Exploring literature unveils the richness of human experience through diverse narratives and poetic expressions that resonate across cultures and time periods. Understanding literary techniques and genres enhances your ability to appreciate and critically analyze texts, deepening emotional and intellectual connections. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how literature shapes our worldview and enriches personal growth.
Table of Comparison
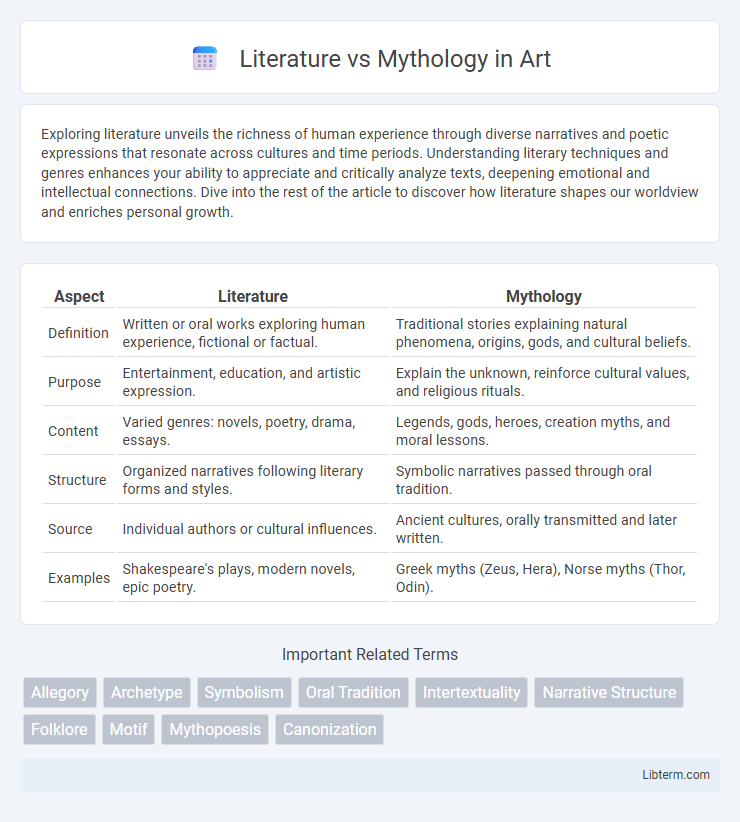
| Aspect | Literature | Mythology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Written or oral works exploring human experience, fictional or factual. | Traditional stories explaining natural phenomena, origins, gods, and cultural beliefs. |
| Purpose | Entertainment, education, and artistic expression. | Explain the unknown, reinforce cultural values, and religious rituals. |
| Content | Varied genres: novels, poetry, drama, essays. | Legends, gods, heroes, creation myths, and moral lessons. |
| Structure | Organized narratives following literary forms and styles. | Symbolic narratives passed through oral tradition. |
| Source | Individual authors or cultural influences. | Ancient cultures, orally transmitted and later written. |
| Examples | Shakespeare's plays, modern novels, epic poetry. | Greek myths (Zeus, Hera), Norse myths (Thor, Odin). |
Defining Literature and Mythology
Literature encompasses a broad range of written works, including fiction, poetry, drama, and essays, that explore human experiences, emotions, and ideas through language and narrative techniques. Mythology consists of traditional stories, often rooted in ancient cultures, that explain natural phenomena, cultural practices, and historical events using gods, heroes, and supernatural elements. Both literature and mythology serve as vehicles for cultural expression, but literature tends to prioritize artistic creativity and diverse genres, whereas mythology emphasizes collective beliefs and symbolic meanings.
Historical Origins of Literature and Mythology
Historical origins of literature trace back to ancient civilizations such as Sumeria and Egypt, where written records emerged around 3000 BCE, primarily for administrative and religious purposes. Mythology predates written literature, originating from oral traditions that explained natural phenomena, cultural values, and cosmological beliefs, thriving in societies like Ancient Greece, Mesopotamia, and India. The development of written literature enabled the preservation and transformation of mythological narratives into structured texts, influencing classical works like Homer's epics and enabling the study of human experience through storytelling.
Major Themes in Literature vs Mythology
Literature explores diverse themes such as identity, conflict, and human nature through complex characters and narratives, emphasizing individual experience and societal reflection. Mythology centers on foundational themes like creation, morality, and the supernatural, using symbolic stories to explain natural phenomena and cultural origins. Both genres examine human values and existential questions but differ in purpose--literature often critiques reality, while mythology conveys collective beliefs and traditions.
Narrative Structure: Storytelling in Literature and Mythology
Narrative structure in literature often emphasizes character development, thematic complexity, and plot intricacy, enabling diverse storytelling techniques such as nonlinear timelines and multiple perspectives. Mythology relies on archetypal narratives and symbolic motifs that convey cultural values and universal truths through repeated patterns like hero's journeys and creation myths. Both forms use narrative devices to engage audiences, but literature typically explores individual experience while mythology presents collective identities and moral lessons.
Symbolism and Allegory in Both Genres
Symbolism and allegory serve as foundational devices in both literature and mythology, enabling deeper layers of meaning and cultural reflection. In literature, symbols often represent complex human emotions and social issues, while allegories convey moral, political, or philosophical messages through extended metaphorical narratives. Mythology employs symbolism and allegory to explain natural phenomena, human origins, and divine interventions, embedding cultural beliefs and values within timeless stories.
Cultural Impact: Literature vs Mythology
Literature and mythology both profoundly shape cultural identity by preserving collective memories and values through storytelling. Literature often reflects historical contexts and societal changes, providing insight into human experiences across time. Mythology, rooted in ancient traditions, influences cultural rituals and moral frameworks, embedding symbolic meanings within a community's heritage.
Characters: Archetypes and Development
Literature often explores complex characters with nuanced development, reflecting individual psychology and growth, while mythology presents archetypal figures embodying universal human traits and cultural values. Mythological characters typically serve symbolic roles and remain consistent across stories, reinforcing moral lessons and communal identity. Literary characters evolve through conflicts and experiences, offering deeper insight into human nature and societal issues.
Evolution and Adaptation Over Time
Literature and mythology demonstrate distinct evolutionary paths, where literature evolves through diverse genres and cultural influences reflecting societal changes, while mythology adapts by integrating symbolic narratives and archetypes that explain universal human experiences. Mythological stories often transform across generations, adapting to historical contexts and regional beliefs, whereas literature continuously reinvents itself through innovative storytelling techniques and thematic explorations. Both fields exemplify dynamic adaptation processes, preserving core human values while responding to the shifting paradigms of time and culture.
Influence on Modern Media and Culture
Literature and mythology significantly shape modern media and culture by providing foundational narratives and archetypes that inspire films, books, and video games. Mythological themes such as heroism, creation, and apocalypse permeate contemporary storytelling, while literary works contribute complex character development and thematic depth. Together, they influence cultural values, societal norms, and artistic expression, reinforcing enduring motifs across global media platforms.
Comparative Analysis: Lessons from Literature and Mythology
Literature and mythology both serve as rich sources of cultural values and human experiences, with literature often providing contemporary reflections while mythology offers timeless archetypes and symbolic narratives. Comparative analysis reveals literature's ability to reinterpret mythological themes to address modern social issues, thereby creating a dynamic dialogue between past and present. Lessons from mythology emphasize universal moral principles and heroic archetypes, whereas literature expands these lessons through complex character development and diverse perspectives.
Literature Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com