Surrealism revolutionized art and literature by unlocking the power of the subconscious mind, blending dreamlike imagery with reality to challenge traditional perceptions. This movement, rooted in Freudian psychoanalysis, encourages exploration of the irrational and fantastical, allowing artists to express their deepest emotions and ideas. Discover how surrealism can transform your creative perspective by diving into the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
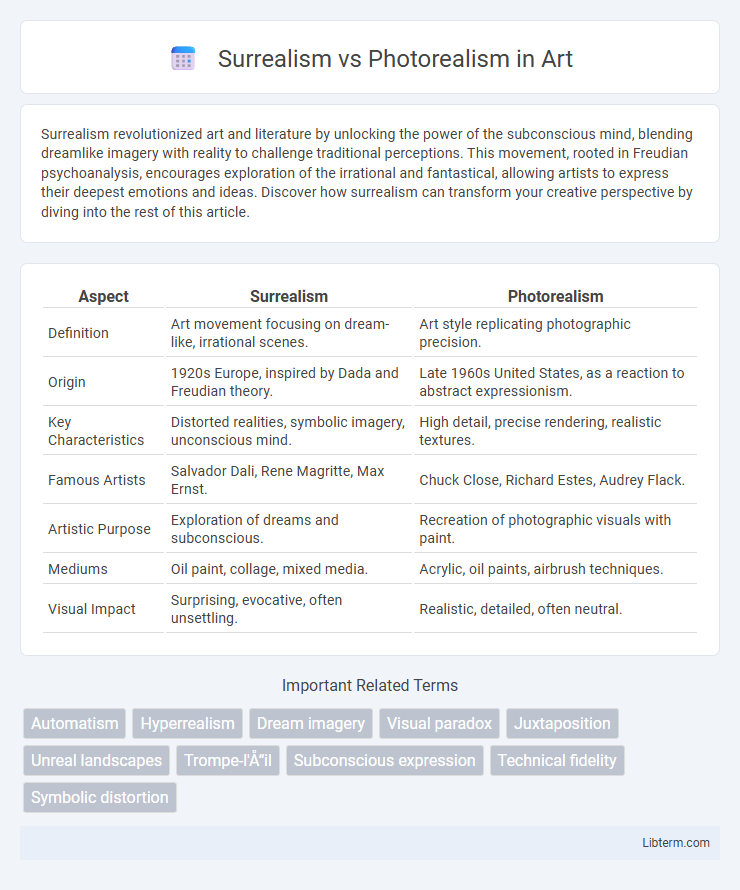
| Aspect | Surrealism | Photorealism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art movement focusing on dream-like, irrational scenes. | Art style replicating photographic precision. |
| Origin | 1920s Europe, inspired by Dada and Freudian theory. | Late 1960s United States, as a reaction to abstract expressionism. |
| Key Characteristics | Distorted realities, symbolic imagery, unconscious mind. | High detail, precise rendering, realistic textures. |
| Famous Artists | Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, Max Ernst. | Chuck Close, Richard Estes, Audrey Flack. |
| Artistic Purpose | Exploration of dreams and subconscious. | Recreation of photographic visuals with paint. |
| Mediums | Oil paint, collage, mixed media. | Acrylic, oil paints, airbrush techniques. |
| Visual Impact | Surprising, evocative, often unsettling. | Realistic, detailed, often neutral. |
Introduction to Surrealism and Photorealism
Surrealism emerged in the early 1920s as an avant-garde movement that explores the unconscious mind through dream-like, fantastical imagery, often blending reality with illogical scenes to challenge perceptions. Photorealism developed in the late 1960s as a genre where artists meticulously replicate photographs with precise accuracy, emphasizing detailed representation and clarity. Both movements contrast significantly, with Surrealism prioritizing imaginative depth and Photorealism focusing on technical precision and visual reality.
Defining Surrealism: Art Beyond Reality
Surrealism transcends reality by merging dreamlike imagery with unexpected juxtapositions, challenging conventional perceptions and exploring the unconscious mind. This art movement emphasizes the liberation of imagination through bizarre, fantastical scenes that defy logical interpretation. Unlike photorealism's precise depiction of subjects, surrealism prioritizes emotional intensity and symbolic meaning over exact replication.
