Enhancing your skills in any field requires a strategic approach focused on continuous learning and practical application. Leveraging the latest tools and techniques can significantly accelerate your progress and improve outcomes. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective methods for boosting your personal and professional growth.
Table of Comparison
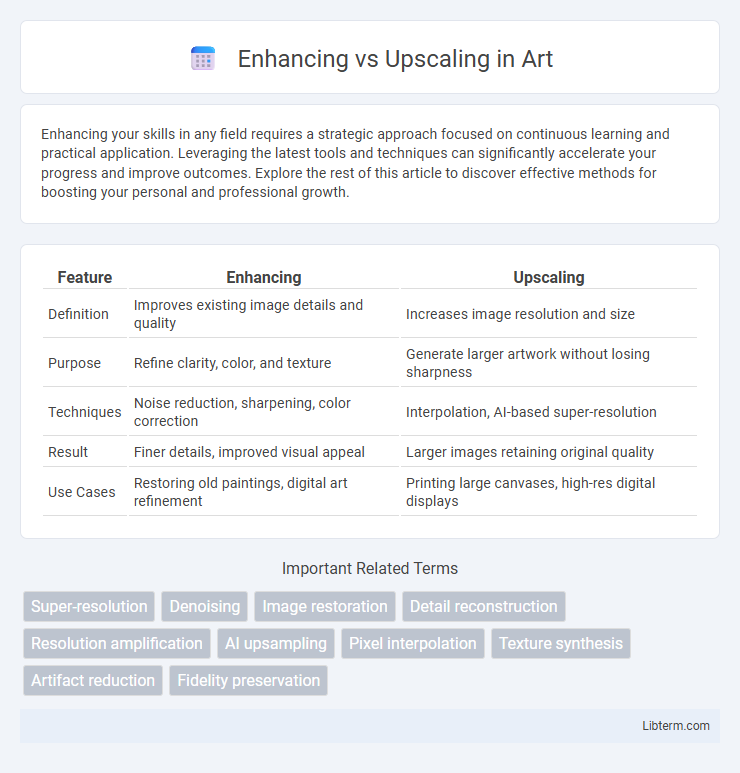
| Feature | Enhancing | Upscaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Improves existing image details and quality | Increases image resolution and size |
| Purpose | Refine clarity, color, and texture | Generate larger artwork without losing sharpness |
| Techniques | Noise reduction, sharpening, color correction | Interpolation, AI-based super-resolution |
| Result | Finer details, improved visual appeal | Larger images retaining original quality |
| Use Cases | Restoring old paintings, digital art refinement | Printing large canvases, high-res digital displays |
Introduction to Image Enhancement and Upscaling
Image enhancement involves improving the visual quality of an image by adjusting elements such as contrast, sharpness, and color balance to make details more distinguishable. Upscaling refers to increasing the resolution of an image, often using algorithms like deep learning-based super-resolution to add pixels and preserve image clarity. Both techniques aim to improve image perception, but enhancement focuses on qualitative improvements while upscaling targets size and resolution expansion.
Defining Image Enhancement
Image enhancement refers to processing techniques that improve the visual appearance or highlight specific features of an image without changing its dimensions. Unlike upscaling, which increases image resolution by enlarging pixel count, enhancement adjusts contrast, brightness, sharpness, or noise levels to make images clearer and more detailed. Effective enhancement algorithms target pixel intensity modifications to optimize perceptual quality for human viewers or subsequent analysis.
Understanding Image Upscaling
Image upscaling increases the resolution of digital images by adding pixels to create a larger, more detailed version without significant quality loss. Advanced algorithms like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) enable precise pixel interpolation and detail restoration, differentiating upscaling from basic image enhancement techniques. Understanding these methods is crucial for applications in photography, gaming, and medical imaging where clarity and detail are paramount.
Key Differences Between Enhancement and Upscaling
Enhancing improves the existing quality of an image or video by refining details, colors, and sharpness without changing its resolution. Upscaling increases the resolution by adding pixels to enlarge the image or video, often relying on algorithms to predict missing information. The key difference lies in enhancement focusing on quality refinement at the original resolution, while upscaling targets resolution increase with potential quality trade-offs.
Popular Techniques for Enhancing Images
Popular techniques for enhancing images include contrast adjustment, sharpening, and noise reduction, which improve clarity and detail without altering resolution. Algorithms like histogram equalization and unsharp masking are widely applied to boost image quality by enhancing edges and balancing brightness. Deep learning-based methods, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have also gained prominence for their ability to restore fine details and reduce artifacts effectively.
State-of-the-Art Upscaling Algorithms
State-of-the-art upscaling algorithms utilize deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs) to reconstruct high-resolution images from low-resolution inputs. These methods outperform traditional enhancement by predicting missing details and textures, effectively increasing pixel density while preserving natural image quality. Technologies like ESRGAN and Real-ESRGAN exemplify cutting-edge solutions that deliver superior image clarity and sharpness in various applications, including gaming, medical imaging, and video streaming.
Benefits and Limitations of Image Enhancement
Image enhancement improves visual quality by adjusting brightness, contrast, and sharpness, making details more distinguishable without altering resolution. Its benefits include clearer images for analysis and better visual appeal, but limitations arise from potential noise amplification and dependence on the original image quality. Unlike upscaling, which increases resolution artificially, enhancement focuses on optimizing existing pixel data for improved perceptual clarity.
Advantages and Challenges of Upscaling
Upscaling improves image resolution by enlarging the original content, offering clearer visuals for larger displays without the need for higher-resolution sources. Advantages of upscaling include enhanced viewing experience, compatibility with various display technologies, and the ability to repurpose existing media for modern high-definition screens. Challenges involve maintaining image quality during the enlargement process, avoiding artifacts and blurriness, and the computational intensity required for real-time upscaling in video playback and gaming applications.
Practical Applications: When to Enhance or Upscale
Enhancing improves image quality by refining details and correcting colors, ideal for restoring old photos or optimizing graphics for print. Upscaling increases image resolution, making it well-suited for enlarging images for large displays or high-resolution formats without losing clarity. Choosing between enhancing and upscaling depends on the original image quality and the intended use, such as web content needing enhancement versus large-format prints requiring upscaling.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Enhancing improves the quality of an image by refining details and reducing noise, ideal for restoring old photos or boosting clarity without changing dimensions. Upscaling increases the image size by adding pixels using algorithms, suitable for printing large formats or adapting to higher-resolution displays. Selecting the right method depends on the end use--enhance for detail refinement and upscaling for size expansion while maintaining visual fidelity.
Enhancing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com