Symmetry plays a fundamental role in art, nature, and design, creating balance and harmony that appeals to the human eye. Understanding different types of symmetry, such as reflective, rotational, and translational, can enhance your appreciation of patterns and structures around you. Explore the rest of the article to discover how symmetry influences aesthetics and functionality in various fields.
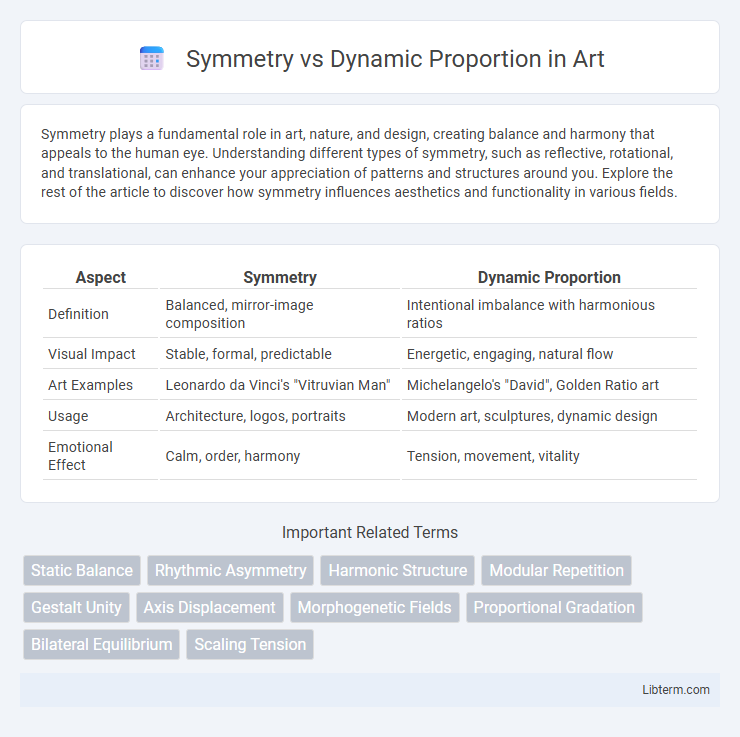
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Symmetry | Dynamic Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Balanced, mirror-image composition | Intentional imbalance with harmonious ratios |
| Visual Impact | Stable, formal, predictable | Energetic, engaging, natural flow |
| Art Examples | Leonardo da Vinci's "Vitruvian Man" | Michelangelo's "David", Golden Ratio art |
| Usage | Architecture, logos, portraits | Modern art, sculptures, dynamic design |
| Emotional Effect | Calm, order, harmony | Tension, movement, vitality |
Introduction to Symmetry and Dynamic Proportion
Symmetry refers to a balanced and mirror-like arrangement of elements, creating harmony and visual stability in design. Dynamic Proportion involves varying the sizes and relationships of components to generate movement and interest, often breaking strict symmetry for a more engaging composition. Understanding both concepts is essential for crafting visually appealing and effective designs.
Defining Symmetry in Art and Design
Symmetry in art and design refers to the balanced arrangement of elements on either side of a central axis, creating a harmonious and visually stable composition. It often involves mirroring shapes, patterns, or colors to achieve formal equilibrium, which can evoke feelings of order and calmness. This principle is fundamental in various artistic disciplines, including architecture, graphic design, and sculpture, where precise repetition enhances aesthetic appeal.
Understanding Dynamic Proportion
Dynamic proportion emphasizes the relationship between elements to create visual balance through variation and movement rather than mirroring. Understanding dynamic proportion involves analyzing how size, scale, and spacing interact to guide the viewer's eye and generate energy within a design. This approach enhances interest and flow by leveraging asymmetry and proportional contrasts, departing from the rigid uniformity of symmetry.
Historical Perspectives on Symmetry and Proportion
Historical perspectives on symmetry and dynamic proportion reveal their foundational roles in classical architecture and art, where symmetry symbolized balance and order in ancient Greek temples and Renaissance masterpieces. Dynamic proportion, emerging in later periods, challenged rigid symmetry by introducing asymmetry to create movement and visual interest, exemplified in Baroque and modernist designs. These evolving concepts reflect shifting aesthetic values and philosophical ideas about harmony and expression across centuries.
Visual Impact: The Power of Balance
Symmetry creates visual stability by evenly distributing elements, enhancing clarity and predictability in design. Dynamic proportion generates visual interest through asymmetrical balance, guiding the viewer's eye with movement and tension. Combining symmetry with dynamic proportion leverages the power of balance to achieve both harmony and excitement in visual compositions.
Expressiveness: Emotion in Dynamic Proportion
Dynamic proportion enhances expressiveness by introducing asymmetry and variation, which evoke stronger emotional responses compared to static symmetry. The intentional imbalance in dynamic proportion creates visual tension and movement, engaging viewers on a deeper psychological level. This variability in form and scale communicates energy and vitality, making designs feel more alive and emotionally resonant.
Symmetry vs Dynamic Proportion in Architecture
Symmetry in architecture emphasizes balanced and mirrored elements, creating a sense of stability and order commonly seen in classical buildings like the Parthenon and Renaissance palaces. Dynamic proportion involves asymmetrical arrangements that achieve visual interest and movement through varied scales and rhythms, often utilized in modern and contemporary designs such as Frank Lloyd Wright's Fallingwater. The choice between symmetry and dynamic proportion significantly influences spatial perception, structural harmony, and aesthetic impact within architectural compositions.
Modern Applications in Visual Arts
Symmetry in modern visual arts creates balance and harmony through mirrored elements, enhancing viewer perception and evoking stability. Dynamic proportion introduces asymmetrical ratios and varied scale, fostering movement, tension, and visual interest in contemporary compositions. Artists leverage these principles to manipulate spatial relationships, guiding the audience's focus and emotional response in digital media, graphic design, and installation art.
Choosing the Right Approach: Context and Purpose
Symmetry offers a balanced, harmonious design ideal for formal contexts requiring stability and order, such as corporate branding and architectural facades. Dynamic proportion introduces movement and visual interest, making it suitable for creative projects and art where expression and engagement are priorities. Selecting between symmetry and dynamic proportion depends on the desired emotional impact and the functional goals of the design environment.
Conclusion: Striking a Harmonious Balance
Striking a harmonious balance between symmetry and dynamic proportion enhances visual appeal by combining stability with movement, creating designs that feel both structured and lively. Symmetry offers predictability and order, while dynamic proportion introduces variation and interest, engaging viewers on multiple sensory levels. Integrating these elements thoughtfully results in compositions that are aesthetically pleasing and emotionally resonant, achieving a perfect equilibrium between form and function.
Symmetry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com