Decorative art enhances everyday objects with aesthetic appeal, blending functionality with beauty through mediums like ceramics, glass, textiles, and metalwork. It reflects cultural heritage and artistic trends, transforming utilitarian items into creative expressions that enrich our living spaces. Explore the rest of this article to discover how decorative art can inspire your personal style and environment.
Table of Comparison
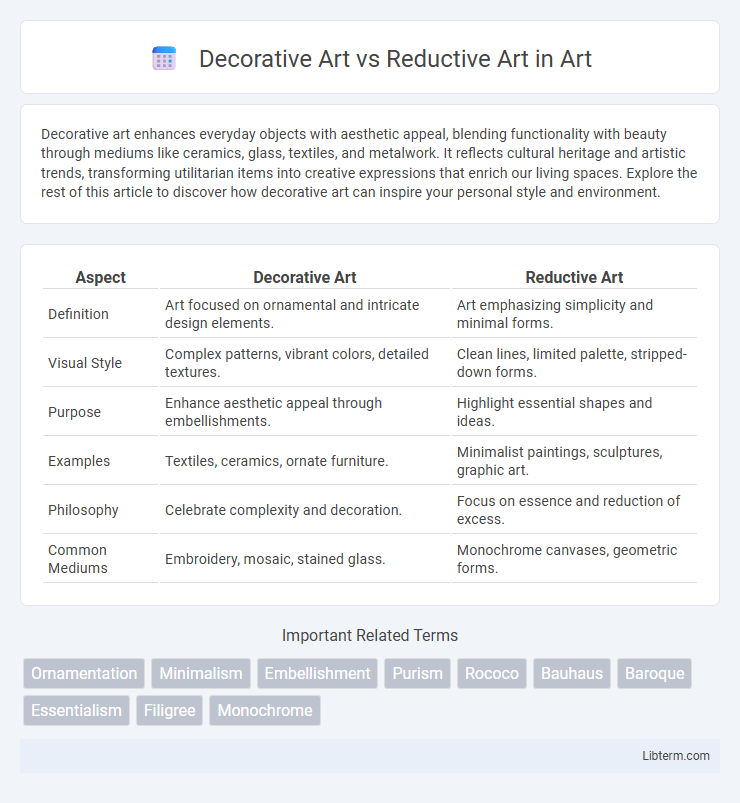
| Aspect | Decorative Art | Reductive Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art focused on ornamental and intricate design elements. | Art emphasizing simplicity and minimal forms. |
| Visual Style | Complex patterns, vibrant colors, detailed textures. | Clean lines, limited palette, stripped-down forms. |
| Purpose | Enhance aesthetic appeal through embellishments. | Highlight essential shapes and ideas. |
| Examples | Textiles, ceramics, ornate furniture. | Minimalist paintings, sculptures, graphic art. |
| Philosophy | Celebrate complexity and decoration. | Focus on essence and reduction of excess. |
| Common Mediums | Embroidery, mosaic, stained glass. | Monochrome canvases, geometric forms. |
Introduction to Decorative Art and Reductive Art
Decorative art emphasizes embellishment and intricate patterns that enhance visual appeal, often incorporating vibrant colors and elaborate designs to create ornamental aesthetics. Reductive art, in contrast, focuses on minimalism and simplicity by stripping elements down to their essentials, highlighting form, color, and composition with little to no decoration. These two approaches represent divergent philosophies in art, where decorative art prioritizes complexity and adornment, while reductive art values clarity and restraint.
Defining Decorative Art: Key Characteristics
Decorative Art is characterized by intricate patterns, ornamental designs, and a focus on aesthetic embellishment that enhances visual appeal. It often incorporates detailed motifs, vibrant colors, and layered textures to create a rich, visually engaging surface. This art form emphasizes decorative elements that serve both functional and artistic purposes, distinguishing it from the minimalist approach of Reductive Art.
