Oil is a vital natural resource used for fuel, heating, and as a key ingredient in numerous industrial products. Understanding the different types of oil and their applications can help you make informed choices for energy efficiency and environmental impact. Discover more about how oil affects your daily life and the global economy in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
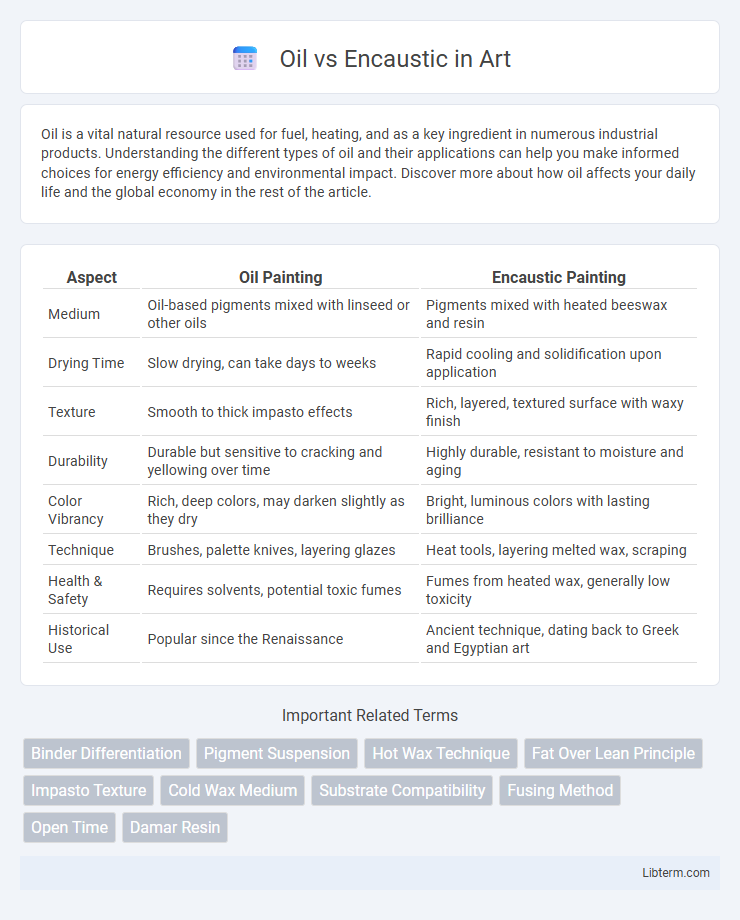
| Aspect | Oil Painting | Encaustic Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Oil-based pigments mixed with linseed or other oils | Pigments mixed with heated beeswax and resin |
| Drying Time | Slow drying, can take days to weeks | Rapid cooling and solidification upon application |
| Texture | Smooth to thick impasto effects | Rich, layered, textured surface with waxy finish |
| Durability | Durable but sensitive to cracking and yellowing over time | Highly durable, resistant to moisture and aging |
| Color Vibrancy | Rich, deep colors, may darken slightly as they dry | Bright, luminous colors with lasting brilliance |
| Technique | Brushes, palette knives, layering glazes | Heat tools, layering melted wax, scraping |
| Health & Safety | Requires solvents, potential toxic fumes | Fumes from heated wax, generally low toxicity |
| Historical Use | Popular since the Renaissance | Ancient technique, dating back to Greek and Egyptian art |
Introduction: Understanding Oil and Encaustic Painting
Oil painting utilizes pigments suspended in drying oils like linseed oil, offering rich color saturation and a smooth blending capability. Encaustic painting employs heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments, creating a textured, layered surface that is durable and vibrant. Both mediums provide unique artistic effects, with oil favoring slow drying and blending ease, while encaustic offers a distinctive tactile quality and longevity.
Historical Origins of Oil and Encaustic Art
Oil painting traces its origins to the early 15th century Northern Europe, with artists like Jan van Eyck pioneering the medium for its rich texture and slow drying time, allowing detailed layering and blending. Encaustic art dates back to ancient Greece and Egypt, where hot beeswax mixed with pigments was applied to surfaces, prized for its durability and vibrant color retention over millennia. Both mediums reflect significant cultural and technological advances that shaped their unique artistic techniques and preservation qualities.
Composition and Materials Used
Oil painting uses pigment suspended in linseed or other drying oils, creating a rich, durable medium that allows for smooth blending and long drying times. Encaustic painting involves pigments mixed with hot beeswax and resin, producing a textured, luminous surface that hardens quickly upon cooling. The differing compositions influence their handling: oil's oily binder offers fluidity and depth, while encaustic's wax base provides a sculptural, layered effect.
Techniques and Application Methods
Oil painting involves layering and blending pigments mixed with linseed oil to create rich textures and gradual transitions, allowing extended drying times for detailed work and glazing techniques. Encaustic painting uses heated beeswax mixed with colored pigments applied swiftly with brushes or heated tools, resulting in a luminous, textured surface that hardens quickly and can be manipulated with heat. The oil technique emphasizes slow, controlled application for depth and realism, while encaustic demands rapid, layered applications for vibrant, tactile effects.
Drying Time and Workability
Oil paint typically has a drying time ranging from several days to weeks, allowing extended workability for blending and layering, making it ideal for artists who prefer slow drying processes. Encaustic paint, composed of heated beeswax mixed with pigments, cools and hardens rapidly, enabling quicker adjustment and layering but requiring swift application before setting. The contrasting drying times impact artistic techniques, with oil suited for detailed, prolonged manipulation, while encaustic demands immediacy and precision during creation.
Visual Effects and Textural Differences
Oil paints create rich, luminous colors with smooth blending and gradual transitions, enhancing depth and realism in artwork. Encaustic paint features a distinctive textured surface due to its wax base, allowing for layered translucency and tactile, sculptural effects. The visual effects in oil emphasize gloss and subtle shading, while encaustic highlights texture and dimensionality through its malleable, layered wax medium.
Durability and Preservation
Oil paint offers superior durability due to its dense, flexible film that resists cracking and fading over time, making it ideal for long-term preservation of artworks. Encaustic, composed of pigmented beeswax, provides exceptional preservation qualities by naturally repelling moisture and resisting environmental pollutants, which helps maintain color vibrancy for centuries. Both mediums require specific care; oil paintings benefit from controlled humidity and UV protection, while encaustic artworks need gentle cleaning to preserve their waxy surface without causing damage.
Health and Safety Considerations
Oil painting involves the use of solvents like turpentine, which emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can cause respiratory issues and skin irritation without proper ventilation. Encaustic painting uses heated beeswax and pigments, presenting burn risks but typically emitting fewer harmful fumes, making it a safer option for indoor environments. Proper handling, personal protective equipment, and workspace ventilation are essential to minimize health hazards with both media.
Cost and Accessibility
Oil paints typically cost more due to higher-quality pigments and longer drying times, while encaustic materials, mainly beeswax and damar resin, can be expensive but vary based on wax purity and resin quality. Oil paints are widely accessible in art stores and online retailers, offering numerous brands and price ranges, whereas encaustic supplies are less common, often requiring specialty shops or online orders. Artists choosing between oil and encaustic should consider the initial investment in tools and ongoing material costs alongside availability in their region.
Choosing the Right Medium: Oil vs Encaustic
Choosing the right medium between oil and encaustic depends on factors like drying time, texture, and finish durability. Oil paints offer rich colors and long drying periods suited for detailed blending, while encaustic wax provides a unique, layered texture with fast drying and excellent archival qualities. Artists prioritize oil for traditional techniques and encaustic for vibrant surface effects and longevity in mixed media works.
Oil Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com