Abstract art transforms shapes, colors, and forms into expressive compositions that evoke emotions beyond realistic representation. This style encourages viewers to interpret meaning based on personal perception, making every experience unique and deeply engaging. Explore the rest of the article to discover how abstract art can inspire your creativity and broaden your artistic appreciation.
Table of Comparison
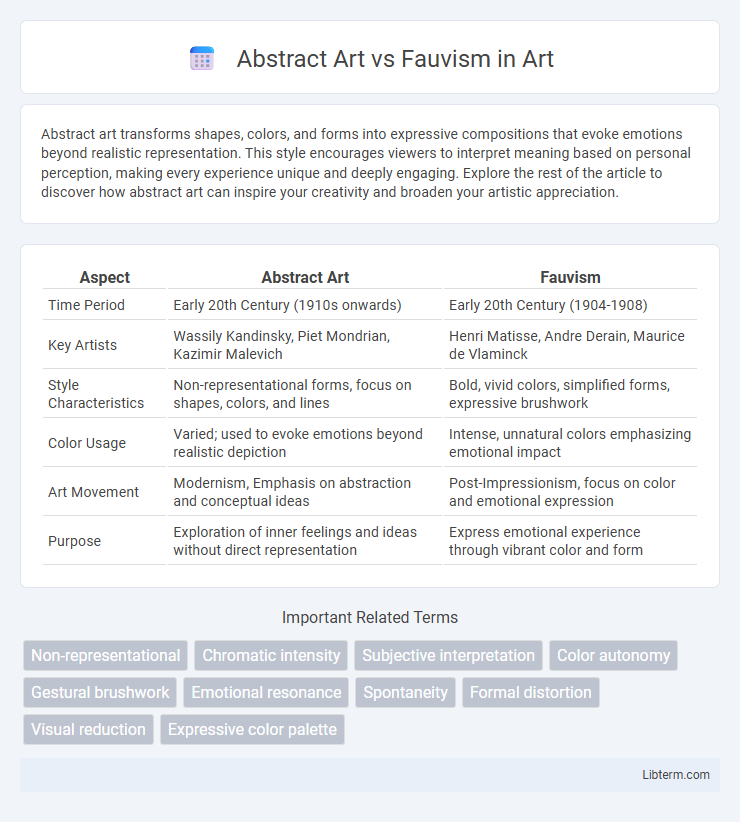
| Aspect | Abstract Art | Fauvism |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | Early 20th Century (1910s onwards) | Early 20th Century (1904-1908) |
| Key Artists | Wassily Kandinsky, Piet Mondrian, Kazimir Malevich | Henri Matisse, Andre Derain, Maurice de Vlaminck |
| Style Characteristics | Non-representational forms, focus on shapes, colors, and lines | Bold, vivid colors, simplified forms, expressive brushwork |
| Color Usage | Varied; used to evoke emotions beyond realistic depiction | Intense, unnatural colors emphasizing emotional impact |
| Art Movement | Modernism, Emphasis on abstraction and conceptual ideas | Post-Impressionism, focus on color and emotional expression |
| Purpose | Exploration of inner feelings and ideas without direct representation | Express emotional experience through vibrant color and form |
Understanding Abstract Art: An Overview
Abstract art emphasizes non-representational forms, utilizing shapes, colors, and textures to evoke emotions and ideas without depicting recognizable objects. It prioritizes conceptual expression over realistic portrayal, often exploring the relationship between form and color to convey meaning. Fauvism, by contrast, uses vivid, non-naturalistic colors and bold brushstrokes but maintains discernible subjects, making abstract art more about pure abstraction than Fauvism's expressive realism.
Delving into Fauvism: Key Characteristics
Fauvism is characterized by vibrant, non-naturalistic colors and bold brushwork that emphasize emotional expression over realistic representation. This early 20th-century movement, pioneered by artists like Henri Matisse and Andre Derain, prioritizes simplified forms and strong contrasts to evoke intensity and spontaneity. In contrast to abstract art's focus on non-representational shapes, Fauvism maintains a connection to recognizable subjects while transforming their visual impact through vivid palette and dynamic compositions.
