Conforming to established standards ensures consistency and reliability across various processes and products, enhancing overall quality and trust. Your adherence to these guidelines can prevent errors and improve communication within teams and with clients. Explore the full article to understand how conformity impacts your daily operations and success.
Table of Comparison
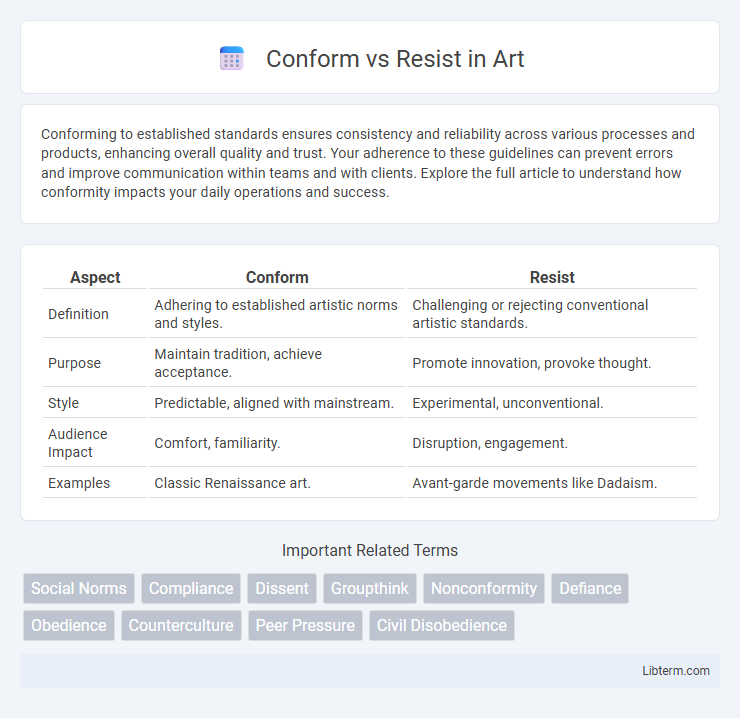
| Aspect | Conform | Resist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adhering to established artistic norms and styles. | Challenging or rejecting conventional artistic standards. |
| Purpose | Maintain tradition, achieve acceptance. | Promote innovation, provoke thought. |
| Style | Predictable, aligned with mainstream. | Experimental, unconventional. |
| Audience Impact | Comfort, familiarity. | Disruption, engagement. |
| Examples | Classic Renaissance art. | Avant-garde movements like Dadaism. |
Understanding Conformity and Resistance
Conformity involves aligning behavior and beliefs with group norms to gain acceptance or avoid conflict, deeply rooted in social influence and psychological mechanisms like normative and informational influence. Resistance emerges when individuals or groups actively oppose conformity pressures to maintain personal integrity, foster innovation, or challenge unjust systems, often driven by factors such as critical thinking, moral conviction, and social identity. Understanding the dynamics of conformity and resistance is crucial for analyzing social behavior, power structures, and cultural change.
The Psychology Behind Conforming
The psychology behind conforming involves social influences such as normative and informational social influence, where individuals align their behavior with group norms to gain acceptance or because they believe the group is better informed. Conformity can be driven by the desire to avoid social rejection, reduce uncertainty in ambiguous situations, and achieve social harmony. Key studies by Solomon Asch and Muzafer Sherif highlight how peer pressure and group consensus powerfully shape individual decision-making and behavior.
Why Do People Resist Social Pressure?
People resist social pressure due to the need to maintain personal identity and autonomy, which drives individuals to uphold their values despite external influence. Psychological factors such as self-confidence and moral convictions strengthen resistance against conforming to group norms. Social support from like-minded peers enhances the ability to withstand pressure, promoting independent decision-making and reducing compliance.
Historical Examples of Conformity
Historical examples of conformity include the widespread obedience to Nazi Germany's regime, where millions adhered to oppressive laws and social norms under Adolf Hitler's rule. The Salem witch trials epitomize conformity as communities collectively sanctioned harmful accusations against alleged witches to maintain social order. In the Soviet Union, citizens conformed to state propaganda and restrictions, suppressing dissent to avoid persecution and align with Communist Party ideologies.
Notable Acts of Resistance in Society
Notable acts of resistance in society include the Civil Rights Movement, where figures like Martin Luther King Jr. led nonviolent protests against racial segregation and discrimination. The anti-apartheid struggle in South Africa, highlighted by Nelson Mandela's leadership, showcased relentless opposition to institutionalized racial oppression. Environmental movements such as the Standing Rock protests have also gained prominence by confronting pipeline construction to protect indigenous lands and water sources.
Benefits of Conforming in Certain Situations
Conforming in certain situations promotes social harmony by aligning individual behavior with group norms, reducing conflict and fostering cooperation. It enhances trust and facilitates smoother communication within teams or communities, leading to improved productivity and collective success. Conformity can also provide psychological comfort by offering a sense of belonging and reducing feelings of isolation.
Risks and Consequences of Resisting
Resisting conformity can lead to social isolation, reduced support networks, and increased stress due to opposition and criticism from peers or authority figures. Persistent resistance may result in professional setbacks, including missed opportunities for collaboration and career advancement. Psychological consequences such as anxiety and decreased self-esteem often arise from continuous conflict with dominant group norms.
Societal Impacts of Conformity
Conformity influences societal structures by promoting social cohesion and stability through shared norms and behaviors, which facilitates cooperation and predictability in communities. However, excessive conformity can suppress individuality, stifle innovation, and perpetuate systemic inequalities by discouraging dissent and critical thinking. Balancing conformity with resistance is crucial for societal progress, fostering both unity and the evolution of cultural values.
Strategies for Balancing Conformity and Resistance
Effective strategies for balancing conformity and resistance include recognizing social norms while maintaining personal values, employing selective conformity to fit into group expectations without compromising identity, and using constructive resistance to challenge unjust norms thoughtfully. Developing emotional intelligence and critical thinking skills enhances the ability to discern when to adapt and when to assert individuality. This balance fosters social harmony while promoting innovation and personal growth.
Personal Growth: When to Conform and When to Resist
Balancing conformity and resistance is essential for personal growth, as conforming can foster social harmony and learning from established norms while resisting encourages innovation and authentic self-expression. Understanding when to conform involves assessing situations where collaboration and adaptation lead to development, whereas resistance is crucial when challenging unjust practices and advocating for personal values. This dynamic interplay cultivates resilience and self-awareness, enabling individuals to navigate growth opportunities effectively.
Conform Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com