Formal variation enhances communication by adjusting tone, vocabulary, and structure to suit different contexts or audiences. Mastering formal variations improves clarity and professionalism in writing or speech, making your message more effective and appropriate. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to apply formal variation in your communication.
Table of Comparison
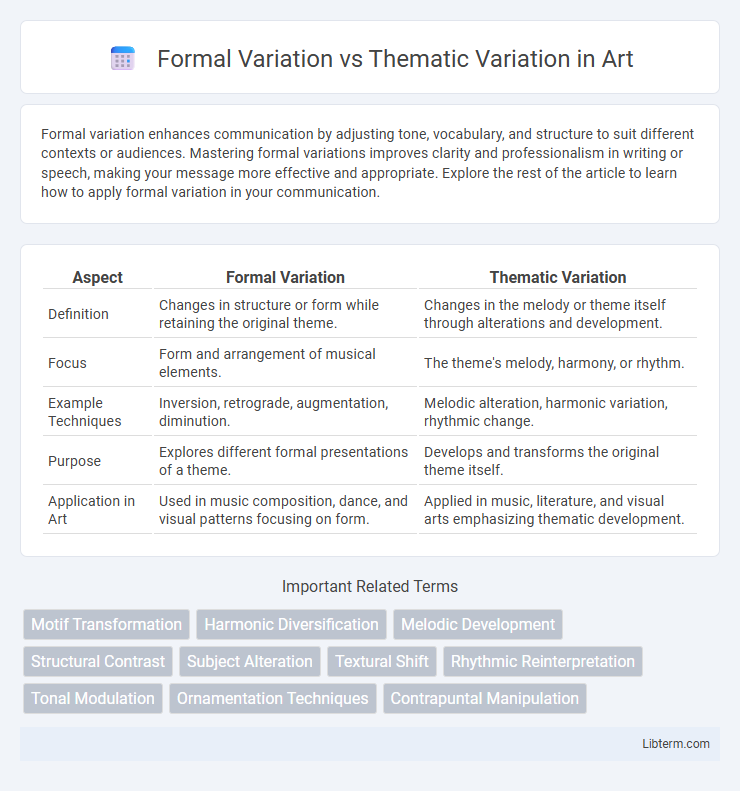
| Aspect | Formal Variation | Thematic Variation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changes in structure or form while retaining the original theme. | Changes in the melody or theme itself through alterations and development. |
| Focus | Form and arrangement of musical elements. | The theme's melody, harmony, or rhythm. |
| Example Techniques | Inversion, retrograde, augmentation, diminution. | Melodic alteration, harmonic variation, rhythmic change. |
| Purpose | Explores different formal presentations of a theme. | Develops and transforms the original theme itself. |
| Application in Art | Used in music composition, dance, and visual patterns focusing on form. | Applied in music, literature, and visual arts emphasizing thematic development. |
Introduction to Formal and Thematic Variation
Formal variation emphasizes changes in the structure or form of a composition, often altering elements such as rhythm, harmony, or melody to create contrast while maintaining coherence. Thematic variation involves modifying a central theme through techniques like ornamentation, inversion, or augmentation, preserving the thematic identity but enriching the musical narrative. Understanding the distinctions between formal and thematic variation is essential for analyzing compositional development and stylistic expression in music.
Defining Formal Variation
Formal Variation refers to changes in the structure, style, or form of a piece without altering its core thematic content. It emphasizes modifications in rhythm, melody, harmony, or arrangement to create diversity while maintaining the original theme's identity. This contrasts with Thematic Variation, where the fundamental melody or theme itself undergoes transformation.
Understanding Thematic Variation
Thematic variation involves altering the main theme while maintaining its core identity, creating diversity within a musical or literary work without losing coherence. It emphasizes emotional and conceptual development by modifying motifs, harmonies, or phrasing to evoke different moods and meanings. Understanding thematic variation enhances appreciation of how creators innovate around a central idea to engage audiences through nuanced expression.
Historical Context of Musical Variation Techniques
Formal variation and thematic variation both evolved significantly during the Classical and Romantic periods, reflecting shifts in compositional style and audience expectations. Formal variation emphasizes structural changes within a fixed form, often found in Baroque and early Classical works, while thematic variation focuses on melodic and harmonic development, gaining prominence in Romantic compositions by composers like Beethoven and Brahms. The historical context reveals a gradual transition from strict contrapuntal techniques to more expressive and improvisational approaches in musical variation.
Key Differences Between Formal and Thematic Variation
Formal variation emphasizes changes in musical elements such as melody, harmony, rhythm, and structure, maintaining the core theme's identity while altering its form. Thematic variation focuses on developing and transforming the main theme's motifs and ideas to explore different emotional or narrative expressions. Key differences lie in formal variation's structural modifications versus thematic variation's interpretive reinterpretations of thematic material.
Functions of Formal Variation in Music
Formal variation in music serves to create structural coherence and maintain listener interest by altering motifs or themes while preserving their core identity. It functions to develop thematic material through techniques such as augmentation, diminution, inversion, and fragmentation, allowing composers to explore contrast and unity simultaneously. This variation enriches the musical narrative and enhances emotional expression without completely departing from the original theme.
Thematic Variation: Purpose and Impact
Thematic variation in literature involves altering core themes to explore diverse perspectives and deepen narrative complexity, enhancing reader engagement and emotional resonance. It enables authors to examine universal human experiences through different cultural, social, or psychological lenses, amplifying the work's relevance and impact. By shifting thematic focus, writers challenge audience expectations and provoke thoughtful reflection on the subject matter.
Case Studies: Examples in Classical Compositions
Formal variation in classical compositions involves altering the structure or form of a musical theme, such as changing sections while maintaining recognizable motifs, exemplified by Beethoven's "Diabelli Variations" which manipulate the original waltz's structure. Thematic variation focuses on transforming the melody or thematic material itself, modifying pitch, rhythm, or harmony, seen in Brahms' "Variations on a Theme by Haydn" where the core theme undergoes distinct melodic and harmonic reinterpretations. Case studies of these variations highlight how composers balance unity and contrast to develop musical ideas, providing insight into their creative processes and the evolution of classical form.
Analyzing Listener Perception of Variations
Listeners perceive formal variation through recognizable changes in musical structure, such as altered melodies or harmonic progressions that maintain the original theme's identity. Thematic variation elicits engagement by transforming core motifs, fostering emotional connection and cognitive recognition of the evolving narrative. Analysis of listener responses reveals that thematic variations often generate deeper memory retention and emotional impact compared to purely formal alterations.
Conclusion: The Artistic Importance of Both Methods
Formal variation emphasizes structural and stylistic modifications within a composition, contributing to the coherence and integrity of the musical form. Thematic variation focuses on transforming a melodic theme to explore expressive possibilities, enriching the emotional and narrative depth of the piece. Both methods are artistically essential, as they balance innovation and familiarity, allowing composers to engage listeners through creativity while maintaining thematic unity.
Formal Variation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com