Zooming enhances user experience by allowing precise control over content visibility, making detailed images or text easier to view on screens of any size. Effective zooming techniques improve accessibility and navigation, ensuring your digital interactions are more intuitive and efficient. Discover how mastering zooming can transform your workflow by reading the rest of the article.
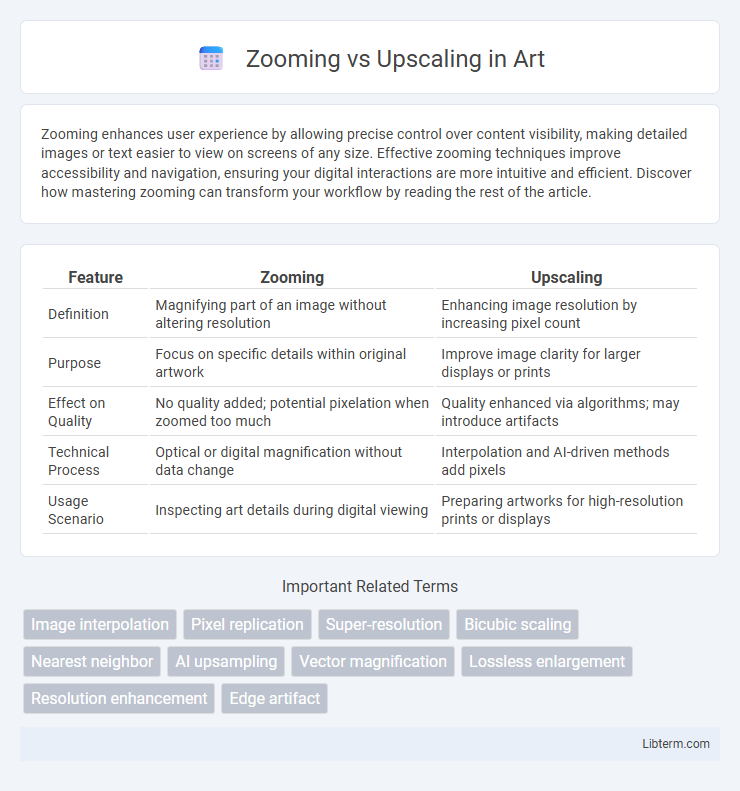
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zooming | Upscaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Magnifying part of an image without altering resolution | Enhancing image resolution by increasing pixel count |
| Purpose | Focus on specific details within original artwork | Improve image clarity for larger displays or prints |
| Effect on Quality | No quality added; potential pixelation when zoomed too much | Quality enhanced via algorithms; may introduce artifacts |
| Technical Process | Optical or digital magnification without data change | Interpolation and AI-driven methods add pixels |
| Usage Scenario | Inspecting art details during digital viewing | Preparing artworks for high-resolution prints or displays |
Introduction to Zooming and Upscaling
Zooming involves adjusting the camera lens or digital interface to magnify a specific part of an image or scene, often resulting in a closer view without altering the image resolution. Upscaling refers to the process of increasing the pixel count of an image or video, using algorithms like interpolation or AI-based techniques to enhance detail and reduce pixelation. Both methods aim to improve visual clarity, but zooming changes the framing while upscaling enhances image quality.
Defining Zooming in Digital Imaging
Zooming in digital imaging refers to the process of enlarging a portion of an image by cropping and displaying it at a higher magnification, without altering the original resolution. Unlike upscaling, which increases pixel count through interpolation algorithms to enhance image size, zooming simply magnifies existing pixels, often leading to a loss of clarity and detail. This technique is commonly used in digital cameras and software to focus on specific image areas without modifying the actual image data.
What is Upscaling? Key Concepts Explained
Upscaling refers to the process of increasing the resolution of an image or video to fit a larger display, enhancing perceived quality without capturing new details. Key concepts in upscaling include interpolation methods such as bicubic, bilinear, and advanced AI-based techniques that predict and generate additional pixels to create smoother edges and reduce artifacts. Unlike zooming, which enlarges the original pixels causing possible pixelation, upscaling reconstructs the image to improve clarity on high-resolution screens.
Technical Differences: Zooming vs Upscaling
Zooming manipulates the display size of an image by enlarging or reducing its viewport without altering the image data, preserving the original resolution but changing the visible portion. Upscaling increases the image resolution by adding pixels through interpolation algorithms like bilinear or bicubic, enhancing image size while potentially introducing artifacts or blurring. The fundamental technical difference lies in zooming's reliance on rendering existing pixels versus upscaling's generation of new pixel data to improve or adapt image dimensions.
Impact on Image Quality: A Comparative Analysis
Zooming typically enlarges the visible area of an image by cropping and magnifying pixels, leading to pixelation and loss of sharpness. Upscaling involves algorithmically increasing the image resolution by adding interpolated pixels, which can enhance perceived detail but may introduce artifacts or blurring depending on the method used, such as bicubic or AI-based super-resolution techniques. Comparing both, upscaling generally provides better image quality preservation than zooming, especially when advanced algorithms are employed to reconstruct missing details.
Use Cases for Zooming and Upscaling
Zooming is ideal for real-time video calls and digital meetings where users need to focus closely on specific details or participants without altering image resolution. Upscaling is commonly used in video streaming platforms and video editing software to enhance low-resolution content, improving visual clarity on high-definition displays. Both techniques serve distinct purposes: zooming adjusts the viewer's focus dynamically, while upscaling algorithms improve the intrinsic quality of the visual data.
Software and Tools for Zooming and Upscaling
Software for zooming often includes features that maintain image clarity through interpolation algorithms, with tools like Adobe Photoshop and GIMP providing real-time zoom adjustments ideal for detailed editing. Upscaling software such as Topaz Gigapixel AI and AI Image Enlarger utilize advanced machine learning models to enhance image resolution by predicting and filling in missing pixels, resulting in higher quality enlargements compared to traditional methods. These tools differ fundamentally, as zooming magnifies the existing pixels while upscaling reconstructs and adds new image data to improve visual fidelity.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Zooming allows real-time magnification of images or videos by enlarging the pixels, offering immediate clarity but often leading to pixelation and loss of detail when pushed beyond native resolution. Upscaling employs advanced algorithms such as AI-driven super-resolution to enhance image quality by predicting and adding missing details, resulting in sharper images but sometimes introducing artifacts or unnatural textures. While zooming is simpler and faster with minimal processing power required, upscaling demands more computational resources and may struggle with significant quality improvements on extremely low-resolution sources.
Best Practices for Optimal Results
Zooming enlarges an image by increasing pixel size, often leading to a loss of detail, while upscaling uses algorithms to add pixels and enhance image quality. Best practices for optimal results include using dedicated upscaling software with AI capabilities to preserve sharpness and avoid pixelation. Maintaining the original aspect ratio and working with high-resolution source files further ensures the clarity and fidelity of the final image.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Zooming and Upscaling
Choosing between zooming and upscaling depends on the desired image quality and context of use. Zooming focuses on enlarging the visible portion of an image by cropping, preserving original pixel data but reducing field of view. Upscaling uses interpolation algorithms to increase image dimensions, which can introduce artifacts but maintains the entire scene at a lower perceived sharpness.
Zooming Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com