Realism captures the world with precise detail, emphasizing accurate representation of everyday life and ordinary people. This artistic and literary movement rejects exaggeration and focuses on the truthful depiction of social conditions and human experiences. Explore the rest of the article to understand how realism shapes your perspective on art and literature.
Table of Comparison
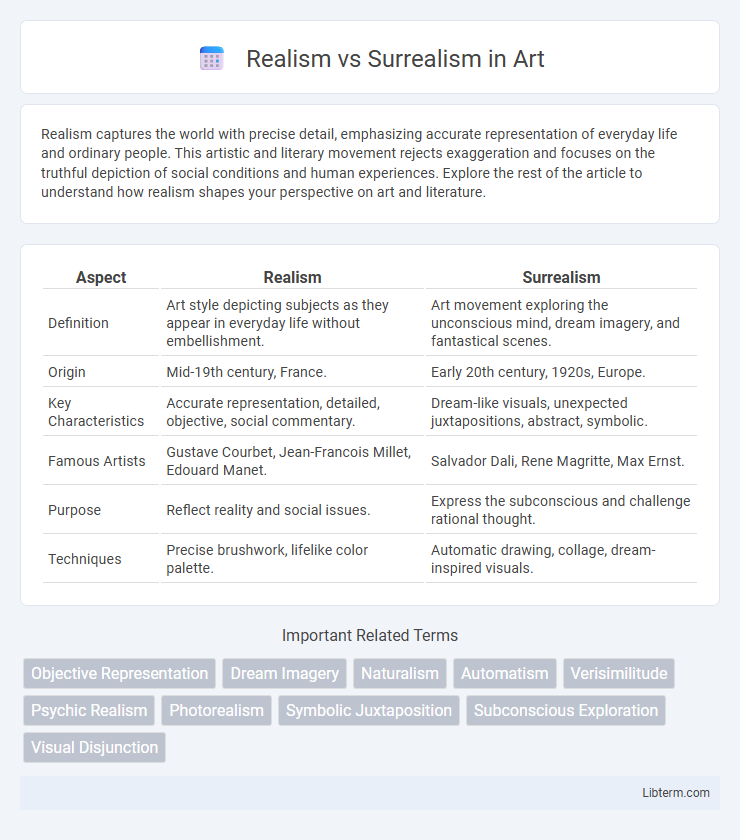
| Aspect | Realism | Surrealism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art style depicting subjects as they appear in everyday life without embellishment. | Art movement exploring the unconscious mind, dream imagery, and fantastical scenes. |
| Origin | Mid-19th century, France. | Early 20th century, 1920s, Europe. |
| Key Characteristics | Accurate representation, detailed, objective, social commentary. | Dream-like visuals, unexpected juxtapositions, abstract, symbolic. |
| Famous Artists | Gustave Courbet, Jean-Francois Millet, Edouard Manet. | Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, Max Ernst. |
| Purpose | Reflect reality and social issues. | Express the subconscious and challenge rational thought. |
| Techniques | Precise brushwork, lifelike color palette. | Automatic drawing, collage, dream-inspired visuals. |
Understanding Realism: Definition and Origins
Realism, originating in mid-19th century France, is an art movement emphasizing accurate, detailed, and unembellished depiction of everyday life and ordinary people. It rejects romanticized or idealized portrayals, aiming instead to represent subjects truthfully without artificiality or speculation. Realism's foundations lie in the socio-political climate of the Industrial Revolution, reflecting a commitment to social issues and the lives of the working class.
Surrealism Explained: History and Key Features
Surrealism emerged in the early 1920s as an avant-garde movement that sought to unlock the unconscious mind, inspired heavily by Freudian psychoanalysis and Dadaism. Key features of Surrealism include dream-like imagery, unexpected juxtapositions, symbolic content, and illogical scenes that challenge rational thought and reality. This movement notably influenced visual arts, literature, and cinema by emphasizing imagination, intuition, and exploring the irrational aspects of the human experience.
