Glazing enhances both the aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency of your windows by creating a protective barrier against heat loss and noise. Modern glazing technologies, such as double or triple glazing, improve insulation while reducing condensation and UV damage to interiors. Discover how different glazing options can transform your space and save you money in the full article.
Table of Comparison
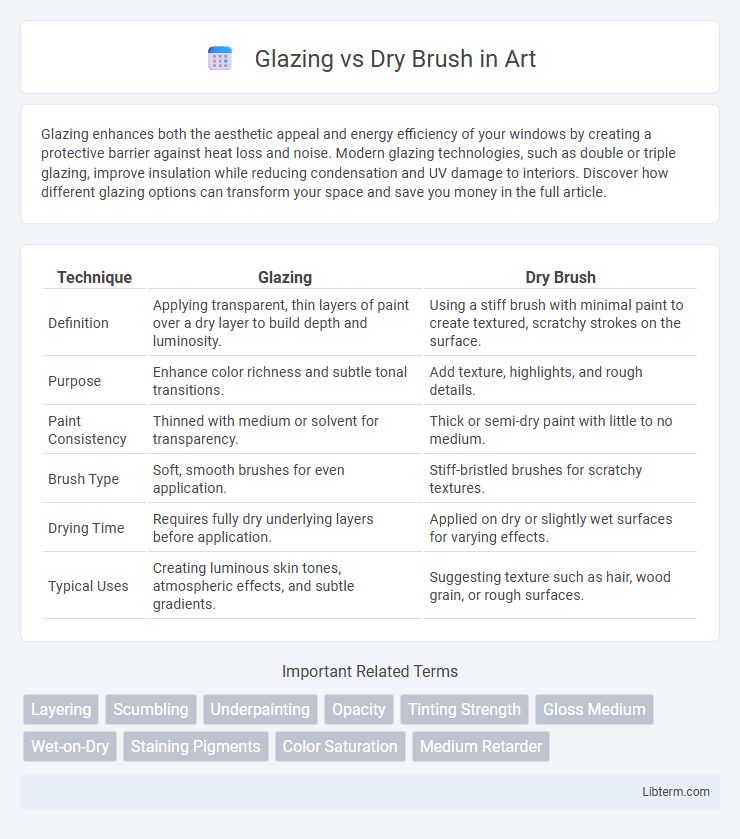
| Technique | Glazing | Dry Brush |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying transparent, thin layers of paint over a dry layer to build depth and luminosity. | Using a stiff brush with minimal paint to create textured, scratchy strokes on the surface. |
| Purpose | Enhance color richness and subtle tonal transitions. | Add texture, highlights, and rough details. |
| Paint Consistency | Thinned with medium or solvent for transparency. | Thick or semi-dry paint with little to no medium. |
| Brush Type | Soft, smooth brushes for even application. | Stiff-bristled brushes for scratchy textures. |
| Drying Time | Requires fully dry underlying layers before application. | Applied on dry or slightly wet surfaces for varying effects. |
| Typical Uses | Creating luminous skin tones, atmospheric effects, and subtle gradients. | Suggesting texture such as hair, wood grain, or rough surfaces. |
Introduction to Glazing and Dry Brush Techniques
Glazing and dry brush are essential painting techniques used to create texture and depth in artworks. Glazing involves applying thin, transparent layers of paint to build rich color and luminosity, while dry brush uses a minimal amount of paint on a dry brush to achieve rough, textured strokes. Mastery of glazing enhances realism through smooth transitions, and dry brush adds expressive detail and surface variation.
What is Glazing in Art?
Glazing in art is a technique where transparent layers of paint are applied over a dry opaque layer to create depth and luminosity. This method allows colors to interact optically, enhancing richness and subtlety in the artwork. Unlike dry brushing, which uses a small amount of paint for texture, glazing emphasizes smooth, translucent color transitions.
Understanding the Dry Brush Method
The dry brush method utilizes a minimal amount of paint on a dry brush to create textured, wispy strokes that emphasize surface details and highlights. Unlike glazing, which involves layering transparent washes to build depth and luminosity, dry brushing produces a more tactile, rough effect ideal for emphasizing textures such as wood grain or fabric. Mastering dry brushing enhances realism and dimension, especially in miniature painting and landscape art.
Key Differences Between Glazing and Dry Brush
Glazing involves applying thin, transparent layers of paint to create depth and subtle color transitions, while dry brushing uses a small amount of paint on a nearly dry brush to add texture and highlight raised surfaces. Glazing emphasizes smooth, luminous effects ideal for achieving realistic shading, whereas dry brushing produces a rough, textured look perfect for accentuating details. The key difference lies in glazing's focus on color blending and light modulation versus dry brushing's ability to emphasize surface texture and contrast.
Materials Needed for Glazing vs Dry Brush
Glazing requires transparent or semi-transparent acrylic or oil paints, glazing medium, soft bristle brushes, and a smooth painting surface to build thin, luminous layers. Dry brush technique uses thicker, less diluted paint, stiff bristle brushes, and textured surfaces like canvas or rough paper to achieve a scratchy, textured effect. Proper selection of brushes and paint consistency is crucial for mastering both glazing and dry brush methods in painting.
Best Paint Types for Each Technique
Oil paints are ideal for glazing due to their slow drying time and ability to achieve translucent layers, enhancing depth and luminosity. Acrylic paints work best for dry brushing because of their quick drying nature and versatility, allowing for textured, scratchy effects on rough surfaces. Watercolors can also be used in glazing for delicate washes but are less suited for dry brushing due to their fluidity and lack of texture retention.
Common Applications in Painting Styles
Glazing is commonly applied in classical oil painting and Renaissance art to create depth, luminosity, and subtle color transitions by layering transparent paint over a dry surface. Dry brush technique is frequently used in watercolor, acrylics, and pastel works to achieve textured effects, fine details, and expressive strokes, often seen in landscapes, portraits, and impressionistic styles. Both methods enhance visual complexity but serve distinct purposes depending on the desired finish and medium.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Glazing
Glazing offers the advantage of creating smooth, transparent layers that enhance color depth and luminosity, making it ideal for achieving realistic textures and subtle shading. It requires patience and multiple thin layers, which can be time-consuming and challenging for beginners due to the need for precise control over paint consistency and drying times. The main disadvantage of glazing lies in its slow process and potential for muddy colors if layers are not properly dried or when mixed improperly with opaque paint.
Pros and Cons of Dry Brush Technique
The dry brush technique offers precise control and textured effects, making it ideal for highlighting fine details and creating weathered or rough surfaces in paintings. Its main drawback is the difficulty in achieving smooth gradients or large even coverage, as the brush holds minimal paint and requires careful handling to avoid streaky or patchy results. This technique works best on textured surfaces such as canvas or rough paper, enhancing visual depth but potentially limiting subtle color blending compared to glazing methods.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Artwork
Glazing involves applying thin, transparent layers of paint to create depth and luminous color effects, ideal for achieving smooth transitions and subtle tonal variations. Dry brushing uses a brush with minimal paint to add texture and highlight raised surfaces, perfect for emphasizing details and creating a rough, textured appearance. Selecting the right technique depends on your artistic goal: use glazing for refined realism and color richness, while dry brushing suits expressive textures and accentuated highlights.
Glazing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com