Tempera is a fast-drying painting medium made from pigment mixed with a water-soluble binder, traditionally egg yolk, creating vivid, long-lasting colors with a matte finish. It was widely used by artists during the Middle Ages and early Renaissance for its precision and durability, particularly in panel paintings and illuminated manuscripts. Discover how tempera techniques can enhance your art skills by exploring the detailed processes and historical significance in the rest of this article.
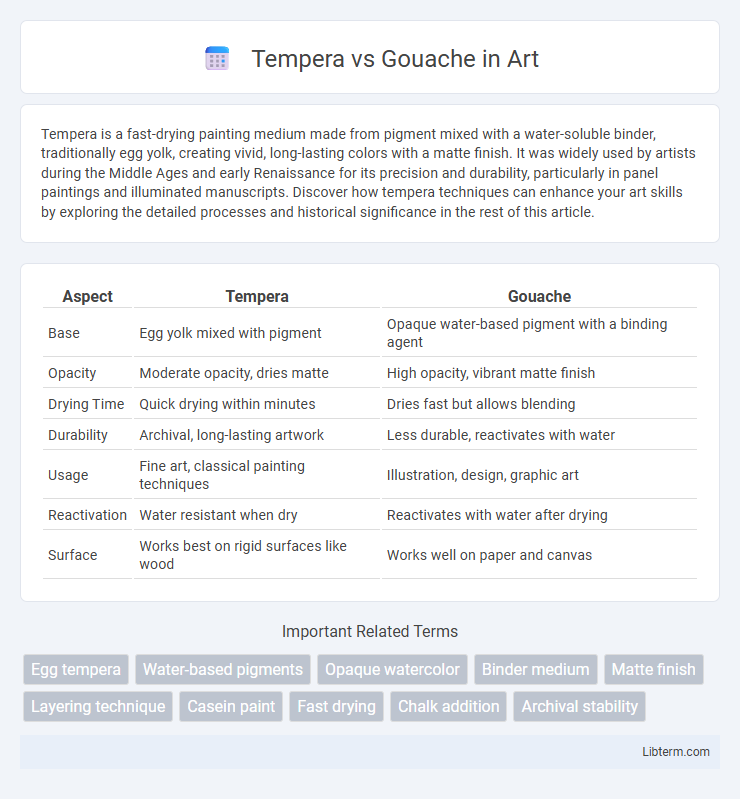
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tempera | Gouache |
|---|---|---|
| Base | Egg yolk mixed with pigment | Opaque water-based pigment with a binding agent |
| Opacity | Moderate opacity, dries matte | High opacity, vibrant matte finish |
| Drying Time | Quick drying within minutes | Dries fast but allows blending |
| Durability | Archival, long-lasting artwork | Less durable, reactivates with water |
| Usage | Fine art, classical painting techniques | Illustration, design, graphic art |
| Reactivation | Water resistant when dry | Reactivates with water after drying |
| Surface | Works best on rigid surfaces like wood | Works well on paper and canvas |
Introduction to Tempera and Gouache
Tempera is a fast-drying painting medium made from pigment mixed with a water-soluble binder, usually egg yolk, known for its longevity and matte finish. Gouache, a water-based opaque watercolor paint, contains larger pigment particles and additives like chalk to create a smooth, vibrant, and matte surface with excellent coverage. Both tempera and gouache offer distinct advantages for artists seeking rich color intensity and quick drying times in their work.
Historical Background of Tempera and Gouache
Tempera, dating back to ancient Egypt and flourishing during the Renaissance, employs pigment mixed with egg yolk or another binder, offering long-lasting, matte finishes ideal for panel paintings and religious art. Gouache emerged in the 18th century as an opaque watercolor technique, using gum arabic as a binder with added chalk to increase opacity and brightness, popular among illustrators and designers. Both mediums have distinct historical roots that influenced their development and preferred artistic applications.
