Subversion involves undermining authority or established systems, often through covert actions that challenge power structures. It plays a critical role in political movements and social change by disrupting the status quo. Explore the rest of the article to understand how subversion affects societies and how you can recognize its impact.
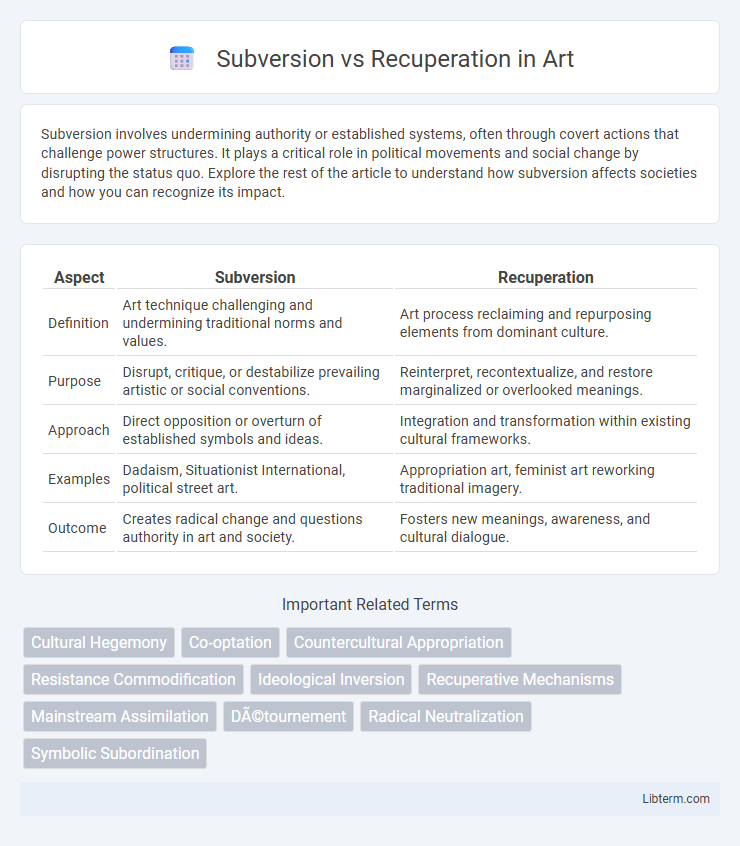
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Subversion | Recuperation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art technique challenging and undermining traditional norms and values. | Art process reclaiming and repurposing elements from dominant culture. |
| Purpose | Disrupt, critique, or destabilize prevailing artistic or social conventions. | Reinterpret, recontextualize, and restore marginalized or overlooked meanings. |
| Approach | Direct opposition or overturn of established symbols and ideas. | Integration and transformation within existing cultural frameworks. |
| Examples | Dadaism, Situationist International, political street art. | Appropriation art, feminist art reworking traditional imagery. |
| Outcome | Creates radical change and questions authority in art and society. | Fosters new meanings, awareness, and cultural dialogue. |
Understanding Subversion: Definition and Origins
Subversion refers to the systematic attempt to overthrow or undermine established authority, often targeting political systems, institutions, or social norms through covert actions and ideological influence. Originating from the Latin word "subvertere," meaning "to overturn," subversion has historically been employed in espionage, revolutionary movements, and psychological warfare to destabilize governments or societal structures. Understanding subversion requires examining its methods such as propaganda, infiltration, and sabotage, which aim to erode public trust and weaken the legitimacy of ruling entities.
What is Recuperation? A Critical Overview
Recuperation refers to the process by which dominant cultural forces absorb and neutralize radical ideas or subversive elements, transforming them into safer, commodified forms that reinforce the status quo. It operates by reinterpreting disruptive symbols or actions as acceptable or mainstream, thereby undermining their original oppositional intent. This concept critically highlights how revolutionary potential can be diluted through cultural assimilation and repackaging.
Historical Context: Subversion vs Recuperation in Social Movements
Subversion in social movements historically challenges dominant power structures by undermining established norms through radical actions or ideas aimed at systemic change. Recuperation occurs when these radical ideas are absorbed, neutralized, or commodified by mainstream culture, transforming subversive practices into sanitized, non-threatening versions that maintain the status quo. Key examples include the punk movement's aesthetic being co-opted by fashion industries and protest slogans becoming marketing tools, illustrating how recuperation dilutes the disruptive potential of subversion within political and cultural contexts.
Key Differences Between Subversion and Recuperation
Subversion involves deliberate actions to undermine or overthrow established systems, authorities, or structures through covert or overt means, often aiming for political or social change. Recuperation refers to the process by which radical ideas or symbols are absorbed and neutralized by mainstream culture, diluting their original rebellious intent. The key difference lies in subversion's active challenge against the status quo, whereas recuperation represents the transformation of that challenge into a controlled, acceptable form.
Case Studies: Subversion Transformed by Recuperation
Case studies reveal how subversion is often transformed by recuperation through the co-optation of radical ideas by mainstream culture, diluting their original intent. For example, punk's rebellious aesthetics were absorbed into fashion and commercial music, reshaping its anti-establishment message into marketable consumer trends. This dynamic illustrates the process where subversive movements are reconstituted within dominant systems, neutralizing their oppositional impact while generating new cultural products.
Media Analysis: Subversive Ideas and Their Mainstream Adoption
Subversion challenges established narratives by introducing radical ideas that disrupt dominant cultural and political paradigms, often analyzed through media studies to understand how these ideas penetrate public consciousness. Recuperation involves the mainstream media's co-optation of subversive concepts, neutralizing their oppositional power by repackaging them into accepted, market-friendly forms. Media analysis reveals the dynamic tension between subversive innovation and recuperative assimilation, highlighting mechanisms of cultural resistance and institutional control.
Corporate Co-optation: When Subversion Becomes Marketing
Corporate co-optation transforms subversive movements into marketable trends, diluting their original intent by repackaging dissent as consumer choice. Brands exploit subversion by embedding countercultural symbols into advertising campaigns, turning rebellion into profitable aesthetics that drive sales. This recuperation process neutralizes radical critique, ultimately converting resistance into a tool for capitalism's expansion.
The Role of Art and Culture in Subversion and Recuperation
Art and culture serve as powerful tools in subversion by challenging dominant ideologies and inspiring social change through provocative expression and critical narratives. In recuperation, these same cultural forms are often absorbed and commodified by mainstream systems, neutralizing their oppositional potential and reinforcing existing power structures. The dynamic interplay between subversion and recuperation highlights how artistic movements simultaneously disrupt and are co-opted within cultural economies.
Strategies to Preserve Subversion and Resist Recuperation
Subversion strategies emphasize disrupting dominant narratives by fostering grassroots mobilization, creating alternative media channels, and leveraging decentralized networks to evade co-optation. Effective resistance to recuperation involves maintaining ideological purity, employing sharp boundary-setting against mainstream appropriation, and continuously evolving discourse to stay ahead of institutional neutralization mechanisms. Prioritizing transparent communication and radical praxis ensures subversive movements retain transformative potential without dilution from dominant power structures.
Future Trends: The Ongoing Battle Between Subversive Acts and Recuperative Forces
Subversion and recuperation continue to shape socio-political landscapes as future trends increasingly highlight digital activism clashing with state-led surveillance and control mechanisms. The rise of decentralized technologies empowers subversive movements to disrupt traditional power structures, while recuperative forces adapt by integrating co-optation strategies and counter-narratives through artificial intelligence and mass media platforms. Understanding this dynamic interplay is crucial for anticipating how resistance and authority will evolve in the digital age.
Subversion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com