Understanding Reductive Art: Essential Elements
Reductive art emphasizes simplicity by focusing on essential elements such as form, color, and texture, stripping away unnecessary details to highlight core visual components. It often employs minimalistic shapes and a limited color palette to create impactful, contemplative works that invite viewers to engage deeply with the material essence. This approach contrasts with decorative art, which relies on elaborate patterns, ornate details, and vibrant embellishments to enhance aesthetic appeal.
Historical Evolution of Decorative and Reductive Art
Decorative art originated in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt, where ornamental designs emphasized intricate patterns and symbolic motifs reflecting cultural narratives and craftsmanship. In contrast, reductive art emerged prominently in the 20th century with movements like Minimalism and Abstract Expressionism, focusing on simplicity, geometric forms, and the elimination of superfluous detail to evoke purity and essentialism. The historical evolution of decorative and reductive art illustrates a shift from complexity and embellishment towards abstraction and minimalism, reflecting changing aesthetic philosophies and cultural contexts.
Major Movements Influencing Each Style
Decorative art is heavily influenced by movements such as Art Nouveau, characterized by intricate patterns and elaborate ornamentation, and the Arts and Crafts movement, which emphasizes craftsmanship and detailed design. Reductive art draws its foundations from Minimalism and Abstract Expressionism, focusing on simplicity, essential forms, and reducing elements to their core essence. Key figures like Charles Rennie Mackintosh in decorative art and Donald Judd in reductive art exemplify the defining principles of each style.
Techniques and Materials Used in Both Approaches
Decorative art typically employs techniques such as painting, embroidery, and mosaic work, utilizing materials like ceramics, textiles, glass, and metals to create intricate patterns and ornamental designs that emphasize surface beauty and detailed craftsmanship. Reductive art focuses on simplifying forms through techniques like carving, etching, and minimalistic design, often using materials such as wood, stone, metal, or concrete to strip away excess detail and highlight essential shapes and textures. Both approaches reflect distinct aesthetic philosophies, with decorative art enhancing visual richness and reductive art emphasizing clarity and structural purity.
Aesthetic Purposes: Ornamentation vs. Simplicity
Decorative Art emphasizes aesthetic purposes through intricate ornamentation, utilizing elaborate patterns, vibrant colors, and detailed textures to enhance visual richness and appeal. Reductive Art prioritizes simplicity, stripping away excess elements to focus on clean lines, basic forms, and minimalistic design that evoke clarity and purity. The contrast between the two lies in Decorative Art's complexity aimed at visual embellishment versus Reductive Art's restrained approach targeting essential beauty and functional elegance.
Impact on Contemporary Art Trends
Decorative Art, characterized by intricate patterns and vibrant colors, influences contemporary art trends by inspiring bold visual aesthetics and craftsmanship techniques seen in modern textile design and digital media. Reductive Art's emphasis on simplicity and minimalism shapes current artistic movements, promoting clarity, spatial balance, and conceptual depth in installations and graphic arts. These contrasting approaches drive innovation by blending ornamental richness with pared-down forms, enriching the diversity of contemporary creative expression.
Leading Artists in Decorative and Reductive Art
Leading artists in Decorative Art include Gustav Klimt, renowned for his ornate patterns and gold leaf embellishments, and Henri Matisse, whose vibrant color palettes and intricate designs epitomize decorative richness. In contrast, key figures in Reductive Art such as Donald Judd and Agnes Martin emphasize minimalism, focusing on simplicity, geometric forms, and restrained color schemes to evoke purity and essence. These artists distinctly represent the core principles of their respective movements, showcasing the spectrum from elaborate ornamentation to fundamental reduction.
Choosing Between Decorative and Reductive Art in Modern Design
Choosing between decorative and reductive art in modern design depends on the desired visual impact and functionality of the space. Decorative art emphasizes intricate patterns, textures, and embellishments to create rich, visually engaging environments, while reductive art prioritizes simplicity, clean lines, and minimalism to foster clarity and openness. Designers often balance these approaches by integrating decorative elements as accent features within predominantly reductive frameworks to maintain both aesthetic appeal and spatial efficiency.
Decorative Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com