Key Ingredients and Composition
Tempera is primarily made from pigment mixed with a water-soluble binder, usually egg yolk, which creates a fast-drying and durable paint with a matte finish. Gouache consists of pigment combined with a gum arabic binder and often includes chalk or other inert white pigments to increase opacity and provide a smooth, opaque, and vibrant appearance. The key difference in composition lies in tempera's egg-based binder versus gouache's gum arabic and added fillers, which influence their texture, drying time, and finish.
Differences in Painting Techniques
Tempera painting requires precise layering with thin, semi-opaque pigments mixed with egg yolk, resulting in a matte, durable finish that dries quickly and requires careful blending. Gouache uses opaque, water-based pigments with a chalky binder, allowing for smooth, solid color application and reactivation with water after drying for easy corrections. The techniques differ significantly as tempera demands fine, detailed brushwork and rapid drying skills, while gouache emphasizes bold, vibrant coverage with flexible manipulation during and after painting.
Color Vibrancy and Texture Comparison
Tempera paint offers a matte finish with moderate color vibrancy, as its pigment particles are suspended in a water-soluble binder like egg yolk, resulting in a smooth, firm texture once dried. Gouache provides higher color vibrancy due to its opaque, chalky composition and larger pigment load, creating a velvety texture that dries to a matte yet more reflective surface. The denser pigment concentration in gouache enhances opacity and richness, while tempera's layering technique allows for subtle tonal variations without the intense brightness found in gouache.
Drying Time and Workability
Tempera paint dries significantly faster than gouache, often within minutes, making it ideal for layered techniques and quick corrections. Gouache remains workable for a longer period, allowing artists to blend and rehydrate the paint on the surface for extended manipulation. The faster drying time of tempera suits detailed, precise work, whereas gouache favors smooth, adjustable finishes with its slower drying profile.
Surface Compatibility and Preparation
Tempera paint works best on rigid, absorbent surfaces like wood panels and paper, requiring a smooth, primed ground to prevent cracking and ensure adhesion, whereas gouache is versatile on various paper types and canvas but demands a well-prepared, textured surface for optimal paint grip. Both mediums benefit from a properly sized and primed substrate to enhance durability and color vibrancy, with gouache favoring heavier, textured papers such as cold-press or rough watercolor paper. Surface preparation for tempera involves sealing and sanding, while gouache requires minimal priming but benefits from a slightly absorbent texture for controlled opacity and matte finish.
Archival Quality and Longevity
Tempera paint, known for its exceptional archival quality, utilizes egg yolk as a binder, resulting in a durable, long-lasting finish resistant to fading and yellowing over centuries. Gouache, while vibrant and opaque, employs a gum arabic binder that makes it more susceptible to cracking, flaking, and color fading under prolonged exposure to light and humidity. Artists prioritizing longevity often prefer tempera for archival projects due to its proven stability in historical artworks compared to the more fragile nature of gouache.
Common Uses and Applications
Tempera is commonly used in fine art and educational settings for creating detailed, long-lasting paintings on surfaces like wood panels and paper due to its fast-drying and durable nature. Gouache is favored by illustrators and designers for its opaque, matte finish and ability to re-wet, making it ideal for vibrant, flat washes in advertising, comics, and animation backgrounds. Both mediums excel in producing vivid colors but differ in flexibility and texture, influencing their application in different artistic contexts.
Choosing Between Tempera and Gouache
Choosing between tempera and gouache depends on the desired finish and application; tempera offers a matte, durable surface ideal for detailed work and long-lasting projects, while gouache provides a vibrant, opaque finish with easy reactivation for corrections and layering. Tempera dries quickly and is favored for traditional art and educational settings due to its non-toxic nature, whereas gouache is more versatile for fine art and illustration thanks to its rich pigment density and smooth blending capabilities. Artists seeking permanence may prefer tempera, while those prioritizing flexibility and color intensity often opt for gouache.
Tempera Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com