Foreground elements in design and photography play a crucial role in creating depth and guiding the viewer's focus toward the main subject. By carefully positioning objects or textures in the foreground, you can enhance visual interest and establish a strong spatial relationship within the composition. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective techniques for using foreground to elevate your creative projects.
Table of Comparison
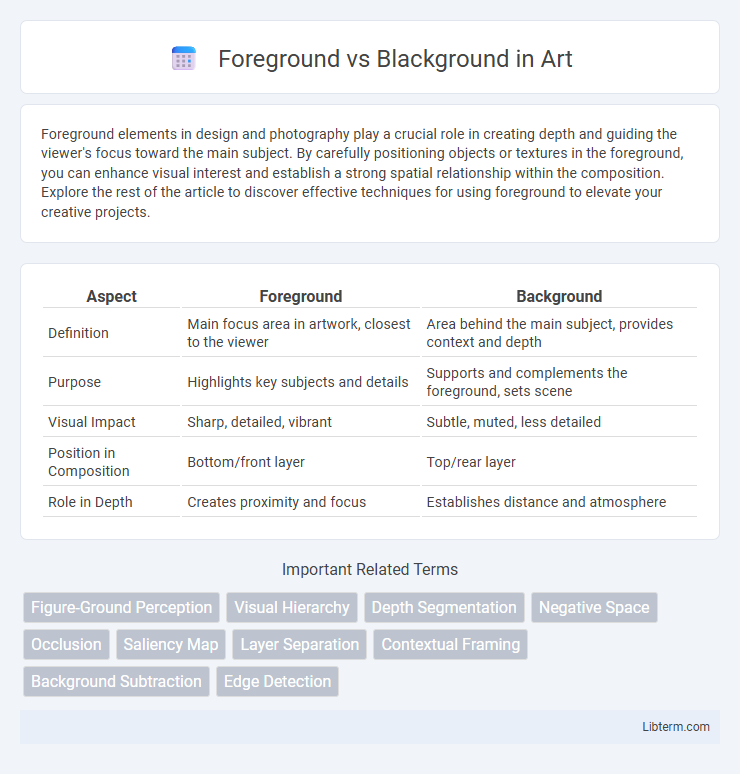
| Aspect | Foreground | Background |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Main focus area in artwork, closest to the viewer | Area behind the main subject, provides context and depth |
| Purpose | Highlights key subjects and details | Supports and complements the foreground, sets scene |
| Visual Impact | Sharp, detailed, vibrant | Subtle, muted, less detailed |
| Position in Composition | Bottom/front layer | Top/rear layer |
| Role in Depth | Creates proximity and focus | Establishes distance and atmosphere |
Introduction to Foreground and Background
Foreground refers to the prominent part of a visual composition that captures the viewer's immediate attention, often containing key subjects or focal points. Background serves as the context or setting behind the foreground elements, providing depth and supporting the overall scene without overpowering the primary focus. Understanding the distinction between foreground and background is essential for effective visual storytelling, design, and image composition.
Defining Foreground: Concepts and Examples
Foreground refers to the part of an image or scene that is closest to the viewer and contains the main subject or focus, often emphasized through clarity, contrast, or color intensity. In graphic design and photography, the foreground is key to attracting attention and enhancing depth perception, such as a person standing sharply in front of a blurred background. Examples include a flower in sharp detail at the front of a garden scene or a clear silhouette in front of a sunset.
Understanding Background: Key Characteristics
Background in visual design refers to the area behind the main subject, typically providing context and depth without drawing attention away from the foreground elements. Key characteristics include subtle color schemes, reduced contrast, and less detailed textures, which help maintain focus on the primary content. Effective background design enhances readability and overall composition by supporting rather than competing with the foreground.
Importance of Foreground in Visual Design
Foreground elements are crucial in visual design as they capture the viewer's immediate attention and convey the primary message or focal point. Effective use of foreground enhances clarity and directs user interaction by distinguishing important content from background details. Prioritizing foreground ensures better visual hierarchy, improving overall communication and user experience.
The Role of Background in Composition
The background in composition plays a crucial role in enhancing visual storytelling by providing context and depth, allowing the foreground elements to stand out more effectively. It establishes the mood and atmosphere, guiding the viewer's eye through contrast, color harmony, and spatial relationships. Proper manipulation of background elements can balance the overall composition and emphasize the subject without overwhelming it.
Foreground vs Background: Key Differences
Foreground refers to the part of an image or scene that appears closest to the viewer, often containing the main subject or focal point. Background, in contrast, encompasses the area behind the foreground, providing context or environment without drawing primary attention. Key differences include depth perception, visual emphasis, and the role each plays in composition, with foreground elements typically sharper and more detailed than background elements.
Techniques to Separate Foreground from Background
Techniques to separate foreground from background primarily include chroma keying, depth sensing, and image segmentation algorithms. Chroma keying leverages distinct color contrasts, typically green or blue screens, to isolate subjects, while depth sensing uses hardware like LiDAR or stereo cameras to distinguish layers based on distance. Advanced image segmentation employs convolutional neural networks (CNNs) such as U-Net or Mask R-CNN to accurately segment objects by analyzing pixel-level features and contextual information.
Impact of Foreground and Background on Viewer Perception
Foreground elements command immediate attention by creating a focal point, significantly influencing viewer perception through clarity and detail, which enhances engagement and emotional response. Backgrounds provide context and depth, shaping the overall mood and supporting the foreground without overwhelming it, thus guiding the viewer's interpretation subconsciously. The interplay between foreground and background balances visual hierarchy, directing focus while enriching the narrative and spatial understanding.
Foreground and Background in Various Media (Photography, Art, UI)
Foreground in photography and art typically highlights the main subject, creating depth and focus by contrasting with the background, which provides context and spatial orientation. In UI design, the foreground consists of interactive elements such as buttons and text, designed for user engagement, while the background offers a supportive, often neutral environment to ensure clarity and readability. Effective use of foreground and background enhances visual hierarchy, guiding attention and improving user experience across various media.
Practical Tips for Balancing Foreground and Background
Balancing foreground and background in design enhances visual hierarchy and ensures content clarity, with practical tips including using contrasting colors, controlling depth of field in photography, and adjusting opacity levels for layered elements. Employing selective focus techniques in images helps highlight the subject while subtly integrating background details. Consistent alignment and spacing prevent clutter, maintaining harmony between foreground and background components.
Foreground Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com