Key Differences Between Realism and Surrealism
Realism emphasizes accurate, detailed depictions of everyday life and natural settings, focusing on ordinary people and events without embellishment. Surrealism, by contrast, delves into the subconscious mind, showcasing dream-like, fantastical imagery that defies logical interpretation. Key differences include Realism's commitment to objectivity and plausible scenes, whereas Surrealism embraces imagination, symbolism, and unexpected juxtapositions to evoke emotional and psychological responses.
Influential Realist Artists and Works
Influential Realist artists like Gustave Courbet and Jean-Francois Millet revolutionized 19th-century art by emphasizing everyday subjects and social realities, with Courbet's "The Stone Breakers" and Millet's "The Gleaners" exemplifying this commitment to depicting ordinary life. These works reject romanticism and idealization, focusing instead on raw, unembellished scenes that highlight the dignity and struggles of the working class. Their detailed, lifelike portrayals contrast sharply with Surrealism's dreamlike, fantastical imagery, setting the foundation for modern artistic explorations of reality.
Prominent Surrealist Artists and Movements
Prominent surrealist artists such as Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, and Max Ernst revolutionized visual art by exploring dreamlike scenes and subconscious imagery, contrasting sharply with the objective representation favored in Realism. The Surrealist movement, founded in the early 1920s by Andre Breton, emphasized automatic writing, unexpected juxtapositions, and symbolism to challenge rational thought and conventional aesthetics. This avant-garde movement influenced not only painting but also literature, film, and theater, marking a radical departure from the precise, detailed depictions characteristic of Realist art.
Philosophical Foundations: Realism vs Surrealism
Realism is grounded in the philosophical belief that reality exists independently of perception, emphasizing objective representation and truth as experienced through the senses. Surrealism, influenced by Freudian psychoanalysis and the exploration of the unconscious mind, rejects rational constraints to access deeper truths through dreams and irrational imagery. The contrast between these philosophies highlights realism's commitment to external reality versus surrealism's pursuit of internal, subconscious realities.
Techniques and Styles in Realism and Surrealism
Realism employs precise, detailed techniques such as careful brushwork and accurate perspective to depict everyday scenes with true-to-life clarity, emphasizing natural light and texture. Surrealism, by contrast, utilizes dreamlike imagery, unexpected juxtapositions, and distorted forms through techniques like automatism, collage, and exaggerated perspectives to evoke the unconscious mind. Both movements rely on distinct stylistic approaches: Realism focuses on objective representation, while Surrealism embraces imaginative, symbolic compositions that challenge reality.
Impact on Literature and Visual Arts
Realism emphasized authentic representation of everyday life, profoundly influencing literature with detailed character development and social critique, while visual arts embraced precise, lifelike depictions that challenged romanticized ideals. Surrealism revolutionized literature and visual arts by unlocking subconscious creativity, using dream-like imagery and illogical scenes to explore human psychology and challenge rational thought. Both movements reshaped artistic expression, with Realism grounding work in tangible reality and Surrealism expanding imaginative possibilities.
Modern Interpretations and Contemporary Trends
Modern interpretations of Realism emphasize detailed representation and social commentary, reflecting contemporary issues through true-to-life depictions. Surrealism in contemporary art explores dreamlike imagery and subconscious themes, blending reality with imaginative elements to challenge perceptions. Current trends show artists integrating digital media and mixed techniques to expand both genres, creating hybrid works that question the boundaries between reality and fantasy.
Which Is More Relevant Today: Realism or Surrealism?
Realism remains highly relevant today as it emphasizes accurate representation of everyday life, resonating with audiences seeking authenticity and social commentary. Surrealism, with its imaginative and dream-like qualities, continues to inspire creative expression and challenge conventional perceptions, particularly in digital art and multimedia. The growing interest in virtual realities and psychological exploration suggests surrealism's increasing significance alongside realism's foundational role.
Realism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com