Resampling techniques enhance data analysis by allowing you to estimate the accuracy of sample statistics through repeated sampling from a dataset. Methods like bootstrapping and cross-validation help improve model reliability and reduce bias in predictions. Explore the article to discover how resampling can optimize your data-driven decisions.
Table of Comparison
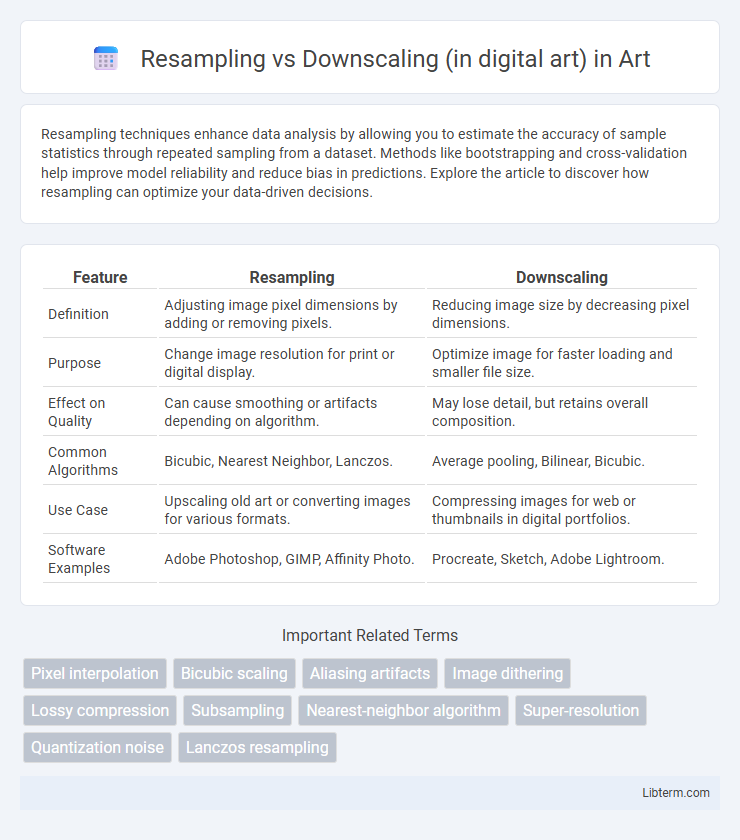
| Feature | Resampling | Downscaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusting image pixel dimensions by adding or removing pixels. | Reducing image size by decreasing pixel dimensions. |
| Purpose | Change image resolution for print or digital display. | Optimize image for faster loading and smaller file size. |
| Effect on Quality | Can cause smoothing or artifacts depending on algorithm. | May lose detail, but retains overall composition. |
| Common Algorithms | Bicubic, Nearest Neighbor, Lanczos. | Average pooling, Bilinear, Bicubic. |
| Use Case | Upscaling old art or converting images for various formats. | Compressing images for web or thumbnails in digital portfolios. |
| Software Examples | Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, Affinity Photo. | Procreate, Sketch, Adobe Lightroom. |
Understanding Resampling and Downscaling in Digital Art
Resampling in digital art involves changing the pixel dimensions of an image, either increasing or decreasing pixel count, which directly impacts image resolution and quality. Downscaling specifically refers to reducing the pixel dimensions, leading to a smaller file size and often smoother image appearance but with potential loss of fine detail. Understanding the difference between resampling and downscaling helps artists maintain control over image sharpness, clarity, and performance optimization in digital workflows.
Key Differences Between Resampling and Downscaling
Resampling changes the total number of pixels in an image, either increasing or decreasing resolution by adding or removing pixel data, which affects image quality and file size. Downscaling specifically reduces the image dimensions and pixel count, typically improving sharpness and reducing file size, but potentially losing detail. The key difference lies in resampling's flexibility to both enlarge and shrink images, while downscaling exclusively decreases image size to optimize performance or fit specific display requirements.
When to Choose Resampling Over Downscaling
Choose resampling over downscaling when you need to change image dimensions while preserving detail and quality, such as preparing artwork for different output sizes or digital platforms. Resampling algorithms, like bicubic or Lanczos, add or remove pixels through interpolation, maintaining sharpness and reducing artifacts. Downscaling simply reduces resolution by discarding pixels, best suited for reducing file size without altering image quality requirements.
Effects on Image Quality: Resampling vs Downscaling
Resampling in digital art alters the pixel count of an image, often introducing interpolation artifacts that can blur fine details or create unnatural edges, impacting image quality negatively. Downscaling reduces image dimensions by removing pixels, which typically enhances sharpness and reduces noise, preserving essential details but potentially causing loss of fine textures. Understanding the effects on image quality enables artists to choose between resampling for resizing flexibility and downscaling for maintaining clarity in smaller images.
Common Tools for Resampling and Downscaling Digital Images
Common tools for resampling and downscaling digital images include Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, and Affinity Photo, each offering specialized algorithms like bicubic, nearest neighbor, and Lanczos for resizing. Photoshop's Preserve Details 2.0 and GIMP's Sinc (Lanczos3) method ensure high-quality resampling by maintaining sharpness and minimizing artifacts. Downscaling benefits from these tools' ability to reduce image dimensions while preserving important visual information, crucial for web optimization and print quality.
Resolution, Size, and Detail: Impacts of Each Method
Resampling alters an image's resolution by adding or removing pixels, which can affect both the size and detail, often leading to either pixelation or smoothing depending on the method used. Downscaling specifically reduces the image size by decreasing pixel dimensions, which typically enhances perceived sharpness and detail by concentrating existing information but sacrifices finer details. In digital art, understanding the trade-offs in resolution, size, and detail preservation is crucial for choosing between resampling and downscaling to achieve optimal visual quality and file efficiency.
Workflow Integration: Best Practices for Digital Artists
Resampling in digital art involves altering the pixel count of an image, either upscaling or downscaling, while downscaling specifically reduces the image size, preserving essential details and improving file efficiency. For workflow integration, artists should maintain original high-resolution files and apply non-destructive resampling techniques to ensure quality retention during editing and export stages. Utilizing software with advanced interpolation algorithms helps achieve smoother results, optimizing image clarity and consistency across various platforms and devices.
File Size Management: Resampling vs Downscaling
Resampling in digital art alters the pixel count, either increasing or decreasing resolution, directly impacting file size by adding or removing data points. Downscaling reduces image dimensions while preserving pixel integrity, leading to smaller file sizes primarily through dimension reduction without pixel interpolation. Efficient file size management requires understanding resampling as a modification of pixel data, whereas downscaling optimally trims image size to maintain quality with less storage demand.
Preserving Artwork Integrity During Size Adjustments
Resampling changes the pixel count of digital artwork, which can impact image clarity and detail, whereas downscaling reduces dimensions by decreasing pixel information while attempting to maintain sharpness. Preserving artwork integrity during size adjustments requires using algorithms like bicubic or Lanczos that minimize distortion and prevent loss of fine details. Maintaining color accuracy and edge definition ensures the resized digital art remains true to the original composition and quality.
Frequently Asked Questions About Image Rescaling Techniques
Resampling in digital art involves changing an image's pixel count, adding or removing pixels to either increase or decrease resolution, which impacts image clarity and file size. Downscaling specifically refers to reducing the pixel dimensions of an image, often improving performance and compatibility on various devices but potentially losing fine detail. Common FAQs include inquiries about the best algorithms for preserving quality during resampling, how downscaling affects image sharpness, and the differences between nearest neighbor, bilinear, and bicubic methods in practical art applications.
Resampling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com