fluid techniques that vary with the artist's intent.
Artistic Expression: Comparing Creative Possibilities
Printmaking offers precise replication and intricate detailing through techniques like etching and screenprinting, enabling artists to explore repeated patterns and textures. Mixed media combines diverse materials such as paint, collage, and found objects, fostering limitless creative freedom and tactile experimentation in artistic expression. Both methods expand creative possibilities, with printmaking emphasizing reproducibility and mixed media prioritizing spontaneity and material diversity.
Visual Impact: Texture, Depth, and Composition
Printmaking offers precise textures and sharp contrasts through techniques like etching and screenprinting, creating a visually striking depth with layered ink applications. Mixed media combines diverse materials such as paint, fabric, and found objects, enhancing tactile texture and dynamic composition through varied surface treatments. The interplay of dimensional elements in mixed media often results in a richer, more complex visual impact compared to the structured repetition and clarity characteristic of printmaking.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works in Each Medium
Printmaking features iconic artists such as Albrecht Durer, renowned for his detailed woodcuts like "Melencolia I," and Andy Warhol, whose silkscreen prints "Marilyn Diptych" transformed pop art. Mixed media showcases pioneers like Robert Rauschenberg, famous for his "Combines" that merge painting and sculpture, and Pablo Picasso, who integrated collage elements in works like "Still Life with Chair Caning." These artists exemplify the distinct creative approaches and historical significance embedded in each medium.
Preservation, Display, and Longevity Considerations
Printmaking typically offers greater longevity and preservation due to the use of archival-quality papers and inks that resist fading and deterioration over time. Mixed media artworks often combine various materials, which can complicate preservation efforts due to differing aging processes and vulnerabilities to environmental factors like humidity and light exposure. Proper display conditions, including UV-protective glazing and controlled climate environments, are crucial for both media but especially vital for mixed media to maintain structural integrity and color stability.
Choosing Between Printmaking and Mixed Media: Which Fits Your Vision?
Printmaking offers precise control over repeated images and textures, ideal for artists prioritizing consistency and traditional techniques like etching or screen printing. Mixed media allows for blending materials such as paint, fabric, and found objects, providing versatility and depth suited for experimental and multidimensional artwork. Selecting between printmaking and mixed media depends on whether you seek uniformity and structure or creative freedom and textural complexity in your artistic vision.
Printmaking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com