Modeling involves creating representations of systems or concepts to analyze and predict behaviors effectively. It plays a crucial role in fields like engineering, finance, and computer science by simplifying complex realities into understandable frameworks. Explore the rest of this article to discover how modeling can enhance Your decision-making and problem-solving skills.
Table of Comparison
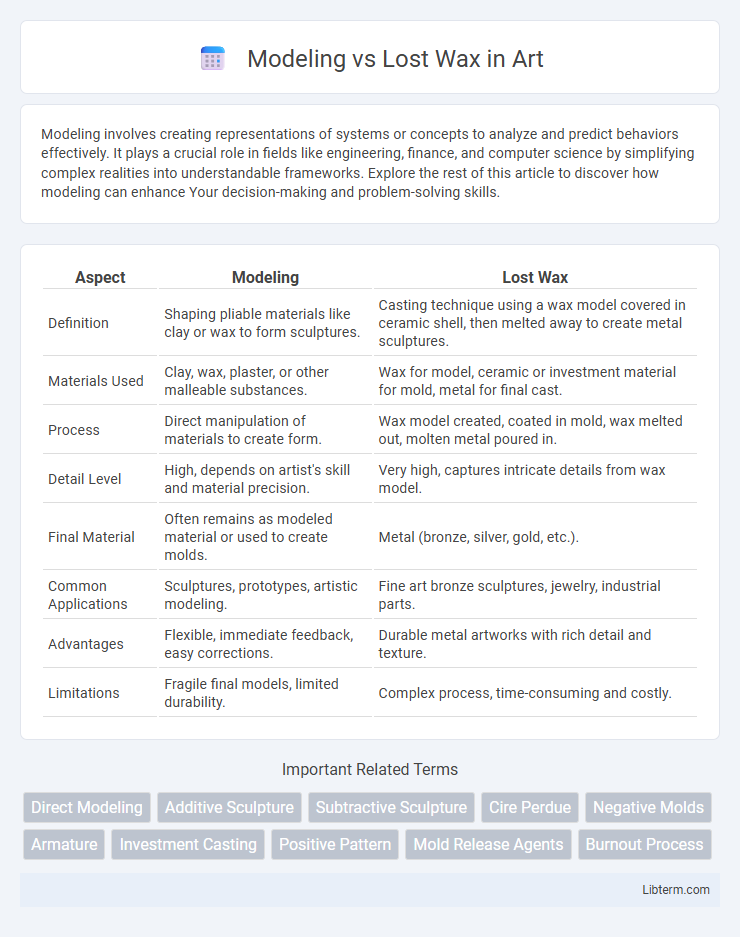
| Aspect | Modeling | Lost Wax |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shaping pliable materials like clay or wax to form sculptures. | Casting technique using a wax model covered in ceramic shell, then melted away to create metal sculptures. |
| Materials Used | Clay, wax, plaster, or other malleable substances. | Wax for model, ceramic or investment material for mold, metal for final cast. |
| Process | Direct manipulation of materials to create form. | Wax model created, coated in mold, wax melted out, molten metal poured in. |
| Detail Level | High, depends on artist's skill and material precision. | Very high, captures intricate details from wax model. |
| Final Material | Often remains as modeled material or used to create molds. | Metal (bronze, silver, gold, etc.). |
| Common Applications | Sculptures, prototypes, artistic modeling. | Fine art bronze sculptures, jewelry, industrial parts. |
| Advantages | Flexible, immediate feedback, easy corrections. | Durable metal artworks with rich detail and texture. |
| Limitations | Fragile final models, limited durability. | Complex process, time-consuming and costly. |
Introduction to Modeling and Lost Wax Techniques
Modeling involves shaping malleable materials such as clay or wax directly to create detailed forms, allowing artists precise control over texture and structure. Lost wax technique is a traditional process where a wax model is encased in a mold material, then melted away to leave a cavity for molten metal casting. The modeling phase is crucial in lost wax casting as it determines the intricacy and accuracy of the final metal sculpture.
