Die casting is a high-precision manufacturing process where molten metal is forced into a mold cavity under high pressure, producing complex and durable metal parts with excellent surface finishes. This technique is widely used in the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries due to its ability to create lightweight, strong components with tight tolerances. Discover how die casting can improve your production efficiency and product quality by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
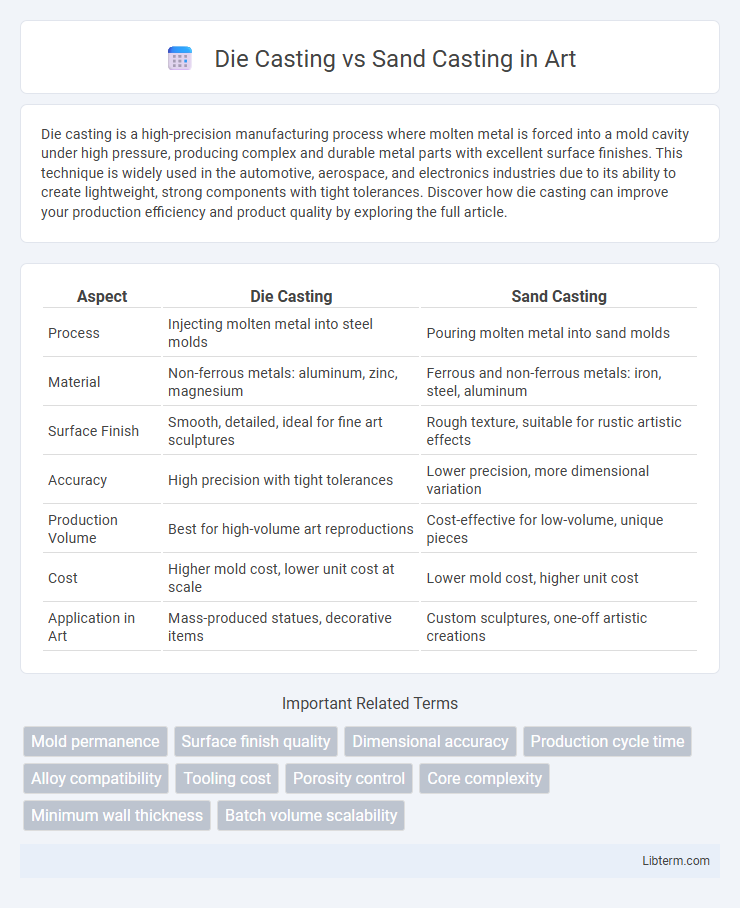
| Aspect | Die Casting | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Injecting molten metal into steel molds | Pouring molten metal into sand molds |
| Material | Non-ferrous metals: aluminum, zinc, magnesium | Ferrous and non-ferrous metals: iron, steel, aluminum |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, detailed, ideal for fine art sculptures | Rough texture, suitable for rustic artistic effects |
| Accuracy | High precision with tight tolerances | Lower precision, more dimensional variation |
| Production Volume | Best for high-volume art reproductions | Cost-effective for low-volume, unique pieces |
| Cost | Higher mold cost, lower unit cost at scale | Lower mold cost, higher unit cost |
| Application in Art | Mass-produced statues, decorative items | Custom sculptures, one-off artistic creations |
Introduction to Die Casting and Sand Casting
Die casting is a high-pressure metal casting process where molten metal is injected into a steel mold or die, resulting in precise, complex, and high-volume production of components often made from non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Sand casting involves creating a mold from compacted sand, allowing for versatility in size and shape, and is commonly used for producing large parts with complex geometries, typically involving ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Both die casting and sand casting differ significantly in mold construction, production speed, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy, impacting their suitability for different manufacturing applications.
Key Differences Between Die Casting and Sand Casting
Die casting uses high-pressure injection of molten metal into steel molds for precise, high-volume production of complex shapes, while sand casting relies on sand molds and gravity pour, suited for lower volumes and larger parts. Die casting offers superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy, whereas sand casting is more cost-effective for small runs and accommodates a broader range of metal alloys. The choice between die casting and sand casting depends on factors like production volume, part complexity, material type, and budget constraints.
Materials Used in Die Casting vs Sand Casting
Die casting primarily uses non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper alloys, which offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent surface finishes. Sand casting accommodates a broader range of metals, including ferrous metals like cast iron and steel, due to its ability to withstand higher melting temperatures. Material selection in die casting favors lightweight, corrosion-resistant alloys for precision parts, whereas sand casting supports more diverse and heat-resistant materials for larger, complex components.
Process Overview: Die Casting Explained
Die casting is a high-pressure metal casting process where molten metal is injected into a steel mold, or die, enabling rapid production of complex, precise components with smooth surfaces. Unlike sand casting, which uses expendable sand molds and involves slower cooling and rougher finishes, die casting ensures high dimensional accuracy and superior repeatability. Common metals used in die casting include aluminum, zinc, and magnesium, making it ideal for automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics manufacturing.
Process Overview: Sand Casting Explained
Sand casting involves creating a mold by compacting sand around a pattern, which is then removed to form a cavity for molten metal. This process offers high versatility in producing complex shapes and is cost-effective for low-volume production. The key steps include mold preparation, metal pouring, cooling, and mold breaking to retrieve the cast part.
Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy Comparison
Die casting produces a smoother surface finish with finer details due to high-pressure metal injection into precision-machined molds, resulting in minimal post-processing requirements. Sand casting often yields rougher surfaces with visible grain patterns from the sand mold, necessitating additional machining or grinding for improved finish. Dimensional accuracy in die casting is typically superior, with tolerances as tight as +-0.005 inches, whereas sand casting tolerances vary widely, often around +-0.01 to +-0.02 inches, making die casting more suitable for intricate, high-precision components.
Cost Considerations and Production Volume
Die casting offers lower per-unit costs in high-volume production due to reusable molds and faster cycle times, making it ideal for mass manufacturing. Sand casting incurs higher initial costs and longer lead times but remains cost-effective for low to medium production volumes or larger, complex parts. Choosing between die casting and sand casting depends on balancing upfront tooling expenses against desired production volume and part complexity.
Advantages of Die Casting
Die casting offers superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish compared to sand casting, resulting in reduced need for machining and lower post-processing costs. It enables high-volume production with consistent quality, making it ideal for complex and intricate components with thin walls. The reuse of metal in die casting minimizes material wastage, enhancing overall manufacturing efficiency.
Advantages of Sand Casting
Sand casting offers significant advantages including the ability to produce large and complex metal parts with intricate geometries and hollow sections. It provides cost-effective and flexible production for low to medium volumes due to reusable sand molds and minimal tooling expenses. The process supports a wide variety of metals and alloys, making it versatile for diverse industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Casting Method for Your Project
Die casting offers high precision and excellent surface finish, ideal for mass production of complex metal parts with tight tolerances. Sand casting provides greater flexibility for large or intricate designs and lower tooling costs, making it suitable for prototypes and small production runs. Selecting the right casting method depends on factors such as production volume, part complexity, desired surface quality, and budget constraints.
Die Casting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com