Bauhaus revolutionized modern design by merging art, craft, and technology into functional simplicity that remains influential today. Its principles emphasize clean lines, minimalism, and the unity of form and function, shaping everything from architecture to graphic design. Discover how Bauhaus principles can inspire and transform your creative projects in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
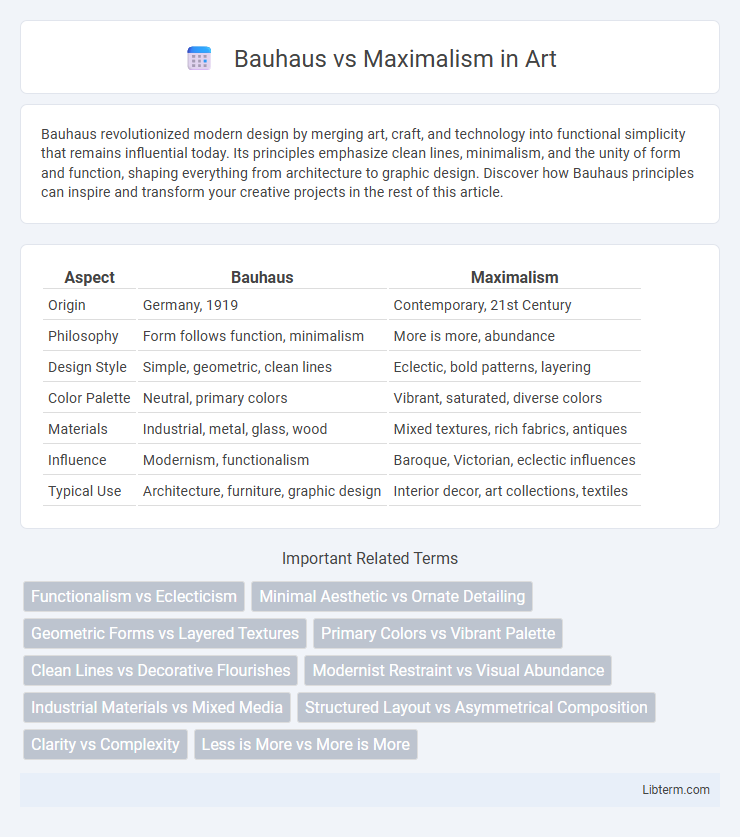
| Aspect | Bauhaus | Maximalism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Germany, 1919 | Contemporary, 21st Century |
| Philosophy | Form follows function, minimalism | More is more, abundance |
| Design Style | Simple, geometric, clean lines | Eclectic, bold patterns, layering |
| Color Palette | Neutral, primary colors | Vibrant, saturated, diverse colors |
| Materials | Industrial, metal, glass, wood | Mixed textures, rich fabrics, antiques |
| Influence | Modernism, functionalism | Baroque, Victorian, eclectic influences |
| Typical Use | Architecture, furniture, graphic design | Interior decor, art collections, textiles |
Introduction to Bauhaus and Maximalism
Bauhaus, founded in 1919 by Walter Gropius in Germany, emphasizes simplicity, functionality, and the integration of art, craft, and technology, promoting minimalism and clean geometric forms. Maximalism, by contrast, embraces bold colors, intricate patterns, and eclectic decor to create visually rich, layered interiors that celebrate abundance and individuality. Both movements reflect distinct philosophies of design that influence contemporary aesthetics and spatial experiences.
Core Principles of Bauhaus Design
Bauhaus design emphasizes simplicity, functionality, and the integration of art, craft, and technology, prioritizing clean lines, minimal ornamentation, and efficient use of materials. The core principles include geometric shapes, primary colors, and an emphasis on practicality to create timeless, utilitarian designs. In contrast to maximalism, Bauhaus avoids excess detail and decoration, focusing instead on form following function and the harmony between aesthetics and purpose.
Defining Features of Maximalism
Maximalism is characterized by bold colors, eclectic patterns, and an abundance of decorative elements that create vibrant, layered spaces. Unlike Bauhaus' minimalist and functional approach, Maximalism embraces complexity and visual richness, combining various textures and cultural influences to evoke personality and warmth. This design style often features ornate furnishings, dynamic art pieces, and a mix of vintage and contemporary decor to express individuality and creative freedom.
Historical Origins and Influences
Bauhaus originated in Germany in 1919 as a revolutionary school combining crafts and fine arts, emphasizing functional design, simplicity, and mass production influenced by industrialization and modernism. Maximalism emerged as a reaction against minimalism, drawing from Baroque, Victorian, and Art Deco styles with an emphasis on eclectic, bold patterns, vibrant colors, and ornamental detail. The historical context of Bauhaus is rooted in early 20th-century efficiency and rationalism, while Maximalism embraces a more theatrical and expressive approach inspired by diverse cultural and artistic movements.
Color and Material Choices
Bauhaus design emphasizes primary colors and neutral tones, using materials like steel, glass, and wood to create functional and minimalist aesthetics. Maximalism embraces a vibrant, eclectic color palette with rich textures and diverse materials such as velvet, brass, and patterned fabrics to evoke boldness and complexity. The contrast lies in Bauhaus's restrained, industrial approach versus Maximalism's layered, decorative richness in both color and material selection.
Form, Function, and Aesthetics
Bauhaus emphasizes simplicity, functionality, and geometric forms, prioritizing clean lines and minimal ornamentation to enhance usability and efficient design. Maximalism, in contrast, embraces bold shapes, rich textures, and vibrant colors, focusing on visual complexity and personal expression to create dynamic, layered spaces. While Bauhaus merges form and function seamlessly with restrained aesthetics, Maximalism celebrates eclecticism, where form often serves decorative and emotional impact as much as practical use.
Furniture and Decor Elements
Bauhaus furniture emphasizes functionality, clean lines, and minimal ornamentation, featuring materials like steel, glass, and wood to create sleek, geometric designs that prioritize practicality and simplicity. Maximalism in furniture and decor embraces bold colors, diverse textures, and intricate patterns, combining vintage and modern pieces to craft visually rich and eclectic environments. The contrasting use of space in Bauhaus advocates for minimal clutter and open areas, whereas Maximalism fills spaces with layered accessories and statement furnishings to create dynamic, vibrant interiors.
Modern Interpretations and Trends
Bauhaus emphasizes minimalist design, clean lines, and functional aesthetics, influencing modern interiors with a focus on simplicity and industrial materials like steel and glass. Maximalism embraces bold colors, eclectic patterns, and layered textures, reflecting a trend towards personalized and vibrant spaces that challenge traditional design norms. Contemporary design trends blend Bauhaus minimalism with maximalist accents to create balanced environments that are both practical and visually dynamic.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Style
Bauhaus design emphasizes simplicity, functionality, and clean lines, offering advantages such as timeless aesthetics, efficient use of space, and minimal maintenance. However, its minimalist approach may be seen as cold or restrictive by some, limiting personal expression and warmth in interiors. Maximalism embraces bold colors, diverse textures, and eclectic decor, creating vibrant, personalized spaces that stimulate creativity, but can lead to visual clutter and require careful balance to avoid overwhelming the environment.
Choosing Between Bauhaus and Maximalism
Choosing between Bauhaus and Maximalism depends on your design goals and personal style preferences. Bauhaus emphasizes simplicity, functionality, and minimalism with clean lines and neutral color palettes, perfect for those seeking a modern, uncluttered aesthetic. Maximalism embraces bold colors, eclectic patterns, and layered textures, making it ideal for individuals who prefer expressive, vibrant, and visually rich environments.
Bauhaus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com