Emphasizing key points in your writing enhances clarity and retention, making your message more impactful. Techniques such as repetition, varied sentence structure, and strategic word choice help highlight important information effectively. Explore the rest of the article to master these emphasizing strategies and improve your communication skills.
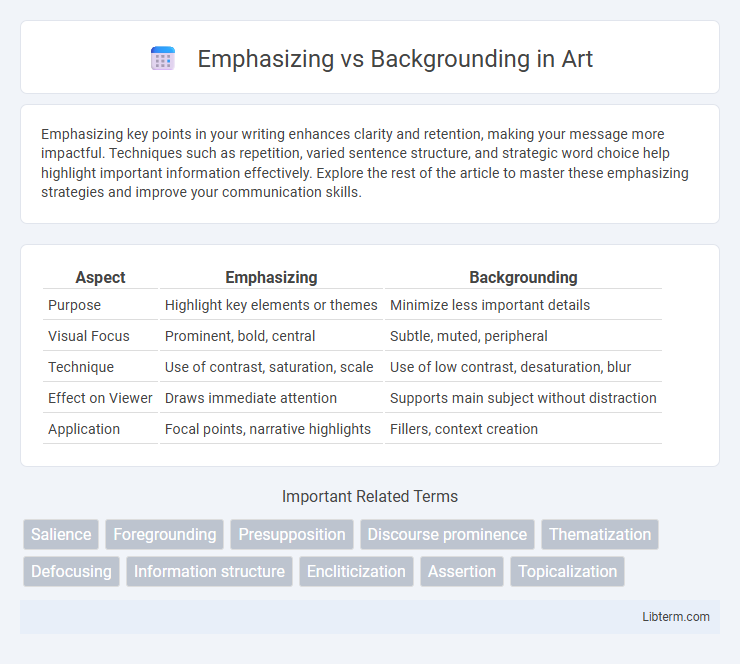
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Emphasizing | Backgrounding |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Highlight key elements or themes | Minimize less important details |
| Visual Focus | Prominent, bold, central | Subtle, muted, peripheral |
| Technique | Use of contrast, saturation, scale | Use of low contrast, desaturation, blur |
| Effect on Viewer | Draws immediate attention | Supports main subject without distraction |
| Application | Focal points, narrative highlights | Fillers, context creation |
Understanding Emphasizing and Backgrounding
Emphasizing involves highlighting key information to draw the reader's attention to the most critical aspects, often using techniques such as fronting, cleft sentences, or inversion for increased prominence. Backgrounding, in contrast, places lesser emphasis on certain details by positioning them later in the sentence or using passive constructions, thereby guiding the reader to prioritize other information. Mastering these discourse strategies enhances text clarity and effectiveness by strategically managing the salience of information within communication.
Key Differences Between Emphasizing and Backgrounding
Emphasizing highlights essential information by making it more prominent through repetition, increased volume, or altered tone, aiming to draw the listener's or reader's immediate attention. Backgrounding involves downplaying less critical details by using softer tones, less frequent mention, or less prominent placement to ensure the main message remains clear. The key difference lies in their purpose: emphasizing seeks to foreground important content, while backgrounding relegates secondary information to the periphery.
The Role of Emphasizing in Communication
Emphasizing in communication highlights key information to ensure message clarity and audience retention, often using vocal stress, repetition, or visual cues. It directs the listener's or reader's attention to the most critical points, enhancing understanding and persuasive impact. This technique is essential in speeches, marketing, and writing where prioritizing information affects engagement and comprehension.
How Backgrounding Shapes Perception
Backgrounding subtly alters perception by minimizing the prominence of certain elements, guiding the audience's attention toward more salient information. This cognitive framing shapes the interpretation and emotional impact of a message by relegating less critical details to the periphery. Neuroscientific studies reveal that backgrounding influences neural pathways associated with attention and memory retention, thereby reinforcing specific viewpoints while downplaying alternative perspectives.
Techniques for Effective Emphasizing
Techniques for effective emphasizing include using strong, vivid language and varying sentence structure to highlight key points. Incorporating repetition and strategic positioning of important information at the beginning or end of sentences enhances emphasis. Visual aids, such as bold text or bullet points, also serve to foreground essential concepts, making them more memorable and impactful.
Strategies for Subtle Backgrounding
Subtle backgrounding techniques involve minimizing the prominence of less critical information through linguistic choices such as passive voice, reduced clause complexity, or placing details in subordinate clauses to guide reader focus. Employing backgrounding strategies enhances textual coherence by maintaining emphasis on primary concepts while providing context without distraction. Mastery of these methods allows writers to control narrative flow effectively, ensuring key messages receive priority in communication.
Emphasizing vs Backgrounding in Visual Design
Emphasizing in visual design involves using contrast, color, size, and placement to draw the viewer's attention to key elements, ensuring they stand out prominently. Backgrounding minimizes the visual importance of other elements through subtle colors, smaller sizes, and less contrast, creating a clear hierarchy within the composition. This strategic balance enhances user experience by guiding focus and improving comprehension of the most critical information.
The Psychological Impact of Highlighting vs Backgrounding
Emphasizing information activates the brain's attentional networks, enhancing memory retention and emotional response by making key details more salient. Backgrounding, by contrast, relegates information to peripheral awareness, reducing cognitive load but potentially diminishing recall and perceived importance. This psychological balance affects decision-making, as highlighted elements are more likely to influence judgments and behavior compared to backgrounded content.
Common Mistakes in Emphasizing and Backgrounding
Common mistakes in emphasizing include overusing bold or italics, which can dilute the intended impact and confuse readers about key points. Backgrounding errors often arise from burying crucial information in lengthy paragraphs or using vague language that makes important details less noticeable. Effective communication balances emphasis with clear, concise presentation to guide readers' attention accurately.
Best Practices for Balancing Emphasis and Background
Balancing emphasis and background in writing requires strategically highlighting key information while ensuring supporting details provide necessary context without overshadowing the main points. Use clear signal words and sentence structure to differentiate between emphasized concepts and background material, maintaining reader engagement and clarity. Apply the principle of information hierarchy by placing critical ideas in prominent positions within sentences and paragraphs for maximum impact.
Emphasizing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com