Binders and solvents play crucial roles in various industries, from paints to pharmaceuticals, by influencing the texture, adhesion, and drying time of products. Binders act as the glue that holds particles together, while solvents dissolve these binders to ensure a smooth application and controlled evaporation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these components impact your products and their performance.
Table of Comparison
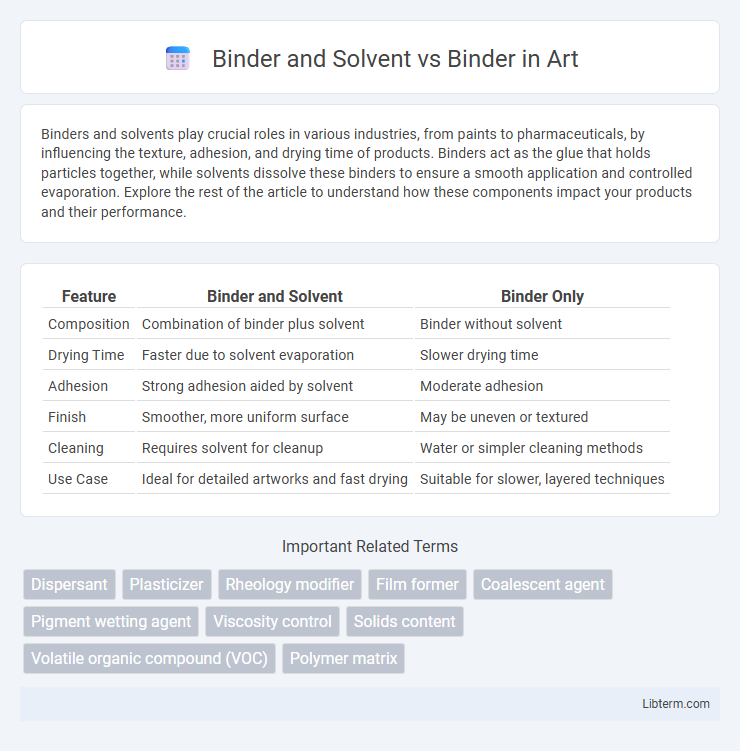
| Feature | Binder and Solvent | Binder Only |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Combination of binder plus solvent | Binder without solvent |
| Drying Time | Faster due to solvent evaporation | Slower drying time |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion aided by solvent | Moderate adhesion |
| Finish | Smoother, more uniform surface | May be uneven or textured |
| Cleaning | Requires solvent for cleanup | Water or simpler cleaning methods |
| Use Case | Ideal for detailed artworks and fast drying | Suitable for slower, layered techniques |
Introduction to Binders and Solvents
Binders are essential components in formulations, providing adhesion, cohesion, and structural integrity to materials such as coatings, adhesives, and composites. Solvents serve primarily to dissolve or disperse binders, adjusting viscosity and enabling application by facilitating the transfer of the binder to the substrate. Understanding the interaction between binders and solvents is crucial for optimizing drying time, film formation, and overall performance of the final product.
What is a Binder?
A binder is a crucial component in coatings, adhesives, and composites that holds particles together, providing mechanical strength and durability. Unlike solvents, which primarily dissolve or disperse substances to create a workable mixture, binders form a solid film upon drying or curing, ensuring adhesion and cohesion. Common binders include polymers like acrylics, epoxies, and polyurethanes, which determine the overall properties and performance of the finished product.
The Role of Solvents in Binder Systems
Solvents in binder systems dissolve and disperse binder polymers, enabling uniform application and optimal film formation upon drying. The solvent's evaporation rate critically influences drying time, porosity, and adhesion properties of the final coating or adhesive. Proper solvent selection enhances binder performance, improving durability, flexibility, and resistance properties in coatings and composite materials.
Binder and Solvent: How Do They Work Together?
Binders and solvents work together in formulations by each playing a distinct but complementary role: binders provide adhesion, cohesion, and film-forming properties essential for the structural integrity of coatings, adhesives, and inks, while solvents dissolve or disperse the binder to adjust viscosity and aid in application. Upon drying or curing, solvents evaporate, allowing the binder to form a continuous, durable film that adheres to the substrate. This synergy ensures optimal performance, durability, and finish quality in various industrial and commercial products.
Binder vs Binder: Comparing Different Types
Different binder types, such as polymeric, asphaltic, and natural binders, offer distinct adhesion, flexibility, and durability properties crucial for various construction and manufacturing applications. Polymeric binders provide superior chemical resistance and flexibility, while asphaltic binders excel in waterproofing and load-bearing capacity. Selecting the appropriate binder hinges on environmental conditions, mechanical requirements, and compatibility with the intended solvent or additive.
Advantages of Using Solvents with Binders
Using solvents with binders enhances film formation by improving the binder's dispersion and viscosity control, leading to smoother, more uniform coatings. Solvents facilitate better substrate penetration and adhesion, increasing the durability and performance of the final product. These benefits are critical in applications such as paints, adhesives, and inks, where precise control of drying time and texture is essential.
Drawbacks of Binder-Only Applications
Binder-only applications often suffer from insufficient adhesion and mechanical durability due to the lack of solvent-mediated dispersion and film formation. Without solvents, binders may form uneven coatings with poor wetting properties, leading to decreased surface coverage and weak bonding strength. This results in compromised performance and reduced longevity in coatings, adhesives, and composite materials.
Choosing Between Binder-Only and Binder-Solvent Systems
Binder-solvent systems enhance the dispersion and adhesion properties by combining the cohesive strength of binders with the film-forming capabilities of solvents, improving application smoothness and drying times. Binder-only systems provide stronger structural integrity and are preferable for applications requiring robustness and chemical resistance, avoiding solvent-related issues such as shrinkage or VOC emissions. Selecting between these depends on factors like desired drying time, environmental regulations, substrate compatibility, and final product durability.
Environmental Impact: Binder and Solvent vs Binder
Binder and solvent combinations often result in higher environmental toxicity due to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during application and curing processes. In contrast, binders without solvents typically offer reduced VOC content, minimizing air pollution and improving indoor air quality. Selecting solvent-free binders significantly decreases hazardous waste generation and enhances compliance with environmental regulations.
Applications and Industry Examples
Binders and solvents are essential in coatings and adhesives, with binders providing film formation and adhesion while solvents control viscosity and drying time. In paint manufacturing, the automotive industry uses binders like acrylic or epoxy resins for durability, combined with solvents for application ease and surface finish. Packaging industries rely on water-based binders with minimal solvents to meet environmental regulations, enhancing safety and performance in food packaging adhesives.
Binder and Solvent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com