Serigraphy is a versatile printing technique that uses a mesh screen to transfer ink onto various surfaces, creating vibrant and long-lasting designs. This method is popular in art, fashion, and commercial printing for its precision and ability to work on materials like fabric, paper, and wood. Explore the full article to understand how serigraphy can enhance your creative projects and business needs.
Table of Comparison
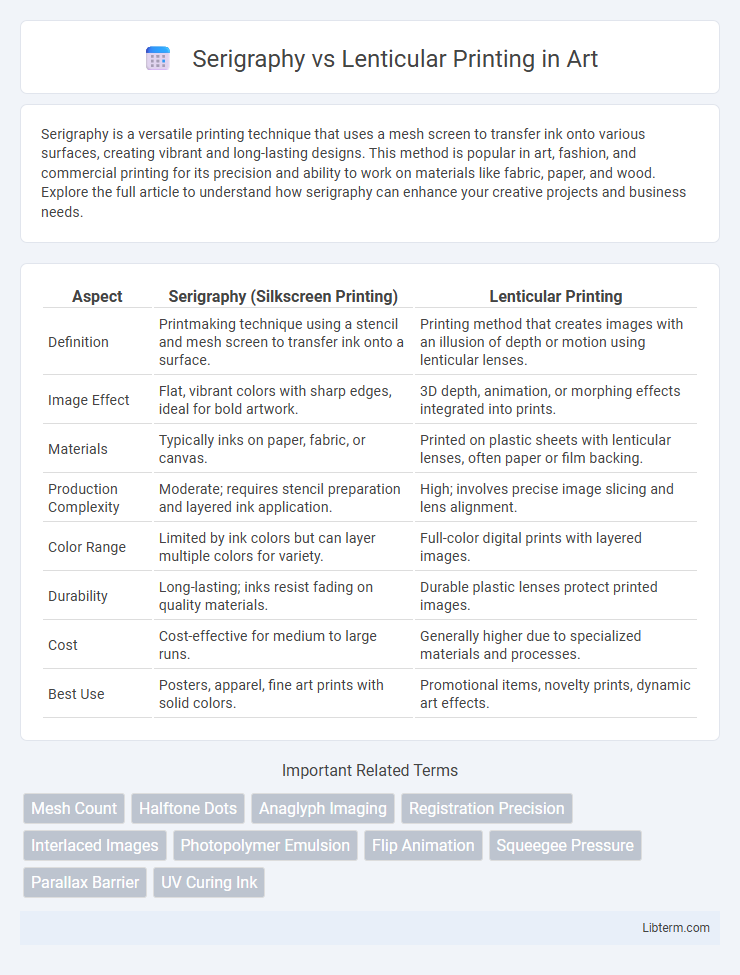
| Aspect | Serigraphy (Silkscreen Printing) | Lenticular Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Printmaking technique using a stencil and mesh screen to transfer ink onto a surface. | Printing method that creates images with an illusion of depth or motion using lenticular lenses. |
| Image Effect | Flat, vibrant colors with sharp edges, ideal for bold artwork. | 3D depth, animation, or morphing effects integrated into prints. |
| Materials | Typically inks on paper, fabric, or canvas. | Printed on plastic sheets with lenticular lenses, often paper or film backing. |
| Production Complexity | Moderate; requires stencil preparation and layered ink application. | High; involves precise image slicing and lens alignment. |
| Color Range | Limited by ink colors but can layer multiple colors for variety. | Full-color digital prints with layered images. |
| Durability | Long-lasting; inks resist fading on quality materials. | Durable plastic lenses protect printed images. |
| Cost | Cost-effective for medium to large runs. | Generally higher due to specialized materials and processes. |
| Best Use | Posters, apparel, fine art prints with solid colors. | Promotional items, novelty prints, dynamic art effects. |
Introduction to Serigraphy and Lenticular Printing
Serigraphy, also known as screen printing, involves pushing ink through a fine mesh screen to create vibrant, detailed images on various surfaces like fabric, paper, and plastic. Lenticular printing uses lenticular lenses to produce images with depth, motion, or changing visuals when viewed from different angles, typically applied to posters, labels, and promotional materials. Both techniques serve distinct purposes in graphic arts, with serigraphy excelling in durability and color richness, while lenticular printing offers dynamic visual effects.
