Woodcut is a traditional printmaking technique where artists carve images into wooden blocks, creating detailed and textured prints. This method has been used for centuries to produce intricate artwork and illustrations, offering a timeless aesthetic that appeals to both collectors and creators. Explore the article to discover how woodcut art evolves and how you can start your own woodcut journey.
Table of Comparison
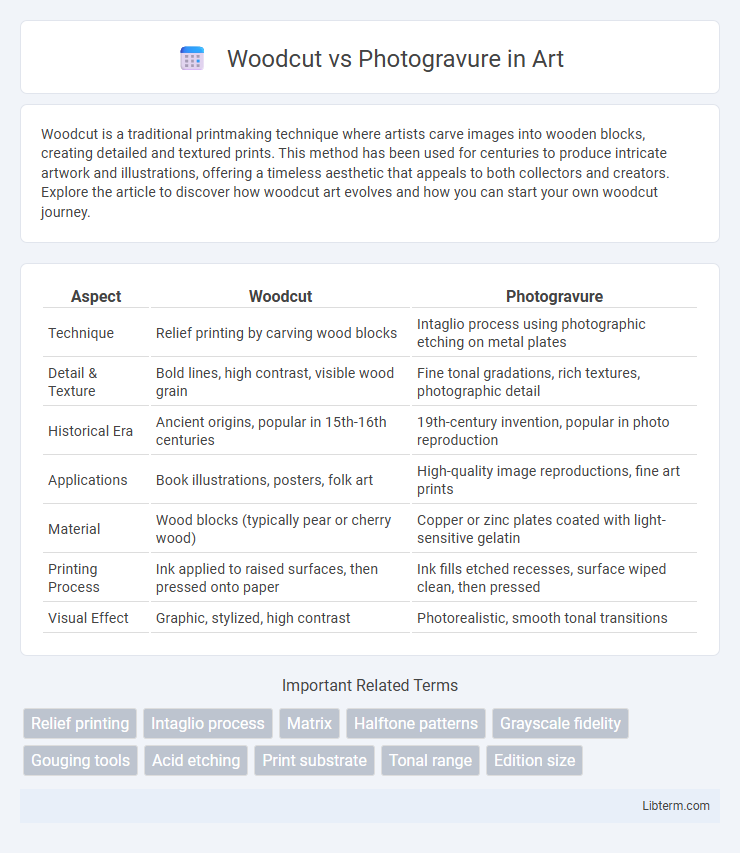
| Aspect | Woodcut | Photogravure |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Relief printing by carving wood blocks | Intaglio process using photographic etching on metal plates |
| Detail & Texture | Bold lines, high contrast, visible wood grain | Fine tonal gradations, rich textures, photographic detail |
| Historical Era | Ancient origins, popular in 15th-16th centuries | 19th-century invention, popular in photo reproduction |
| Applications | Book illustrations, posters, folk art | High-quality image reproductions, fine art prints |
| Material | Wood blocks (typically pear or cherry wood) | Copper or zinc plates coated with light-sensitive gelatin |
| Printing Process | Ink applied to raised surfaces, then pressed onto paper | Ink fills etched recesses, surface wiped clean, then pressed |
| Visual Effect | Graphic, stylized, high contrast | Photorealistic, smooth tonal transitions |
Introduction to Printmaking Techniques
Woodcut and photogravure represent foundational printmaking techniques distinguished by their processes and visual effects. Woodcut involves carving an image into a wooden block to create bold, high-contrast prints, emphasizing texture and line work. Photogravure uses photochemical etching on metal plates to produce rich tonal variations and detailed photographic reproductions, making it highly valued for fine art prints and archival quality.
What is Woodcut?
Woodcut is a relief printing technique where an artist carves an image into the surface of a wooden block, leaving the raised areas to receive ink and create the print. This traditional method emphasizes bold lines and high contrast, often resulting in stark, graphic artworks. Popular since medieval times, woodcut remains valued for its textured and tactile qualities in fine art printmaking.
What is Photogravure?
Photogravure is a high-quality intaglio printmaking process that transfers photographic images onto etched copper plates, allowing for fine detail and rich tonal variation. Unlike woodcut, which relies on carving images into woodblocks for relief printing, photogravure captures continuous tones through chemical etching and acid baths. This technique is prized in fine art and archival reproductions for its ability to produce precise, high-resolution prints with deep blacks and delicate gradients.
Historical Evolution of Woodcut
Woodcut, originating in ancient China during the Tang Dynasty, evolved significantly through the Middle Ages in Europe as a primary method for reproducing images and texts before the advent of movable type printing. The technique involves carving an image in relief on a wooden block, allowing for mass production of prints and playing a pivotal role in spreading religious and cultural materials across medieval societies. As technology advanced, woodcut's influence persisted but was gradually supplanted by photogravure in the 19th century, a process that allowed for finer detail and gradation by transferring photographic images onto metal plates for printing.
The Development of Photogravure
Photogravure emerged in the late 19th century as an advanced intaglio printmaking technique that surpassed the limitations of traditional woodcut relief printing by allowing fine tonal gradations and photographic detail reproduction. The process involved transferring a photographic image onto a metal plate, which was then etched to create varying depths, enabling rich and continuous tones ideal for high-quality art and photographic prints. This development revolutionized image reproduction, providing artists and publishers with a method to achieve greater precision and durability compared to the coarse textures characteristic of woodcuts.
Key Artistic Differences
Woodcut employs a relief printing technique where the artist carves into a wooden block, creating bold, high-contrast images defined by sharp lines and simplified forms. Photogravure uses a photographic process to etch images onto metal plates, capturing intricate details, tonal gradients, and subtle textures with a high degree of precision. The key artistic difference lies in woodcut's emphasis on expressive line work and texture versus photogravure's capability for continuous tone and fine photographic detail.
Technical Process Comparison
Woodcut involves carving an image into a wooden block, where raised areas are inked and pressed onto paper, relying on relief printing that emphasizes bold lines and high contrast. Photogravure uses a chemically etched copper plate to reproduce photographic images with continuous tones, capturing intricate details through a photomechanical process involving light-sensitive gelatin and acid. The woodcut process is manual and tactile, ideal for graphic, stylized images, whereas photogravure offers superior tonal range and fine detail, suited for photographic art and high-quality reproductions.
Visual Texture and Aesthetic Appeal
Woodcut prints offer bold, high-contrast visual textures with distinct, carved lines that emphasize a handcrafted aesthetic. Photogravure produces rich tonal gradations and delicate details, resulting in a smoother, more photographic texture ideal for capturing subtle shadows and depth. The aesthetic appeal of woodcut lies in its expressive, rustic feel, while photogravure appeals with its refined, intricate finish reminiscent of fine art photography.
Modern Applications and Trends
Woodcut printmaking, known for its bold lines and textured finish, remains popular in contemporary art for its tactile aesthetic and sustainable materials. Photogravure, a photo-mechanical process producing high-resolution tonal gradations, continues to be favored in fine art reproduction and limited-edition prints due to its superior detail and depth. Modern trends integrate digital technology with both techniques, enhancing precision in woodcut carving and optimizing photogravure plate preparation for hybrid analog-digital workflows.
Choosing Between Woodcut and Photogravure
Choosing between woodcut and photogravure depends on the desired artistic effect and production method. Woodcut offers bold, high-contrast images with a tactile texture, ideal for traditional printmaking and expressive designs. Photogravure provides fine tonal gradations and photographic detail, making it suitable for high-quality photographic reproductions and subtle image nuances.
Woodcut Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com