Understanding Photorealism: Precision and Detail
Photorealism emphasizes meticulous attention to detail and precise replication of photographic images, capturing textures, light reflections, and minute imperfections with exceptional accuracy. Artists use techniques such as airbrushing and layering to achieve sharp, lifelike results that challenge the viewer's perception of reality. This movement contrasts with Surrealism's dreamlike and imaginative interpretations by focusing solely on visual fidelity and objective representation.
Historical Origins and Influences
Surrealism originated in the early 1920s as a revolutionary movement influenced by the psychoanalytic theories of Sigmund Freud and the chaos following World War I, emphasizing dream-like, illogical scenes to explore the subconscious mind. Photorealism emerged in the late 1960s as a reaction to Abstract Expressionism, heavily influenced by advances in photography and technology, aiming to create hyper-realistic paintings that mimic high-resolution photographs. Both movements reflect distinct historical contexts, with Surrealism rooted in psychological exploration and political upheaval, while Photorealism draws from technological precision and urban culture.
Key Artists in Surrealism and Photorealism
Surrealism features key artists like Salvador Dali, known for his dreamlike, bizarre imagery, and Rene Magritte, who blended ordinary objects in unusual contexts to challenge reality. Photorealism includes pioneers such as Chuck Close, recognized for his hyper-detailed portraits, and Richard Estes, celebrated for his precise urban scenes mimicking high-resolution photography. Both movements emphasize meticulous technique, but Surrealism explores subconscious symbolism while Photorealism focuses on replicating photographic clarity.
Visual Techniques and Artistic Processes
Surrealism employs dreamlike imagery, unexpected juxtapositions, and symbolic motifs to challenge reality and ignite the subconscious, using techniques like automatism, collage, and exaggerated forms. Photorealism emphasizes precise, detailed replication of photographs through meticulous layering, airbrushing, and attention to light, shadow, and texture to achieve hyper-realistic visuals. Surrealist artists prioritize imaginative interpretation and emotional expression, whereas photorealists focus on technical accuracy and objective depiction of subjects.
Themes and Symbolism Explored
Surrealism explores themes of dreams, the unconscious mind, and fantastical imagery, often using symbolic elements that challenge reality and provoke emotional or psychological responses. Photorealism emphasizes detailed, lifelike representations of everyday scenes, focusing on clarity and accuracy rather than symbolic meaning. While surrealism delves into abstract concepts and metaphors, photorealism highlights meticulous observation and the technical skill of replication, often evoking themes of modern life and consumer culture through its precision.
Surrealism vs Photorealism: Core Differences
Surrealism explores dream-like, fantastical imagery that challenges reality through symbolic and abstract forms, prioritizing imagination over accuracy. Photorealism emphasizes precise, detailed replication of photographs to achieve lifelike representations, focusing on visual fidelity and objectivity. The core difference lies in Surrealism's embrace of subconscious expression versus Photorealism's dedication to meticulous, realistic depiction.
Impact on Contemporary Art and Culture
Surrealism revolutionized contemporary art by challenging perceptions of reality and encouraging exploration of the subconscious, influencing diverse creative fields such as literature, film, and fashion. Photorealism, with its meticulous attention to detail and emphasis on representing reality, pushed boundaries in visual accuracy and technique, impacting advertising, digital media, and hyperrealistic art forms. Both movements have profoundly shaped cultural dialogues by expanding the possibilities of artistic expression and redefining the relationship between reality and imagination in contemporary society.
Choosing Your Artistic Path: Surrealism or Photorealism
Choosing your artistic path between Surrealism and Photorealism depends on your creative goals and technical skills. Surrealism emphasizes dreamlike, imaginative scenes that challenge reality and encourage symbolic expression, appealing to artists seeking to explore subconscious and abstract concepts. Photorealism demands precise attention to detail and mastery of technique to create hyper-realistic images, ideal for those dedicated to replicating life with photographic accuracy.
Surrealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com