Understanding the Basics of Serigraphy
Serigraphy, also known as screen printing, involves pushing ink through a mesh stencil to create vibrant, durable designs on various surfaces like fabric, paper, and plastic. This technique allows for precise color layering and is ideal for producing bold, solid areas of color with a high level of detail. Compared to lenticular printing, which uses lenses to create motion or depth effects, serigraphy focuses on static, crisp imagery with a tactile quality.
The Fundamentals of Lenticular Printing
Lenticular printing uses lenses to create images with depth, motion, or morphing effects by interlacing multiple frames and aligning them with a lenticular lens sheet. The process involves precise image slicing, lens alignment, and printing on a specialized substrate to achieve dynamic visual effects that change with viewing angles. This technique differs from serigraphy, which relies on stencil-based screen printing for static, vibrant, and textured artworks.
Key Differences Between Serigraphy and Lenticular Printing
Serigraphy, also known as screen printing, uses a stencil and mesh screen to apply layers of ink onto a surface, creating vibrant, durable prints ideal for textiles and posters. Lenticular printing employs lenticular lenses to produce images with depth, motion, or transformation effects, making it suitable for promotional materials and 3D visuals. Key differences include serigraphy's reliance on ink layering for color richness and lenticular's use of optical lenses for dynamic imagery and viewer interaction.
Applications and Artistic Uses
Serigraphy excels in applications requiring vibrant, durable prints on textiles, posters, and fine art editions, providing rich color saturation and texture ideal for artistic expression. Lenticular printing is favored for creating dynamic visual effects like 3D depth and motion in advertising, packaging, and promotional materials, enhancing viewer engagement through optical illusion. Both methods support distinct artistic uses: serigraphy offers tactile quality and color precision for limited edition art, while lenticular printing innovates with interactive visuals, expanding creative possibilities in multimedia design.
Material Requirements for Each Printing Method
Serigraphy requires mesh screens, stencils, and oil-based or plastisol inks suitable for textiles, paper, or plastic substrates, emphasizing durable and porous materials to ensure ink adhesion. Lenticular printing demands specialized lenticular lenses and compatible substrates like coated paper or plastic sheets, engineered to align precisely with interlaced images for optimal 3D or motion effects. Material precision and compatibility are crucial for both methods to achieve high-quality, visually effective prints.
Visual Effects and Image Quality Comparison
Serigraphy provides vibrant, high-opacity colors with precise detail, making it ideal for bold, graphic visuals and sharp lines. Lenticular printing excels in creating dynamic, moving images or 3D effects by using lenticular lenses to manipulate light, resulting in visually engaging depth and motion illusions. While serigraphy offers superior color saturation and tactile texture, lenticular printing delivers unique interactive visuals but may sacrifice some image sharpness due to lens distortion.
Production Process and Workflow
Serigraphy involves a stencil-based screen printing process where ink is pushed through a mesh screen onto the substrate, suitable for high-volume production with vibrant color layering and precise detail. Lenticular printing utilizes a specialized lenticular lens sheet to create images with depth, motion, or multiple perspectives by aligning printed interlaced images beneath the lens, requiring precise digital image preparation and alignment. The production workflow for serigraphy emphasizes stencil creation, ink application, and curing, while lenticular printing demands meticulous image processing, lenticular lens calibration, and high-resolution printing for optimal visual effects.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Serigraphy offers lower upfront costs and is more cost-effective for small to medium print runs due to its manual process and minimal setup expenses. Lenticular printing involves higher initial investment because of specialized materials and technology but excels in scalability for large, high-volume orders offering dynamic visual effects. Choosing between serigraphy and lenticular printing depends on balancing budget constraints with desired production volume and advanced visual features.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Serigraphy excels in delivering vibrant, durable colors on flat surfaces, ideal for large-scale prints and limited color palettes, making it perfect for posters, textiles, and art prints. Lenticular printing offers dynamic, eye-catching images with motion or depth effects, suited for promotional materials, packaging, and 3D display products where visual engagement is key. Selecting the right technique depends on project goals, budget constraints, print volume, and desired visual impact, with serigraphy favored for long-lasting, bold designs and lenticular for interactive, attention-grabbing visuals.
Serigraphy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com