Defining Modeling in Art and Craft
Modeling in art and craft refers to the process of shaping pliable materials like clay, wax, or plaster to create three-dimensional forms, emphasizing additive techniques where material is built up. It allows artists to manipulate texture and detail directly with their hands or tools, fostering spontaneous creativity and refinement. Unlike lost wax casting, which involves creating a mold for metal reproduction, modeling remains a primarily hands-on, flexible method for original sculptural creation.
Understanding the Lost Wax Casting Process
Lost wax casting involves creating a detailed wax model that is coated with a refractory ceramic material to form a mold. Once the mold hardens, the wax is melted and drained away, leaving a cavity into which molten metal is poured. This process allows for high precision and intricate designs, making it ideal for jewelry, sculptures, and engineering components compared to traditional modeling methods.
Key Differences Between Modeling and Lost Wax
Modeling involves shaping pliable materials like clay or wax directly to create a form, while lost wax casting uses a wax model to produce a mold for metal casting. The key difference lies in modeling being an additive and subtractive process for final artwork, whereas lost wax serves as an intermediate step where the wax is melted away to leave a cavity for molten metal. Lost wax allows for intricate metal sculptures with fine detail, while modeling is more flexible for exploratory and iterative design.
Historical Evolution of Both Methods
Modeling techniques trace back to prehistoric times, using clay and wax for artistic and functional designs, whereas Lost Wax casting dates to around 6500 BCE, notably in ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt for metal artifacts. Over centuries, modeling evolved with advances in materials and tools, influencing ceramic and sculpture arts, while Lost Wax became refined through metallurgy progress, especially in bronze and gold works. Both methods have shaped craftsmanship, with Lost Wax facilitating intricate metal designs and modeling enabling diverse forms in various substances.
Materials Used in Modeling vs Lost Wax
Modeling typically utilizes pliable materials such as clay, wax, or plasticine, allowing easy manipulation and shaping by hand or tools. Lost wax casting relies on a specific type of wax specifically designed to burn out cleanly, leaving a precise mold to be filled with metals like bronze or gold. In contrast to modeling's versatile bases, lost wax focuses on wax materials that ensure accuracy and fine detail during the casting process.
Applications in Jewelry and Sculpture
Modeling allows artists to shape malleable materials like clay or wax directly for creating detailed jewelry prototypes and sculptural forms with high precision. Lost wax casting transforms these models into durable metals such as gold, silver, or bronze, enabling the production of intricate jewelry pieces and fine art sculptures with complex designs. Both techniques are essential in the jewelry and sculpture industries for achieving detailed artistry and durable final products.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Technique
Modeling offers precise control over shape and texture, allowing artists to make real-time adjustments, but it can be time-consuming and requires skill in manipulating materials like clay or wax. Lost wax casting produces highly detailed, durable metal pieces with complex geometries, ideal for jewelry and sculpture, yet the process involves multiple steps, including investment and melting, which can increase production time and cost. While modeling excels in flexibility and direct creativity, lost wax casting is preferred for mass production of intricate metal artworks with consistent quality.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Choosing between modeling and lost wax techniques depends on project complexity and desired detail. Modeling suits flexible, iterative designs with direct manipulation of materials, while lost wax excels in creating intricate, precise metal castings with fine details. Evaluating factors like material type, production volume, and finish quality ensures selection of the optimal fabrication method.
Future Trends in Modeling and Lost Wax Practices
Future trends in modeling and lost wax practices emphasize the integration of digital technologies such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) to enhance precision and efficiency. Advancements in materials science enable the use of eco-friendly and high-performance waxes, improving sustainability and product quality. The adoption of automation and AI-driven processes is set to revolutionize traditional lost wax techniques, reducing manual labor and accelerating production cycles in jewelry and industrial casting sectors.
Modeling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com