Indifference can create emotional distance, affecting relationships and personal well-being by fostering a lack of empathy or concern. Recognizing signs of indifference helps you address underlying issues before they deepen and impact your connections. Discover more about overcoming indifference and improving your emotional awareness in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
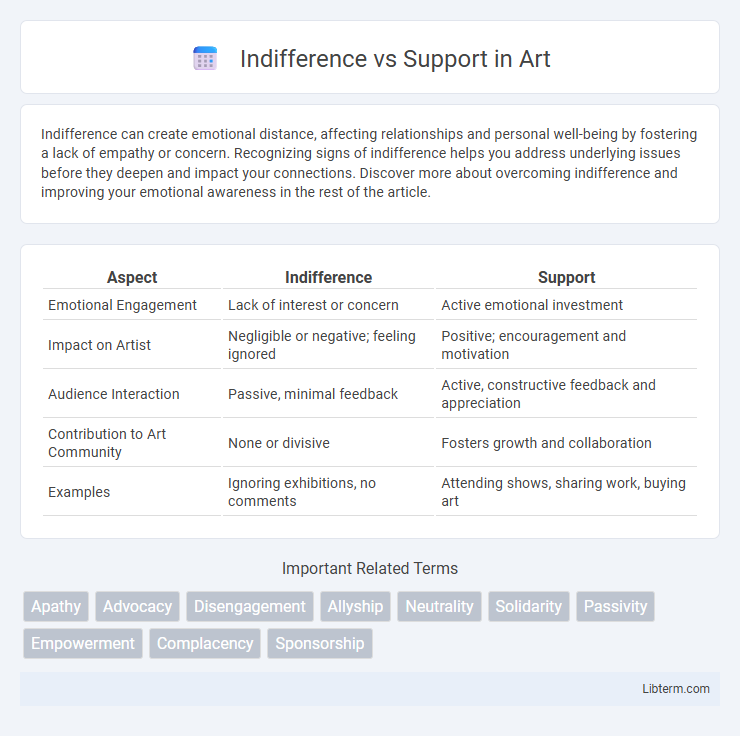
| Aspect | Indifference | Support |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Engagement | Lack of interest or concern | Active emotional investment |
| Impact on Artist | Negligible or negative; feeling ignored | Positive; encouragement and motivation |
| Audience Interaction | Passive, minimal feedback | Active, constructive feedback and appreciation |
| Contribution to Art Community | None or divisive | Fosters growth and collaboration |
| Examples | Ignoring exhibitions, no comments | Attending shows, sharing work, buying art |
Understanding Indifference and Support
Indifference in social contexts refers to a lack of emotional investment or concern, often resulting in neutrality or passivity toward a situation or individual. Support involves active engagement, empathy, and assistance aimed at addressing needs or challenges, fostering positive outcomes and strengthened relationships. Understanding the distinction between indifference and support is crucial for recognizing the impact of emotional responsiveness on social dynamics and personal well-being.
Key Differences Between Indifference and Support
Indifference reflects a lack of interest or concern, where no action or emotional involvement is shown toward a person, cause, or event, whereas support implies active engagement, encouragement, or assistance to promote or uphold something. Indifference results in passivity and detachment, while support leads to proactive behavior and positive reinforcement. The key difference lies in the presence of emotional investment and intentional effort in support versus the absence of these elements in indifference.
Psychological Impact of Indifference
Indifference in social interactions often leads to feelings of isolation, rejection, and decreased self-worth, negatively impacting mental health and emotional well-being. In contrast, support fosters resilience, enhances coping mechanisms, and promotes psychological growth by providing validation, empathy, and encouragement. Studies link sustained indifference from significant others to increased risk of depression and anxiety disorders, highlighting the crucial role of supportive relationships in psychological stability.
Emotional Benefits of Support
Support provides emotional benefits such as increased feelings of security, validation, and belonging, which indifference fails to offer. Emotional support reduces stress, bolsters self-esteem, and fosters resilience during challenging times. In contrast, indifference can lead to feelings of isolation, neglect, and emotional distress.
Causes of Indifference in Relationships
Indifference in relationships often stems from unresolved conflicts, emotional exhaustion, and lack of effective communication, leading partners to disengage emotionally. Causes such as unmet expectations, feelings of neglect, or prolonged stress can erode intimacy and mutual understanding. Addressing these issues early through honest dialogue and empathy is crucial to prevent the shift from support to indifference.
Ways to Foster Genuine Support
Fostering genuine support requires active listening and empathetic engagement to validate others' experiences and emotions. Consistent positive reinforcement and transparent communication build trust, encouraging openness and collaboration in relationships or teams. Creating inclusive environments where diverse perspectives are respected promotes authentic connections and reduces indifference.
Signs You’re Experiencing Indifference
Experiencing indifference often involves a lack of emotional response or engagement, where someone may appear detached during conversations or show little interest in your feelings and accomplishments. Signs include consistent avoidance of meaningful interactions, minimal verbal or nonverbal acknowledgment, and a persistent sense of neglect despite efforts to connect. This emotional disconnect contrasts sharply with support, which is characterized by active listening, encouragement, and genuine concern.
Building a Culture of Support
Building a culture of support requires fostering empathy, active listening, and consistent encouragement within organizations. Indifference undermines trust and productivity, while supportive environments boost collaboration and employee engagement. Implementing structured feedback systems and recognizing contributions can transform indifferent attitudes into proactive support.
Overcoming Indifference in Social Circles
Overcoming indifference in social circles requires fostering genuine empathy and active engagement among group members, which strengthens interpersonal bonds and promotes collective well-being. Encouraging open communication and inclusive activities helps transform passive observers into supportive participants who contribute positively to the group's dynamics. Research shows that social environments emphasizing shared values and mutual respect significantly reduce apathy and increase support networks.
Choosing Support Over Indifference for Growth
Choosing support over indifference fosters personal and professional growth by creating an environment of encouragement, trust, and collaboration. Supportive actions promote resilience, motivation, and positive relationships, which are crucial for overcoming challenges and achieving goals. Indifference, in contrast, breeds disengagement and stagnation, hindering development and progress.
Indifference Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com