A high-quality knife is essential for precision, safety, and efficiency in the kitchen, offering reliable cutting performance for various tasks. Choosing the right blade material and handle design can significantly impact your cooking experience and durability of the tool. Discover the key factors to consider when selecting your perfect knife in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
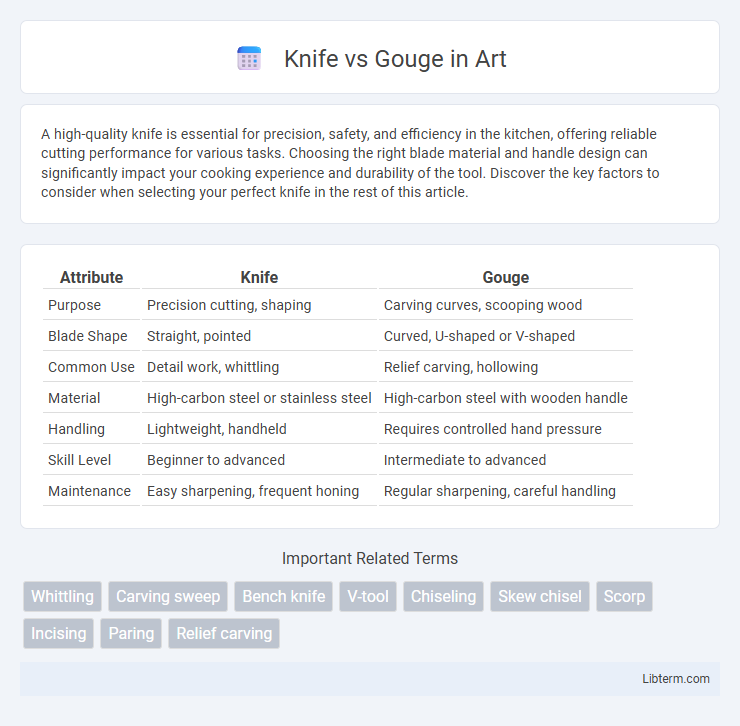
| Attribute | Knife | Gouge |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Precision cutting, shaping | Carving curves, scooping wood |
| Blade Shape | Straight, pointed | Curved, U-shaped or V-shaped |
| Common Use | Detail work, whittling | Relief carving, hollowing |
| Material | High-carbon steel or stainless steel | High-carbon steel with wooden handle |
| Handling | Lightweight, handheld | Requires controlled hand pressure |
| Skill Level | Beginner to advanced | Intermediate to advanced |
| Maintenance | Easy sharpening, frequent honing | Regular sharpening, careful handling |
Introduction: Understanding Knives and Gouges
Knives and gouges are essential carving tools distinguished by their blade shapes and purposes, with knives featuring straight or slightly curved edges for precision cutting and gouges having curved, scooped blades designed for removing material efficiently. Knives excel in detailing and fine cuts, while gouges are ideal for shaping and hollowing wood or other materials. Understanding the differences in blade geometry and applications helps artisans select the right tool for specific carving tasks.
Definition and Structure: Knife vs Gouge
A knife features a straight, sharp blade designed for precise cutting, carving, and slicing tasks, commonly used in woodworking and culinary applications. In contrast, a gouge has a curved, U-shaped or V-shaped blade that facilitates scooping or hollowing out material, ideal for detailed carving and shaping in wood or stone. The structure of a knife emphasizes a single sharp edge for slicing, while a gouge's curved edge allows it to remove material efficiently with controlled depth and contouring.
Primary Functions and Applications
Knives excel at precise cutting, slicing, and shaping materials like wood, leather, and food, making them ideal for detailed carving and general-purpose tasks. Gouges, characterized by their curved blades, are designed primarily for scooping, hollowing, and creating rounded grooves in wood or soft materials, widely used in woodworking and sculpture. Their distinct blade shapes dictate their specialized applications in crafting, with knives offering versatility in flat cuts and gouges enabling contour and relief work.
Blade Shape and Cutting Edge Comparison
Knife blades typically feature a straight or slightly curved edge designed for precise slicing, offering versatility across various materials. Gouges possess a U-shaped or V-shaped curved blade creating concave cuts, ideal for scooping or carving wood and softer substances. The cutting edge of a knife is generally sharper and finer for detailed work, whereas a gouge's edge is thicker and more robust to handle deeper, controlled carving motions.
Material and Construction Differences
Knives typically feature a single, straight-edged blade made from high-carbon or stainless steel, designed for precision cutting and versatility in various tasks. Gouges have curved, chisel-like blades often crafted from hardened tool steel, optimized for carving and scooping wood or other materials. The construction of gouges includes a beveled edge that allows for controlled material removal, contrasting with the flat, sharp edge of knives suited for slicing.
Handling Techniques and Safety
Knife handling techniques emphasize a controlled grip with the thumb and fingers to achieve precise cuts, often requiring a pulling motion toward the body for better control. Gouge tools demand a stable hold with both hands, pushing or scooping actions, and careful attention to blade angle to prevent slips. Safety measures for both tools include using sharp blades to reduce force needed, wearing protective gloves, and always carving away from the body to minimize injury risk.
Performance in Woodworking and Carving
Knives offer precision and control for detailed woodworking and carving tasks, excelling in fine cuts and intricate shaping. Gouges provide superior efficiency in removing larger amounts of wood, thanks to their curved blades that facilitate smoother scooping motions. Both tools complement each other in performance, with knives favored for delicate work and gouges preferred for rapid material removal and shaping.
Pros and Cons of Knives and Gouges
Knives provide precision and control for fine detailing and smooth cuts, making them ideal for intricate carving or whittling projects; however, they may struggle with removing large amounts of material or working on very hard wood. Gouges offer efficient wood removal due to their curved blades, allowing for deep cuts and shaping concave surfaces, but they can be harder to control for detailed work and require more skill to avoid gouging too deeply. Choosing between knives and gouges depends on the desired woodworking task, balancing the need for precision against the need for material removal and contour shaping.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate tool between a knife and a gouge depends on the project's detail and material type. Knives excel in precision carving and fine detailing, ideal for softwoods and delicate cuts, while gouges, with their curved blades, are better suited for scooping out wood and creating rounded, textured surfaces in hardwoods. Evaluating the desired depth and shape of the cut ensures optimal carving results and tool efficiency.
Maintenance, Sharpening, and Longevity
Knives require regular honing and occasional sharpening with fine-grit stones to maintain a razor-sharp edge, making them ideal for precision cutting and longevity when properly cared for. Gouges need specialized curved sharpening tools such as slip stones or diamond files to preserve their concave edges, crucial for detailed carving and preventing blade damage over time. Proper maintenance, including drying thoroughly and applying protective oils, significantly extends the lifespan of both tools, ensuring consistent performance in woodworking tasks.
Knife Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com