Exaggerated expression intensifies emotions and captures attention by amplifying descriptions beyond reality. This technique is commonly used in literature, advertising, and everyday speech to make ideas more memorable and impactful. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can effectively use exaggerated expression in your communication.
Table of Comparison
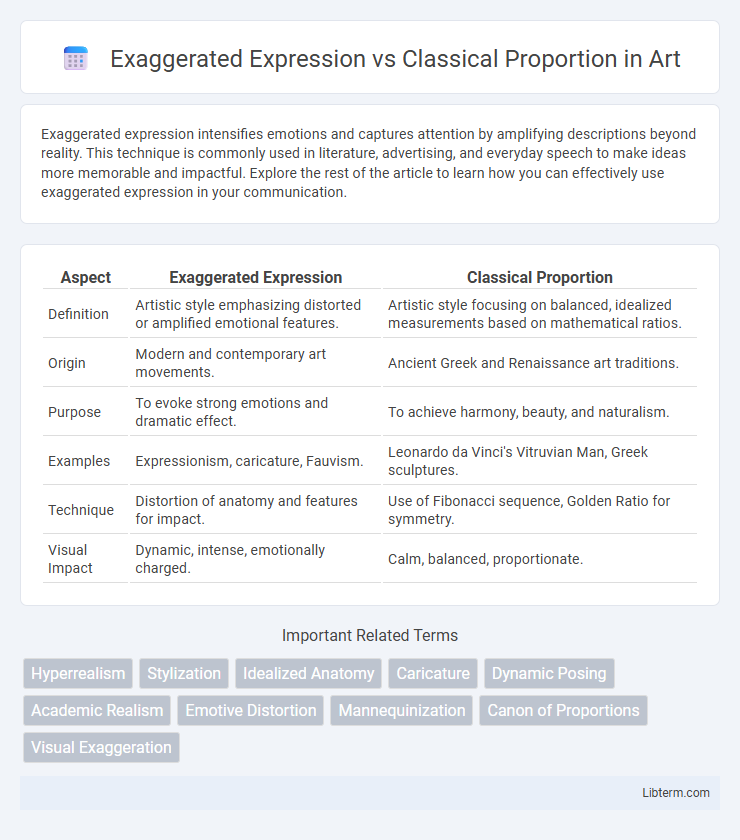
| Aspect | Exaggerated Expression | Classical Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artistic style emphasizing distorted or amplified emotional features. | Artistic style focusing on balanced, idealized measurements based on mathematical ratios. |
| Origin | Modern and contemporary art movements. | Ancient Greek and Renaissance art traditions. |
| Purpose | To evoke strong emotions and dramatic effect. | To achieve harmony, beauty, and naturalism. |
| Examples | Expressionism, caricature, Fauvism. | Leonardo da Vinci's Vitruvian Man, Greek sculptures. |
| Technique | Distortion of anatomy and features for impact. | Use of Fibonacci sequence, Golden Ratio for symmetry. |
| Visual Impact | Dynamic, intense, emotionally charged. | Calm, balanced, proportionate. |
Understanding Exaggerated Expression in Art
Exaggerated expression in art emphasizes distorted forms and amplified emotions to convey intense psychological states or narratives, diverging from the balanced harmony of classical proportion. This approach prioritizes emotional impact over anatomical accuracy, often using elongated limbs, oversized features, or dramatic poses to evoke visceral responses. Understanding exaggerated expression involves recognizing its role in highlighting human experience and subjective perception beyond idealized realism.
Classical Proportion: Foundations of Artistic Balance
Classical proportion serves as the foundational principle of artistic balance, emphasizing harmony and symmetry rooted in mathematical ratios such as the Golden Ratio. This approach ensures visual stability and aesthetic coherence, guiding artists to create figures and compositions that feel natural and pleasing to the eye. By adhering to these established proportions, artworks achieve timeless elegance and structured beauty, contrasting with the dynamic distortions found in exaggerated expression.
Historical Origins of Classical Proportion
The historical origins of classical proportion trace back to ancient Greece, where sculptors like Polykleitos formulated mathematical ratios to achieve idealized human anatomy in art. Classical proportion emphasized balance and harmony, guided by concepts such as the Golden Ratio, which defined the relationships between body parts to create visually pleasing forms. This foundation sharply contrasts with exaggerated expression styles, which intentionally distort these norms to evoke emotional intensity or emphasize certain features.
Evolution of Exaggerated Expression Across Art Movements
Exaggerated expression evolved significantly across art movements, from the emotional intensity of Baroque to the distortion and abstraction in Expressionism and Surrealism, emphasizing subjective experience over Classical Proportion's balanced realism. Modern and contemporary artists harness exaggerated forms to convey psychological depth and societal critique, challenging traditional ideals of anatomical harmony and symmetry. This shift reflects broader cultural changes prioritizing individual emotion and conceptual complexity, marking a departure from the classical pursuit of idealized human form.
Comparing Techniques: Proportion vs. Expression
Exaggerated expression emphasizes emotional intensity through distortion of facial features, body poses, or gestures that break classical proportion rules to evoke strong viewer reactions. Classical proportion relies on balanced, harmonious measurements based on mathematical ratios, such as the Golden Ratio, to create aesthetically pleasing and realistic representations. Comparing these techniques highlights how proportion prioritizes structural accuracy while exaggerated expression prioritizes emotional impact, offering artists distinct approaches to conveying meaning.
Psychological Impact on the Viewer
Exaggerated expression in art often evokes intense emotional responses by amplifying facial features or body language beyond naturalistic norms, heightening feelings of urgency, drama, or distress in the viewer. Classical proportions rely on balanced and harmonious measurements, promoting a sense of calm, order, and ideal beauty that psychologically reassures and comforts. The contrast between these approaches manipulates viewer perception, with exaggerated forms triggering immediate, visceral reactions while classical proportions invite contemplation and emotional stability.
Notable Artists: Champions of Each Style
Notable artists championing exaggerated expression include Egon Schiele and Francis Bacon, known for their intense emotional distortions and dynamic, often unsettling imagery. Classical proportion is epitomized by Leonardo da Vinci and Raphael, whose works emphasize anatomical precision and harmonious balance based on mathematical ratios like the Golden Section. These distinct artistic approaches highlight the tension between emotional impact and idealized realism in art history.
Contemporary Applications in Modern Art
Exaggerated expression in contemporary art emphasizes emotional intensity and distortion, often challenging classical proportion's emphasis on balance and harmony rooted in Renaissance ideals. Contemporary artists employ exaggerated forms to evoke subjective experiences and critique societal norms, diverging from traditional adherence to anatomical accuracy. This approach dominates modern visual culture through movements such as Expressionism and Neo-Expressionism, redefining artistic interpretation beyond classical constraints.
Challenges and Critiques of Both Approaches
Exaggerated expression often faces critiques for sacrificing anatomical accuracy, leading to distorted forms that can hinder realistic representation and limit viewer relatability. Classical proportion emphasizes balanced and harmonious measurements but may be challenged for potentially stifling creativity and failing to capture dynamic emotional intensity. Both approaches must navigate the tension between artistic expression and structural integrity, requiring practitioners to balance innovation with foundational principles.
Finding Harmony: Blending Expression and Proportion
Exaggerated expression challenges classical proportion by distorting traditional forms to evoke emotion and dynamism, while classical proportion emphasizes balance and harmony through precise ratios and symmetry. Finding harmony involves blending these approaches by maintaining structural integrity within exaggerated elements, allowing expressive forms to coexist with foundational principles of design. This integration enhances visual impact and emotional resonance without compromising aesthetic coherence.
Exaggerated Expression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com