Historical Origins: Abstract Art and Fauvism
Abstract Art emerged in the early 20th century, with pioneers like Wassily Kandinsky and Kazimir Malevich pushing boundaries beyond representational forms to explore shapes, colors, and emotions independently. Fauvism, originating around 1904-1908 under leaders such as Henri Matisse and Andre Derain, emphasized vivid, non-naturalistic colors and bold brushwork inspired by Post-Impressionism. Both movements marked revolutionary departures from traditional art, with Fauvism laying groundwork through color expression that influenced later Abstract Art's complete abstraction from reality.
Influential Artists in Abstract Art
Abstract art, characterized by non-representational forms and emphasis on color and shape, has been shaped by influential artists like Wassily Kandinsky, often regarded as the pioneer of abstract expressionism, and Piet Mondrian, known for his geometric compositions. Unlike Fauvism, which emphasized bold, vibrant colors and was led by artists such as Henri Matisse and Andre Derain, abstract art focuses more on conveying emotions through abstract forms rather than vivid color contrasts. The legacy of abstract art continues with artists like Jackson Pollock, whose drip paintings redefined the movement's expressive potential.
Leading Figures of the Fauvist Movement
Leading figures of the Fauvist movement include Henri Matisse and Andre Derain, who revolutionized early 20th-century art with bold, vivid colors and simplified forms that emphasized emotional expression over realistic representation. Unlike abstract art, which often discards recognizable subjects entirely, Fauvism retained figurative elements while enhancing color to evoke mood and atmosphere. These pioneers influenced modern art's trajectory by challenging traditional techniques and prioritizing artistic freedom and subjective experience.
Techniques and Aesthetics: A Comparative Analysis
Abstract Art employs non-representational forms, emphasizing color, shape, and texture to evoke emotions without depicting real objects, often using techniques like gestural brushstrokes and layering. Fauvism is characterized by bold, vivid colors applied in flat, expressive brushwork, prioritizing painterly qualities and strong contrasts to convey emotional intensity. While Abstract Art focuses on conceptual expression and visual abstraction, Fauvism retains recognizable subjects enhanced through exaggerated colors and dynamic composition.
Color Usage: Abstract Art vs Fauvism
Abstract Art employs color to evoke emotions and concepts beyond natural representation, often using bold, non-representational palettes to challenge perception. Fauvism is characterized by its vibrant, unblended, and expressive colors applied directly from the tube, emphasizing painterly qualities and strong contrasts. Both styles prioritize color as a primary element but differ in intent: Abstract Art explores color's symbolic and emotive potential, while Fauvism highlights color's intensity and raw expressiveness.
Emotional Impact and Interpretation
Abstract Art emphasizes emotional impact through non-representational forms and color, inviting viewers to interpret emotions personally without concrete imagery. Fauvism uses vibrant, unnatural colors and bold brushstrokes to evoke raw, immediate feelings, often rooted in recognizable subjects but distorted for expressive effect. Both movements prioritize emotional expression, yet Abstract Art relies on subjective interpretation of shapes and colors, while Fauvism channels intense emotions through exaggerated, figurative elements.
Influence on Modern Art Movements
Abstract Art revolutionized Modern Art by emphasizing non-representational forms and emotional expression, paving the way for movements like Abstract Expressionism and Minimalism. Fauvism's vibrant color palettes and bold brushwork significantly influenced Post-Impressionism and early Expressionism, inspiring artists to explore color as a means of emotional communication. Both movements challenged traditional approaches, shaping the trajectory of 20th-century art through innovation in form and color.
Legacy and Significance in Contemporary Art
Abstract Art revolutionized contemporary art by emphasizing non-representational forms, influencing movements such as Minimalism and Abstract Expressionism with its exploration of color, shape, and emotion. Fauvism's legacy persists through its bold use of vibrant colors and simplified forms, impacting modern design and contemporary painters who prioritize expressive, vivid palettes. Both movements contributed foundational principles that continue to shape artistic innovation and visual culture in the 21st century.
Abstract Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com